Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 29(2); 2016 > Article
-
Original Article
- Usefulness of Computed Tomography on Distal Tibia Intra-Articular Fracture Associated with Spiral Tibia Shaft Fracture
- Seong-Eun Byun, M.D., Sang-June Lee, M.D., Uk Kim, M.D., Young Rak Choi, M.D., Soo-Hong Han, M.D., Ph.D., Byong-Guk Kim, M.D., Ph.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2016;29(2):114-120.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.2.114
Published online: April 19, 2016
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea.
*Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, CHA Gumi Medical Center, CHA University, Gumi, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Byong-Guk Kim, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, CHA Gumi Medical Center, 12 Sinsi-ro 10-gil, Gumi 39295, Korea. Tel: 82-31-780-5289, Fax: 82-31-708-3578, bgkimmd@gmail.com
Copyright © 2016 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 626 Views
- 7 Download
- 1 Crossref
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Treatment of Distal Tibial Spiral Fractures Combined with Posterior Malleolar Fractures
Young Sung Kim, Ho Min Lee, Jong Pil Kim, Phil Hyun Chung, Soon Young Park
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2021; 56(4): 317. CrossRef
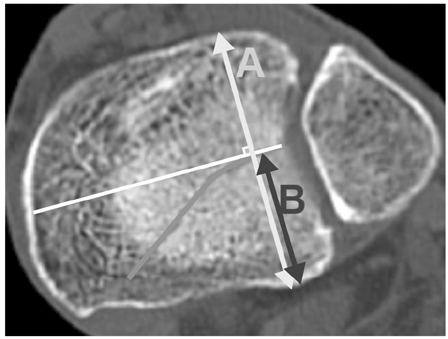
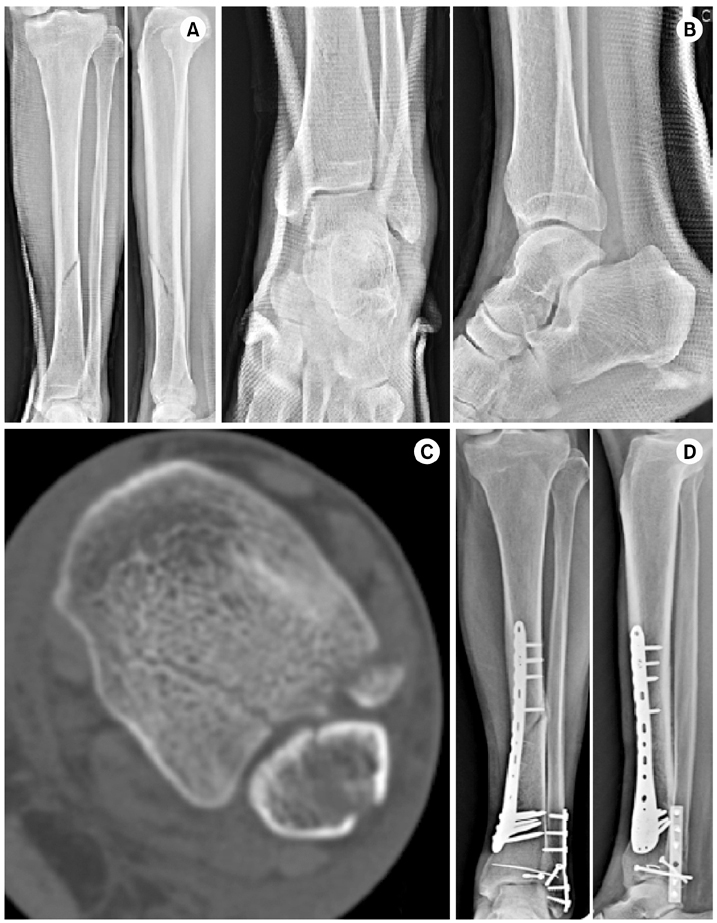
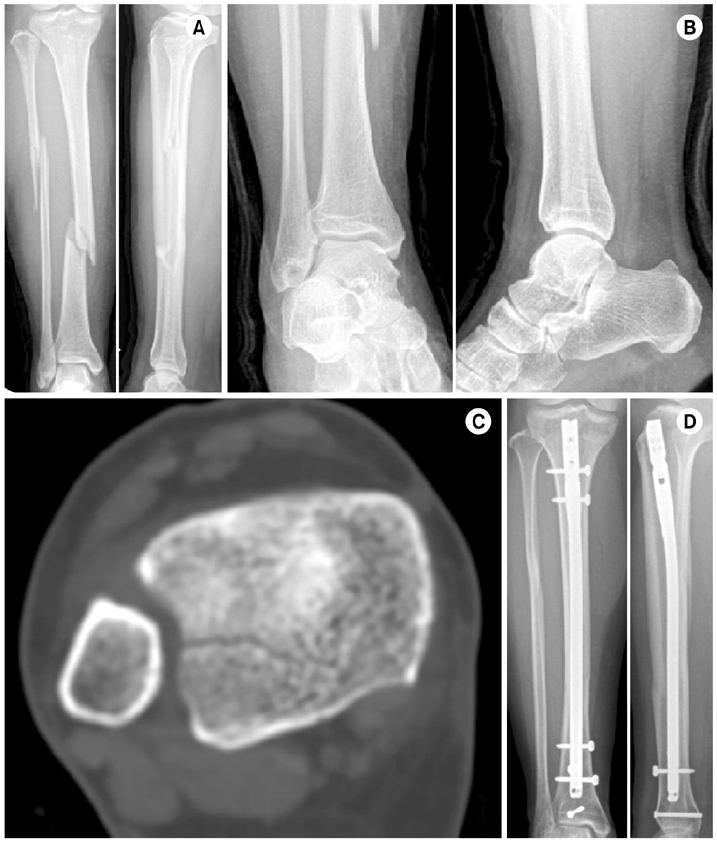
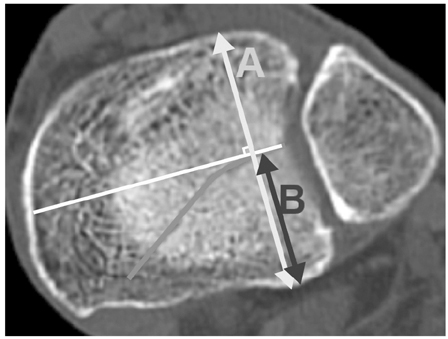
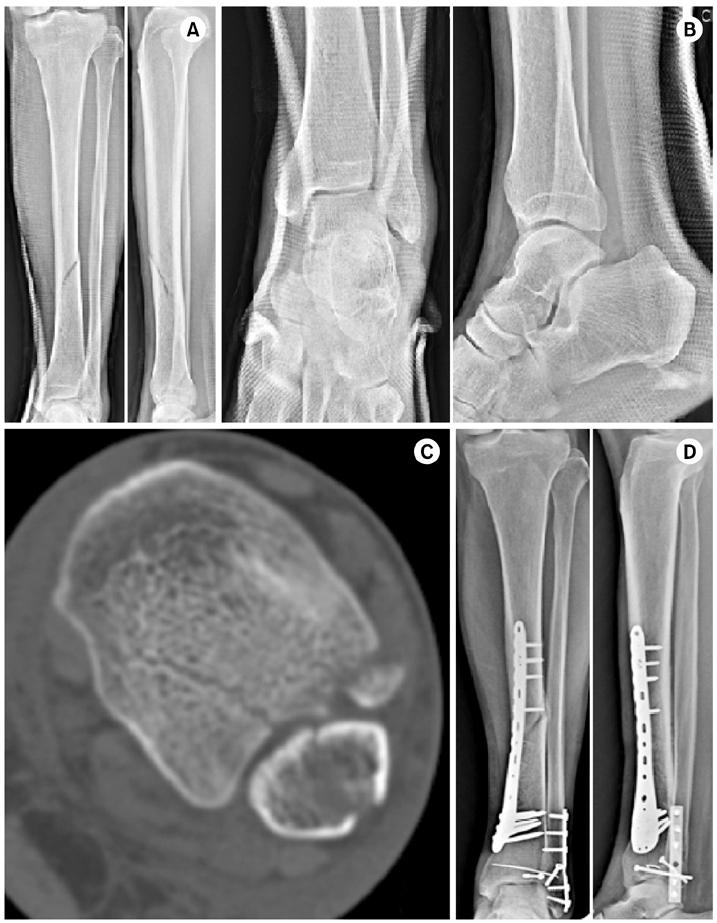
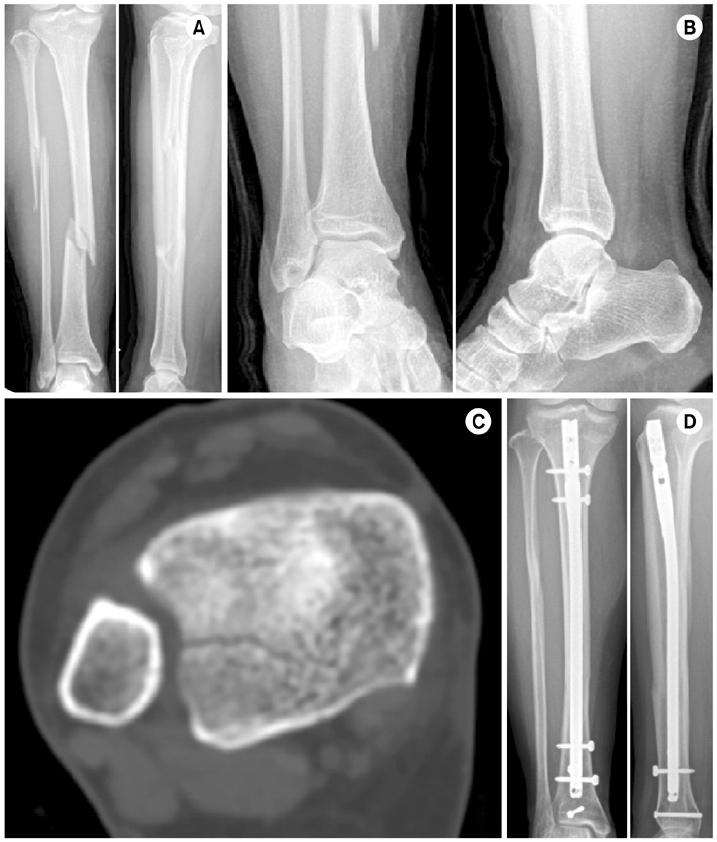
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Types of Associated Distal Tibia Intra-Articular Fracture in Tibia Shaft Fracture
| Variable | PM fracture | ATFL avulsion fracture | MM fracture | Combined fracture | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plain radiograph | 15* | 5* | 5 | 5 | 30 |
| CT | 23 | 5 | 0 | 4 | 32 |
| Total | 37* | 5* | 5 | 15* | 62 |
Values are presented as number only. *One posterior malleolar fracture and 5 anterior tibio-fibular ligament avulsion fractures diagnosed by plain radiograph were revealed as combined injuries after reviewing computed tomography and classified as combined fracture in 'total' line. PM: Posterior malleolus, ATFL: Anterior tibio-fibular ligament, MM: Medial malleolus, CT: Computed tomography.
Component of Associated Combined Fractures
| PM & ATFL avulsion fracture | PM & MM fracture | MM & ATFL avulsion fracture | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of combined fracture | 12 | 3 | 0 |
PM: Posterior malleolus, ATFL: Anterior tibio-fibular ligament, MM: Medial malleolus.
Comparison between PM Diagnosed by Plain Radiograph and CT
| Variable | Diagnosed by radiograph (n=20) | Diagnosed by CT (n=32) |
|---|---|---|
| PM mets indication of surgical fixation | 16 | 26 |
| PM fragment size >25% | 16 | 26 |
| PM >2 mm of gap | 2 | 0 |
| PM fixed | 14 | 18 |
Values are presented in number only. PM: Posterior malleolar fracture, CT: Computed tomography.
Values are presented as number only. *One posterior malleolar fracture and 5 anterior tibio-fibular ligament avulsion fractures diagnosed by plain radiograph were revealed as combined injuries after reviewing computed tomography and classified as combined fracture in 'total' line. PM: Posterior malleolus, ATFL: Anterior tibio-fibular ligament, MM: Medial malleolus, CT: Computed tomography.
PM: Posterior malleolus, ATFL: Anterior tibio-fibular ligament, MM: Medial malleolus.
Values are presented in number only. PM: Posterior malleolar fracture, CT: Computed tomography.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

