Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 22(4); 2009 > Article
-
Original Article
- Treatment of Shatzker Type VI Tibia Plateau Fracture Using Lateral and Posteromedial Dual Incision Approach and Dual Plating
- In-Jung Chae, M.D., Sang-Won Park, M.D., Soon-Hyuck Lee, M.D., Won Noh, M.D., Ho-Joong Kim, M.D., Seung-Beom Hahn, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2009;22(4):252-258.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.4.252
Published online: October 30, 2009
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Korea University Anam Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Seung-Beom Hahn, M.D. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Korea University Anam Hospital, 126-1, Anam-dong 5-ga, Seongbuk-gu, Seoul 136-705, Korea. Tel: 82-2-920-5924, Fax: 82-2-924-2471, oshan@korea.ac.kr
Copyright © 2009 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 515 Views
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Staged Treatment of Bicondylar Tibial Plateau Fracture (Schatzker Type V or VI) Using Temporary External Fixator: Correlation between Clinical and Radiological Outcomes
Seung Min Ryu, Han Seok Yang, Oog Jin Shon
Knee Surgery and Related Research.2018; 30(3): 261. CrossRef - Medial Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis in Proximal Tibial Comminuted Fractures
Jae-Ang Sim, Kwang-Hui Kim, Yong-Seuk Lee, Sang-Jin Lee, Beom-Koo Lee
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2014; 49(4): 278. CrossRef - Current Concepts in Management of Tibia Plateau Fracture
Sang Hak Lee, Kang-Il Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2014; 27(3): 245. CrossRef
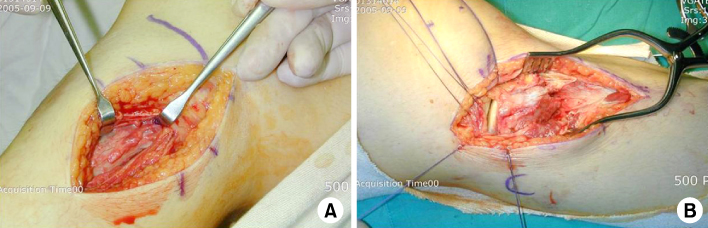

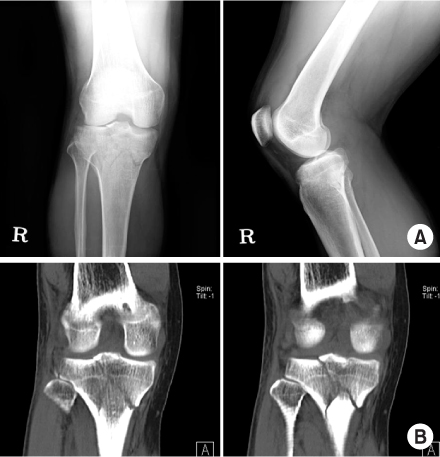
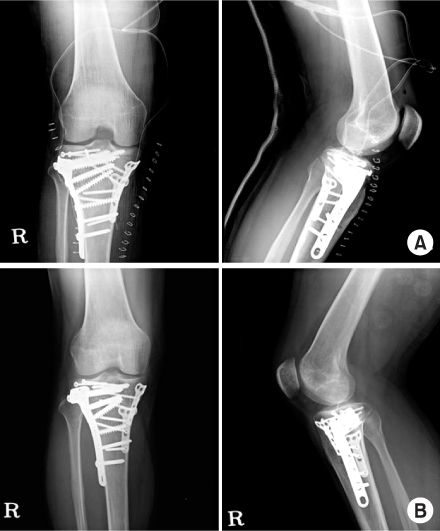
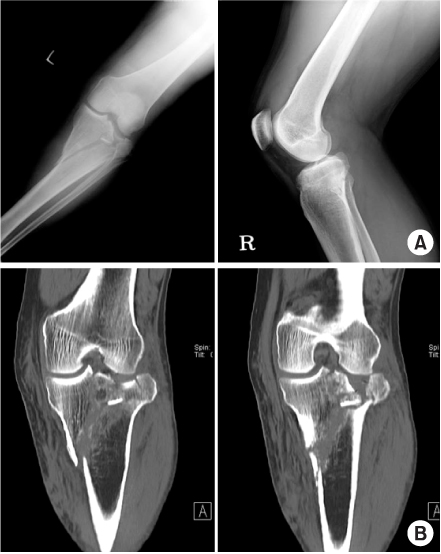
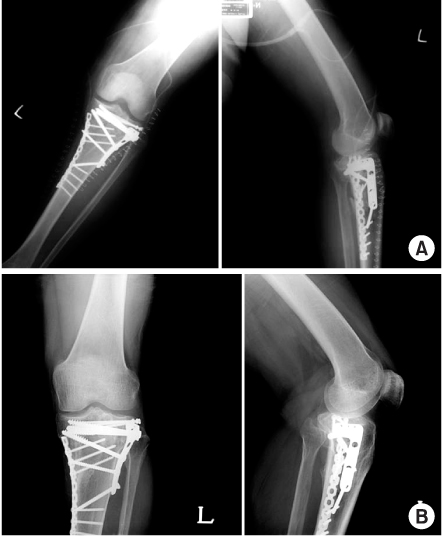

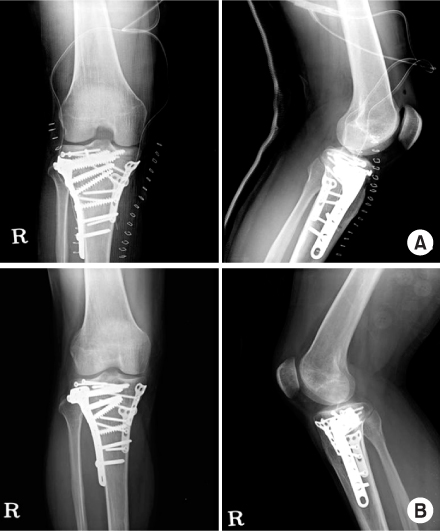
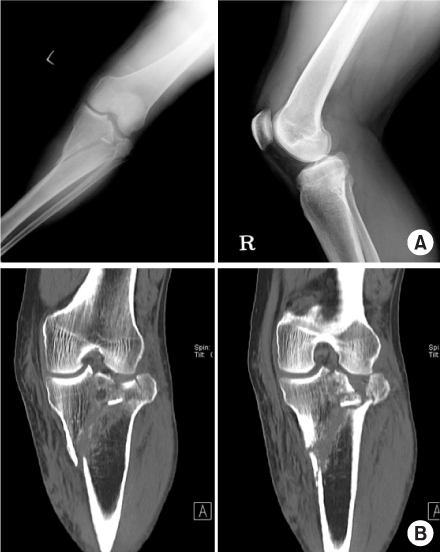
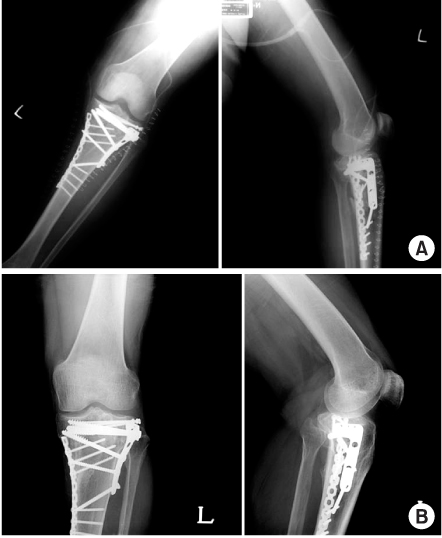
Fig. 1
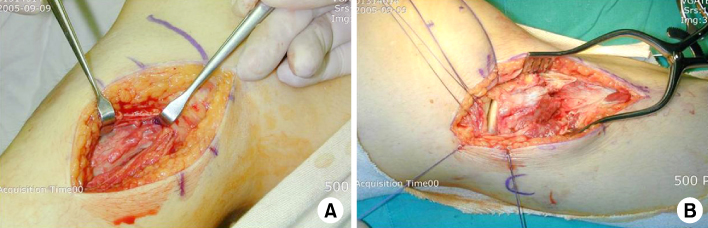
Fig. 2
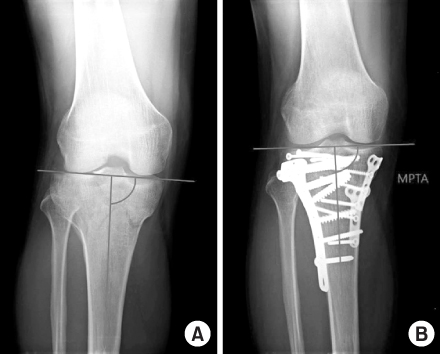
Fig. 3
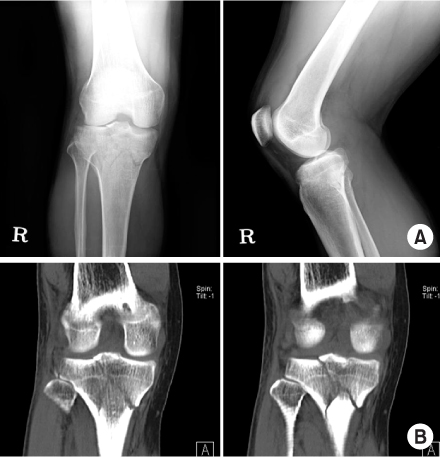
Fig. 4
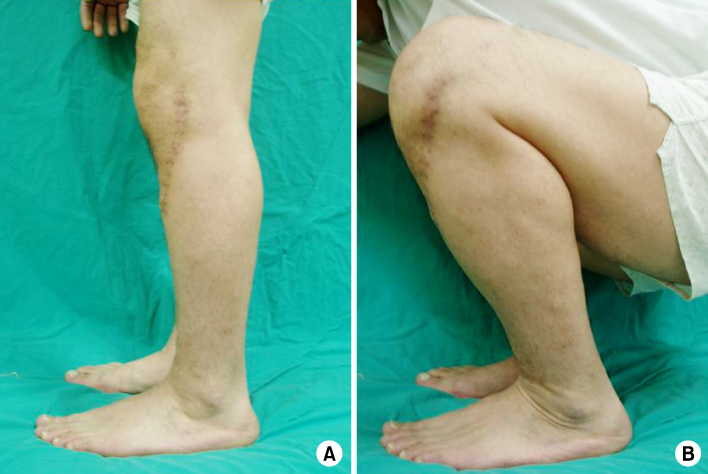
Fig. 5
Fig. 6
Fig. 7
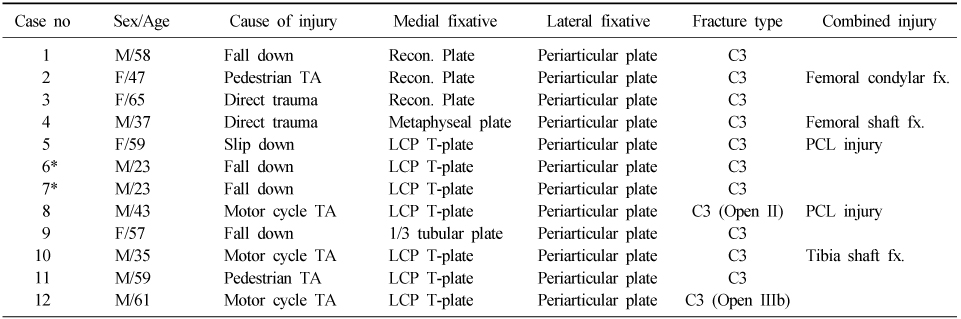
Demographics
*The same patient who sustained the bilateral tibia plateau fracture, case no. 6 and 7 indicates right and left knee joint respectively.
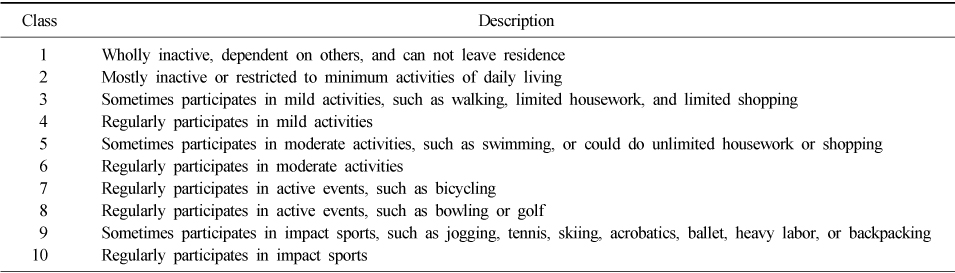
UCLA scale
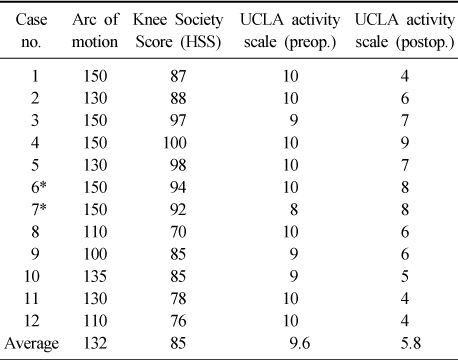
Clinical results
*The same patient who sustained the bilateral tibia plateau fracture, case no. 6 and 7 indicates right and left knee joint respectively.
*The same patient who sustained the bilateral tibia plateau fracture, case no. 6 and 7 indicates right and left knee joint respectively.
*The same patient who sustained the bilateral tibia plateau fracture, case no. 6 and 7 indicates right and left knee joint respectively.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

