Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 25(4); 2012 > Article
-
Original Article
- Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Humeral Proximal or Distal Shaft Fractures Using a 3.5/5.0 Metaphyseal Locking Plate
- Hyoung Keun Oh, M.D., Suk Kyu Choo, M.D., Jung Il Lee, M.D., Dong Hyun Seo, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2012;25(4):305-309.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.4.305
Published online: October 19, 2012
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Hyoung Keun Oh, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, 170, Juhwa-ro, Ilsanseo-gu, Goyang 411-706, Korea. Tel: 82-31-910-7968, Fax: 82-31-910-7967, osd11@paik.ac.kr
• Received: July 5, 2012 • Revised: July 5, 2012 • Accepted: August 19, 2012
Copyright © 2012 The Korean Fracture Society
- 800 Views
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Polarus Intramedullary Nail for Proximal Humeral and Humeral Shaft Fractures in Elderly Patients with Osteoporosis
Youn-Soo Hwang, Kwang-Yeol Kim, Hyung-Chun Kim, Su-Han Ahn, Dong-Eun Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2013; 26(1): 14. CrossRef
Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Humeral Proximal or Distal Shaft Fractures Using a 3.5/5.0 Metaphyseal Locking Plate
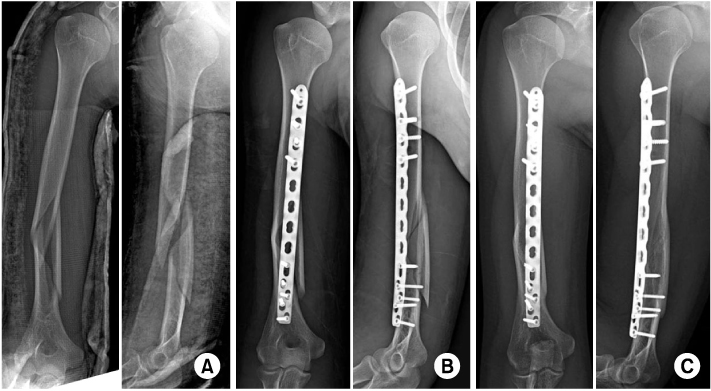
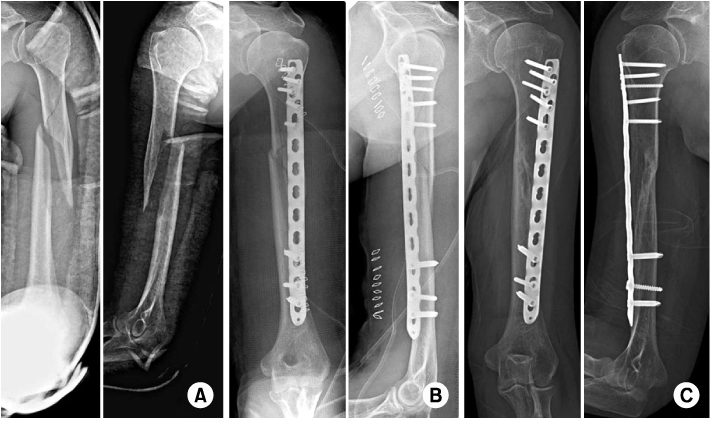
Fig. 1
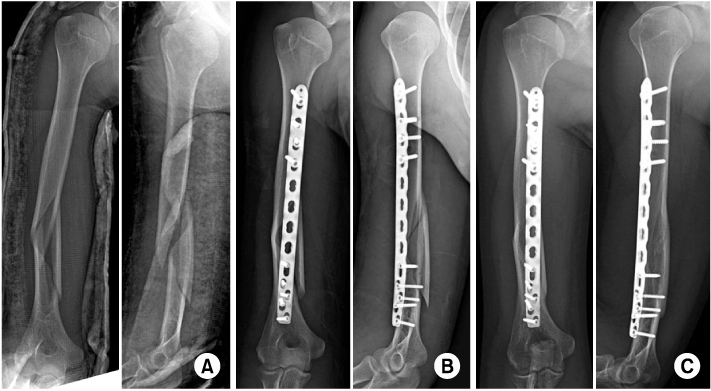
(A) Case of distal humeral shaft fracture of a 21-year-old man. Preoperative radiographs show distal humeral shaft fracture with a butterfly fragment.
(B) Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis using 3.5/5.0 locking compression plate was performed. The short distal fragment was fixed with five 3.5 mm screws.
(C) Last follow-up radiographs show solid bony union without screw loosening.
Fig. 2
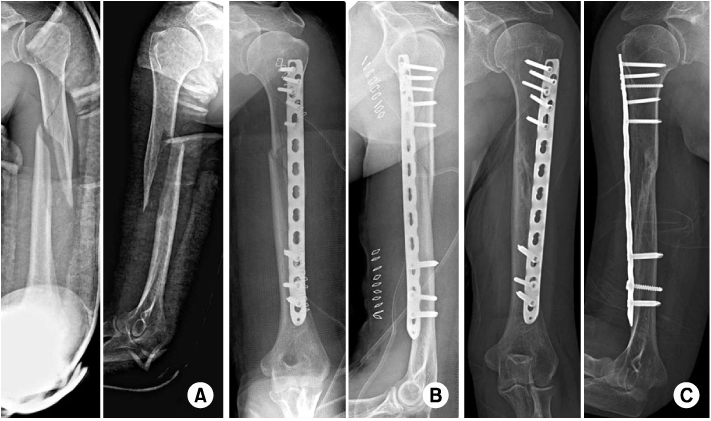
(A) Case of proximal humeral shaft fracture of a 44-year-old woman. Preoperative radiographs show proximal humeral shaft fracture with a butterfly fragment.
(B) Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis using 3.5/5.0 locking compression plate was performed. The short proximal fragment was fixed with five 3.5 mm screws.
(C) Last follow-up radiographs show solid bony union without screw loosening.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Humeral Proximal or Distal Shaft Fractures Using a 3.5/5.0 Metaphyseal Locking Plate

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

