Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 21(4); 2008 > Article
-
Case Report
- Lateral Dislocation of the First Metatarsophalangeal Joint: A Case Report
- Yeong-Sik Yun, M.D., Young-Mo Kim, M.D., Kyung-Cheon Kim, M.D., Pil-Sung Kim, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2008;21(4):312-315.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.4.312
Published online: October 31, 2008
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea.
*Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Saeson Clinic, Daejeon, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Young-Mo Kim, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Chungnam National University, 640, Daesa-dong, Jung-gu, Daejeon 301-721, Korea. Tel: 82-42-280-7352, Fax: 82-42-252-7098, osdr69@cnu.ac.kr
• Received: May 15, 2008 • Revised: July 23, 2008 • Accepted: October 10, 2008
Copyright © 2008 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 696 Views
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref
Abstract
- Dislocation of the metatarsophalangeal joint is rare due to the stability of the ligaments and soft tissue surrounding the joint. The authors have experienced lateral dislocation of the first metatarsophalangeal joint, which required surgery, accompanied by complete injuries of medial collateral ligament and capsule, contributing to medial stability, differing from posterior dislocation with intersesamoid complex rupture, with a review of the relevant literature and previous reported cases.
- 1. Copeland CL, Kanat IO. A new classification for traumatic dislocations of the first metatarsophalangeal joint: type IIC. J Foot Surg, 1991;30:234-237.Article
- 2. Fabeck LG, Zekhnini C, Farrokh D, Descamps PY, Delincé PE. Traumatic hallux valgus following rupture of the medial collateral ligament of the first metatarsophalangeal joint: a case report. J Foot Ankle Surg, 2002;41:125-128.Article
- 3. Gale DW. Lateral dislocation of the first metatarsophalangeal joint, a radiographic indicator of reducibility. Injury, 1991;22:230. Article
- 4. Hwang CS, Kim YM, Oh HH, An YU, Kim JP. Dislocation of first metatarsophalangeal and tarsometatarsal joint -case report-. J Korean Soc Fract, 1995;8:386-390.Article
- 5. Jahss MH. Traumatic dislocations of the first metat-arsophalangeal joint. Foot Ankle, 1980;1:15-21.ArticlePDF
- 6. Jahss MH. Disorders of the hallux and first ray. In: Wickland EH, editor. Disorders of the foot and ankle. Medical and surgical management. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1991. p. 1125-1129.Article
- 7. Kim JH, Shin KH, Kim BJ. Irreducible dorsal dislocation of first metatarsophalangeal joint by closed method-report of a case. J Korean Orthop Assoc, 1988;23:1201-1204.ArticlePDF
- 8. Lohrer H. MP I joint giving way-a case study. Foot Ankle Int, 2001;22:153-157.ArticlePDF
- 9. Piétu G. Lateral dislocation of the first metatarsophalangeal joint: report of two cases. J Trauma, 2005;58:640-642.Article
- 10. Salamon PB, Gelberman RH, Huffer JM. Dorsal dislocation of the metatarsophalangeal joint of the great toe. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1974;56:1073-1075.Article
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
(B) In lateral view, the base of proximal phalanx of the greater toe was overlapped with the head of the first metatarsal bone without dorsal or plantar displacement.

(A) The plain AP radiography showed that the first metatarsophalangeal joint was dislocated and the proximal phalanx was displaced laterally. Also, the space between the first and second metatarsal bone was widened and there was a small avulsive fragment on the medial collateral ligament.

Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- An Unusual Combination of Injuries Involving Lateral Dislocation of the First and Fifth Metatarsophalangeal Joints Along With Fractures of the Other Toes on the Same Foot: A Report of a Rare Case
Mohamed Jiddi, Georges F Bassil, Zied Missaoui
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Dislocation of the first metatarsophalangeal joint concomitant with Lisfranc joint dislocation in a 45-year-old man
Kanoko Mizumoto, Tadashi Kimura, Makoto Kubota, Mitsuru Saito
BMJ Case Reports.2021; 14(6): e243004. CrossRef - Rare Lateral Dislocation of the First Metatarsophalangeal Joint: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Amir Reza Vosoughi, Pascal F. Rippstein
The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery.2017; 56(2): 375. CrossRef
Lateral Dislocation of the First Metatarsophalangeal Joint: A Case Report
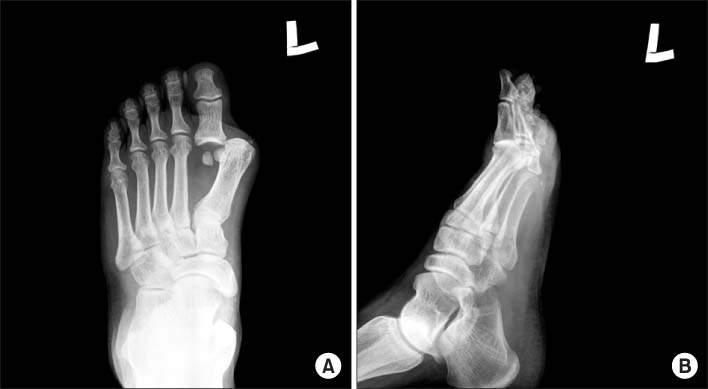
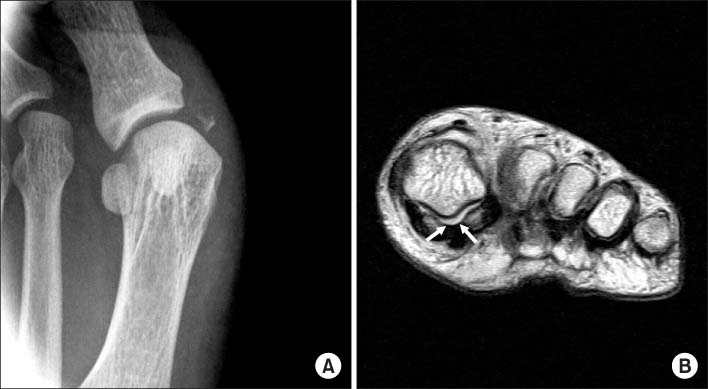
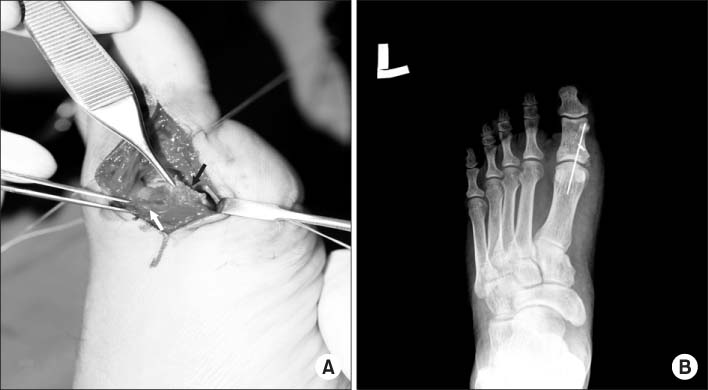
Fig. 1
(A) The plain AP radiography showed that the first metatarsophalangeal joint was dislocated and the proximal phalanx was displaced laterally. Also, the space between the first and second metatarsal bone was widened and there was a small avulsive fragment on the medial collateral ligament.
(B) In lateral view, the base of proximal phalanx of the greater toe was overlapped with the head of the first metatarsal bone without dorsal or plantar displacement.
Fig. 2
(A) After closed reduction, valgus stress radiography showed avulsive bone fragment of the proximal phalanx and medial instability of metatarsophalangeal joint.
(B) MRI showed that the intersesamoidal ligment (space between arrows) were intact.
Fig. 3
(A) An operative finding. The medial collateral ligament (white arrow) was avulsive from the base of the proximal phalanx and the tendon of abductor hallucis (black arrow) was ruptured.
(B) The temporary internal fixation of the first metatarsophalangeal joint was done using K-wire.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Lateral Dislocation of the First Metatarsophalangeal Joint: A Case Report

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS


 Cite
Cite

