Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 23(3); 2010 > Article
-
Original Article
- Treatment of Femur Supracondylar Fracture with Locking Compression Plate
- Seong Ho Bae, M.D., Seung Han Cha, M.D., Jeung Tak Suh, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2010;23(3):282-288.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.3.282
Published online: July 31, 2010
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Jeung Tak Suh, M.D. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Pusan National University School of Medicine, 1-10, Ami-dong 1-ga, Seo-gu, Busan 602-739, Korea. Tel: 82-51-240-7248, Fax: 82-51-247-8395, jtsuh@pusan.ac.kr
• Received: December 30, 2009 • Revised: February 23, 2010 • Accepted: June 16, 2010
Copyright © 2010 The Korean Fracture Society
- 842 Views
- 7 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- To evaluate the effectiveness of locking compression plate by analyzing the clinical outcomes of open reduction and internal fixation with locking compression plate in the treatment of femur supracondylar fracture.
-
Materials and Methods
- We reviewed 21 cases of distal femur fractures which were treated with locking compression plate in our hospital from February 2005 to March 2009 and followed up for minimal 1 year. The types of fractures were seven A1, four A2, two A3, six C2, and two C3 according to AO classification. 2 cases were open fractures. The cases were evaluated by the criteria of Schatzker-Lambert.
-
Results
- The mean time to union was 14.3 weeks. One delayed union, one refracture were observed, but no nonunion and postoperative infection was observed. The outcomes were excellent in 6 cases, good in 11, fair in 3, and failure in 1 by the criteria of Schatzker-Lambert. The overall results were excellent or good in 17 cases (81.0%).
-
Conclusion
- In the treatment of femur supracondylar fracture, open reduction and internal fixation with locking compression plate yields good result and locking compression plate is useful choice of fixation option.
- 1. Ahmad M, Nanda R, Bajwa AS, Candal-Couto J, Green S, Hui AC. Biomechanical testing of the locking compression plate: when does the distance between bone and implant significantly reduce construct stability? Injury, 2007;38:358-364.Article
- 2. Bolhofner BR, Carmen B, Clifford P. The results of open reduction and Internal fixation of distal femur fractures using a biologic (indirect) reduction technique. J Orthop Trauma, 1996;10:372-377.Article
- 3. Bucholz RW, Heckman JD, Court-Brown CM. Rockwood and Greens's fractures in adults, 2006;4th ed. Philadelphia, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 1915-1967.
- 4. Canale ST, Beaty JH. Campbell's operative orthopedics, 2008;11th ed. Philadelphia, PA, Mosby. 3170-3190.
- 5. Chiron HS, Trémoulet J, Casey P, Müller M. Fracture of distal third of femur treated by internal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1974;100:160-170.
- 6. Gellman RE, Paiement GD, Green HD, Coughlin RR. Treatment of supracondylar femoral fractures with a retrograde intramedullary nail. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1996;332:90-97.Article
- 7. Giles JB, DeLee JC, Heckman JD, Keever M. Supracondylar-intercondylar fractures of the femur treated with a supracondylar plate and lag screw. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1982;64:864-870.Article
- 8. Heiney JP, Barnett MD, Vrabec GA, Schoenfeld AJ, Baji A, Njus GO. Distal femoral fixation: a biomechanical comparison of trigen retrograde intramedullary (i.m.) nail, dynamic condylar screw (DCS), and locking compression plate (LCP) condylar plate. J Trauma, 2009;66:443-449.Article
- 9. Higgins TF, Pittman G, Hines J, Bachus KN. Biomechanical analysis of distal femur fracture fixation: fixed-angle screw-plate construct versus condylar blade plate. J Orthop Trauma, 2007;21:43-46.Article
- 10. Janzing HM, Stockman B, Van Damme G, Rommens P, Broos PL. The retrograde intramedullary nail: prospective experience in patients older than sixty-five years. J Orthop Trauma, 1998;12:330-333.Article
- 11. Kayali C, Agus H, Turgut A. Successful results of minimally invasive surgery for comminuted supracondylar femoral fractures with LISS: comparative study of multiply injured and isolated femoral fractures. J Orthop Sci, 2007;12:458-465.Article
- 12. Ketterl R, Köstler W, Wittwer W, Stübinger B. 5-year results of dia-/supracondylar femoral fractures, managed with the dynamic condylar screw. Zentralbl Chir, 1997;122:1033-1039.
- 13. Kim CK, Yoon JH, Ahn BW, et al. Effect of alternative splinting at extension and 90degrees flexion on range of motion after open reduction and internal fixation of distal femur fracture. J Korean Fract Soc, 2005;18:144-148.Article
- 14. Lee KB. Basic Principle of the Locking Compression Plate. J Korean Fract Soc, 2008;21:261-265.Article
- 15. Lucas SE, Seligson D, Henry SL. Intramedullary supracondylar nailing of femoral fractures. A preliminary report of the GSH supracondylar nail. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1993;296:200-206.
- 16. Mize RD, Bucholz RW, Grogan DP. Surgical treatment of displaced, comminuted fractures of distal end of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1982;64:871-879.
- 17. Moon ES, Lee KB, Jeong JW. Anatomical plate fixation for distal femur fracture. J Korean Soc Fract, 1999;12:294-300.Article
- 18. Olerud S. Operative treatment of supracondylar--condylar fractures of the femur. Technique and results in fifteen cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1972;54:1015-1032.
- 19. Perren SM. Evolution and rationale of locked internal fixator technology Introductory remarks. Injury, 2001;32:Suppl 2. B3-B9.
- 20. Rademakers MV, Kerkhoffs GM, Sierevelt IN, Raaymakers EL, Marti RK. Intra-articular fractures of the distal femur: a long-term follow-up study of surgically treated patients. J Orthop Trauma, 2004;18:213-219.
- 21. Sanders R, Swiontkowski M, Rosen H, Helfet D. Double-plating of comminuted, unstable fractures of the distal part of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1991;73:341-346.Article
- 22. Schandelmaier P, Partenhemer A, Koanemann B, Grün OA, Krettek C. Distal femoral fractures and LISS stabilization. Injury, 2001;32:Suppl 3. SC55-SC63.Article
- 23. Schatzker J, Lambert DC. Supracondylar fractures of the femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1979;138:77-83.Article
- 24. Sim JC, Chung NS, Hong KD, Ha SS, Kang JH. Treatment of fractures of the distal radius using locking compression plate. J Korean Fract Soc, 2005;18:100-104.
- 25. Sommer C, Gautier E, Müller M, Helfet DL, Wagner M. First clinical results of the Locking Compression Plate(LCP). Injury, 2003;34:Suppl 2. B43-B54.Article
- 26. Syed AA, Agarwal M, Giannoudis PV, Matthews SJ, Smith RM. Distal femoral fractures: long-term outcome following stabilisation with the LISS. Injury, 2004;35:599-607.Article
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
(A) Preoperative radiograph of 41-year-old male shows type C2 fracture and patellar fracture.
(B) The radiograph at 3 months after operation shows the union.
(C) The radiograph at 1 year after operation shows refracture by traffic accident.
(D) The radiograph at 1 year after refracture shows the good result.
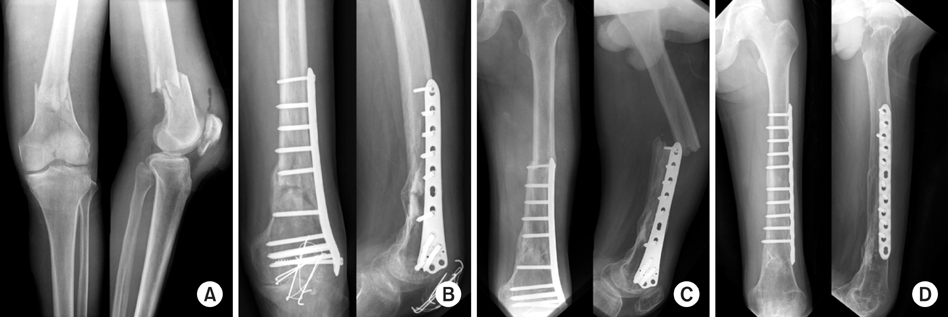

Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Incidence of nonunion after surgery of distal femoral fractures using contemporary fixation device: a meta‐analysis
Byung-Ho Yoon, In Keun Park, Youngwoo Kim, Hyoung-Keun Oh, Suk Kyu Choo, Yerl-Bo Sung
Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery.2021; 141(2): 225. CrossRef
Treatment of Femur Supracondylar Fracture with Locking Compression Plate
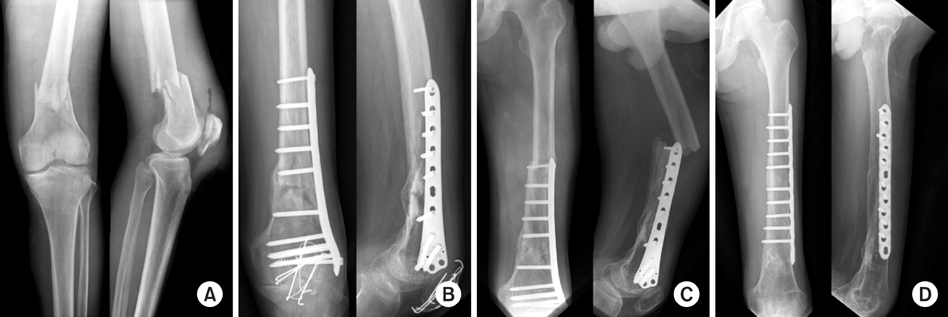
Fig. 1
(A) Preoperative radiograph of 41-year-old male shows type C2 fracture and patellar fracture.
(B) The radiograph at 3 months after operation shows the union.
(C) The radiograph at 1 year after operation shows refracture by traffic accident.
(D) The radiograph at 1 year after refracture shows the good result.
Fig. 1
Treatment of Femur Supracondylar Fracture with Locking Compression Plate
Summary of patient demographics, injury and fracture types, and outcomes
TA: Traffic accident.
The clinical outcomes of the Schatzker and Lambert assessment
Table 1
Summary of patient demographics, injury and fracture types, and outcomes
TA: Traffic accident.
Table 2
The clinical outcomes of the Schatzker and Lambert assessment

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 Cite
Cite

