Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 22(1); 2009 > Article
-
Original Article
- The Treatment of Posterolateral Malleolar Fractures using Percutaneous Reduction Technique
- Jae-Sung Lee, M.D., Han-Jun Lee, M.D., Jae-Hyun Yoo, M.D., Hee-Chun Kim, M.D., Ph.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2009;22(1):19-23.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.1.19
Published online: January 31, 2009
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yong-San Hospital, College of Medicine, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea.
*Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, National Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Han-Jun Lee, M.D. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yong-San Hospital, College of Medicine, Chung-Ang University, 65-207, Hangang-ro 3ga, Yongsan-gu, Seoul 140-757, Korea. Tel: 82-2-748-9774, Fax: 82-2-793-6634, gustinolhj@hanafos.com
• Received: September 25, 2008 • Revised: November 6, 2008 • Accepted: January 3, 2009
Copyright © 2009 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 329 Views
- 0 Download
Abstract
-
Purpose
- To evaluate the usefullness of the percutaneous reduction technique with K-wire that could reduce the displaced posterolateral fracture fragment which persisted even after an anatomical reduction of the lateral malleolar fracture.
-
Materials and Methods
- From January 2004 to December 2006, we reviewed 72 patients who underwent surgical treatment for their trimalleolar fractures. We estimated the clinical and radiological results of 5 cases treated by percutaneous reduction technique with K-wire when more than the distal tibial articular step-off was left after reduction of the lateral malleolar fracture. The method of reduction starts with temporary fixation of lateral malleolar fracture followed by checking ankle radiographic image to confirm the accuracy of reduction. In case of incomplete reduction of the posterior fragment, a K-wire is inserted into the posterior fragment and pushed downward to the ankle joint level, and then lag screws were inserted.
-
Results
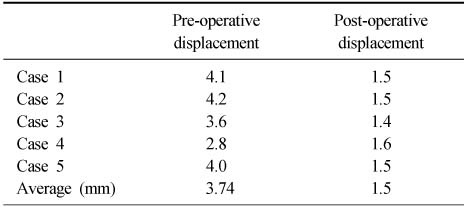
- The average articular involvement by the posterolateral fracture fragment was 30.2%. The average step-off after reduction of the lateral malleolar fracture was 3.7 mm. At the final follow up, step-off was less than 2 mm in all cases. In clinical results by Baird and Jackson score, 3 out of 5 cases were excellent, other 2 were good.
-
Conclusion
- Percutaneous reduction technique for posterolateral fragment using the K-wire is relatively easy. This technique may be useful when the posterolateral fragment is large (more the 25% of articular surface) and not severely comminuted.
- 1. Baird RA, Jackson ST. Fractures of the distal part of the fibula associated disruption of the deltoid ligament. Treatment without repair of the deltoid ligament. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1987;69:1346-1352.
- 2. Boggs LR. Isolated posterior malleolar fractures. Am J Emerg Med, 1986;4:334-336.
- 3. Court-Brown CM, McBirnie J, Wilson G. Adult ankle fractures--an increasing problem? Acta Orthop Scand, 1998;69:43-47.
- 4. De Vries JS, Wijgman AJ, Sierevelt IN, Schaap GR. Long-term results of ankle fractures with a posterior malleolar fragment. J Foot Ankle Surg, 2005;44:211-217.
- 5. Haraguchi N, Haruyama H, Toga H, Kato F. Pathoanatomy of posterior malleolar fractures of the ankle. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2006;88:1085-1092.
- 6. Harper MC, Hardin G. Posterior malleolar fracture of the ankle associated with external rotation-abduction injuries. Results with and without internal fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1988;70:1348-1356.
- 7. Jaskulka RA, Ittner G, Schedl R. Fractures of the posterior tibial margin: their role in the prognosis of malleolar fractures. J Trauma, 1989;29:1565-1570.
- 8. Jeong HJ, Kin CK, Chung SW. Treatment of the posterior malleolar fracture. J Korean Soc Fract, 1998;11:924-931.
- 9. Kim SJ, Choi IY, Ahn TK. A clinical study of the trimalleolar fractures of the ankle. J Korean Soc Fract, 1989;2:145-154.
- 10. Lee CS, Suh JS, Yi JW. Comparative study for th results of ankle fracture depending on the extension of the posterior malleolus Fracture. J Korean Orthop Assoc, 2007;42:470-474.
- 11. McDaniel WJ, Wilson FC. Trimalleolar fractures of the ankle. An end result study. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1977;(122):37-45.
- 12. Michelson JD. Fractures about the ankle. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1995;77:142-152.
- 13. Neumaier Probst E, Maas R, Meenen NM. Isolated fracture of the posterolateral tibial lip (Volkmann's triangle). Acta Radiol, 1997;38:359-362.
- 14. Nugent JF, Gale BD. Isolated posterior malleolar ankle fractures. J Foot Surg, 1990;29:80-83.
- 15. Strenge KB, Indusuyi OB. Technique tip: percutaneus screw fixation of posterior malleolar fractures. Foot ankle Int, 2006;27:650-652.
- 16. Weber M. Trimalleolar fractures with impaction of the posteromedial tibial plafond: implications for talar stability. Foot Ankle Int, 2004;25:716-727.
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

The Treatment of Posterolateral Malleolar Fractures using Percutaneous Reduction Technique
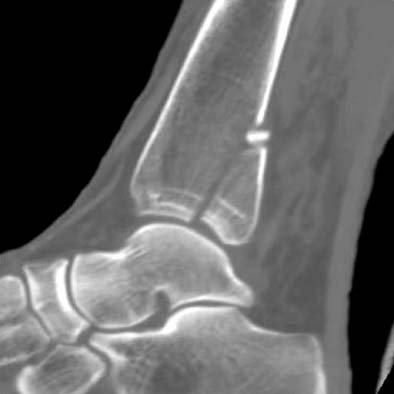
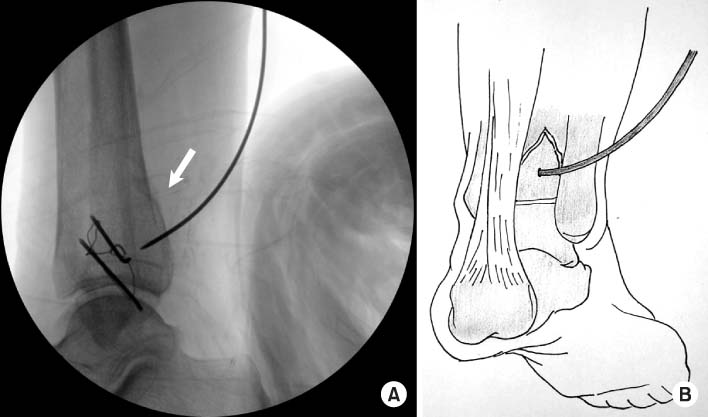
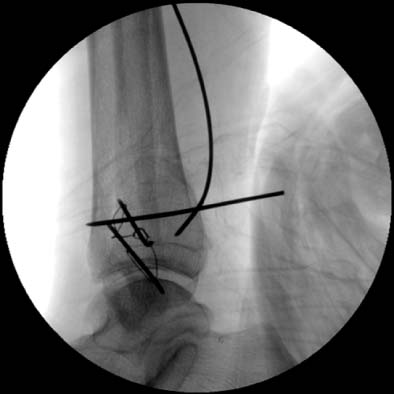
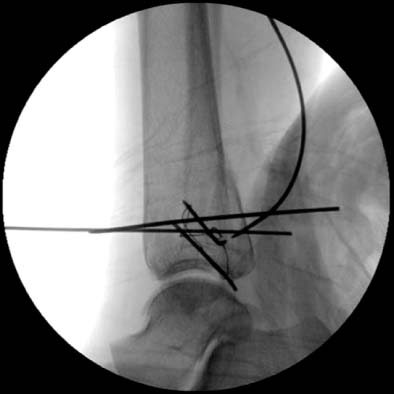
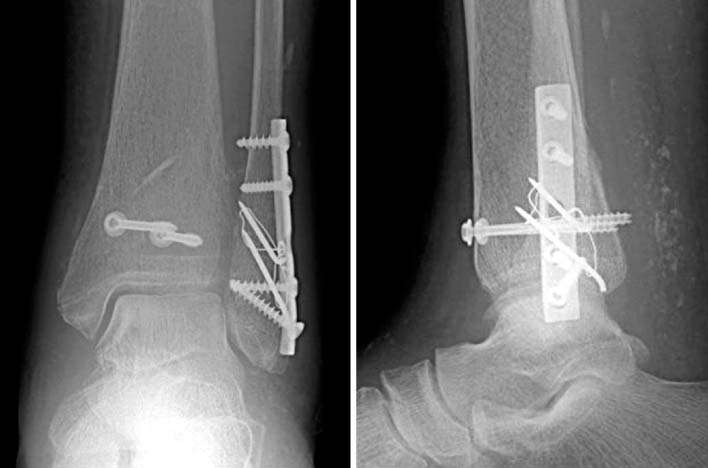
Fig. 1
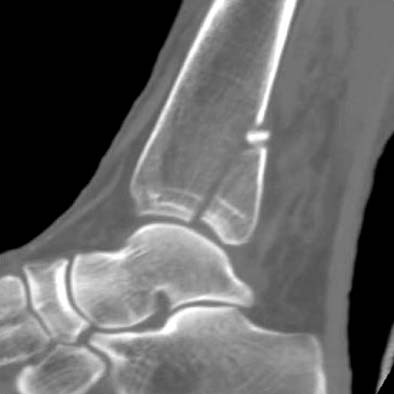
CT image shows large non-comminuted posterior malleolar fragment.
Fig. 2
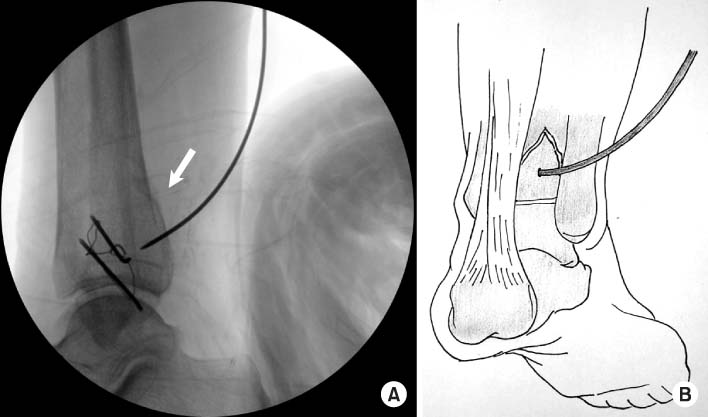
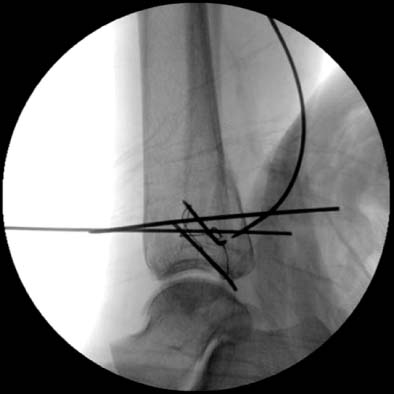
Percutaneous K-wire location is confirmed by C-arm image. Post-reduction image (A) is taken by C-arm image intensifier and the schematic image is shown (B).
Fig. 3
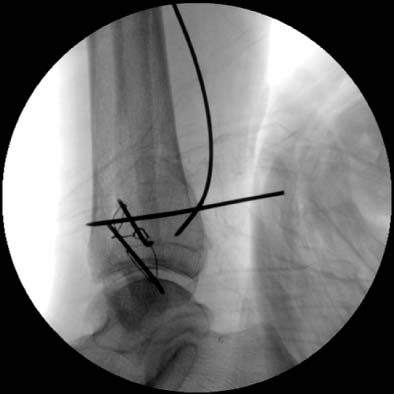
Additional K-wire is inserted to maintain the reduction status.
Fig. 4
A guide wire is inserted from anteromedial to posterior direction under the C-arm monitoring.
Fig. 5
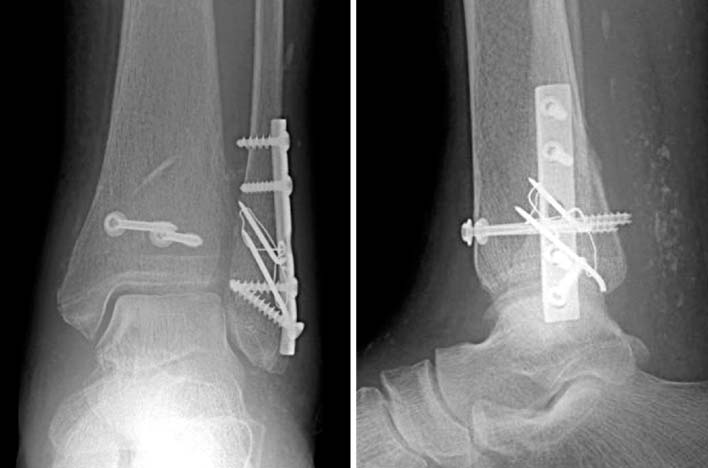
This photo shows completion of definite fixation. The medial malleolar fracture was reduced by non absorbable suture.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
The Treatment of Posterolateral Malleolar Fractures using Percutaneous Reduction Technique
Result clinical assessment (by Baird and Jackson)
The results of radiological assessment (intra-articular step-off of the distal tibia)
Table 1
Result clinical assessment (by Baird and Jackson)
Table 2
The results of radiological assessment (intra-articular step-off of the distal tibia)

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 Cite
Cite

