Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 23(1); 2010 > Article
-
Original Article
- The Use of Fresh Frozen Allogenic Bone Graft in the Impacted Tibial Plateau Fractures
- Yeung Jin Kim, M.D., Soo Uk Chae, M.D., Jung Hwan Yang, M.D., Ji Wan Lee, M.D., Dae Han Wi, M.D., Duk Hwa Choi, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2010;23(1):26-33.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.1.26
Published online: January 31, 2010
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Wonkwang University College of Medicine, Iksan, Korea.
*Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Wonkwang University College of Medicine, Iksan, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Soo Uk Chae, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Wonkwang University College of Medicine, 344-2, Sinyong-dong, Iksan 570-711, Chunbuk, Korea. Tel: 82-63-472-5100, Fax: 82-63-472-5104, oschae@naver.com
• Received: July 1, 2009 • Revised: November 5, 2009 • Accepted: November 8, 2009
Copyright © 2010 The Korean Fracture Society
- 622 Views
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Autograft versus allograft reconstruction of acute tibial plateau fractures: a comparative study of complications and outcome
Abolfazl Bagherifard, Hassan Ghandhari, Mahmoud Jabalameli, Mohammad Rahbar, Hosseinali Hadi, Mehdi Moayedfar, Mohammadreza Minatour Sajadi, Alireza Karimpour
European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology.2017; 27(5): 665. CrossRef - Treatment of Tibial Plateau Fractures Using a Locking Plate and Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Osteosynthesis Technique
Hee-Gon Park, Dae-Hee Lee, Kyung Joon Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(2): 110. CrossRef
The Use of Fresh Frozen Allogenic Bone Graft in the Impacted Tibial Plateau Fractures
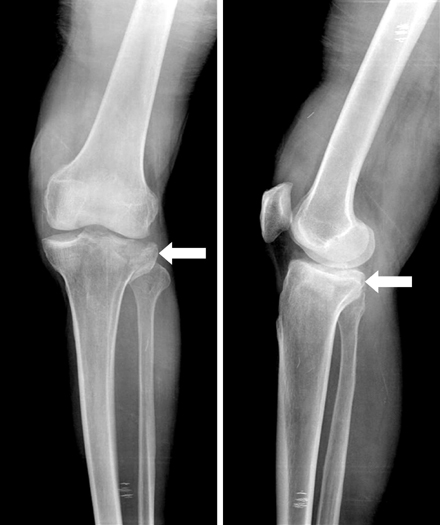
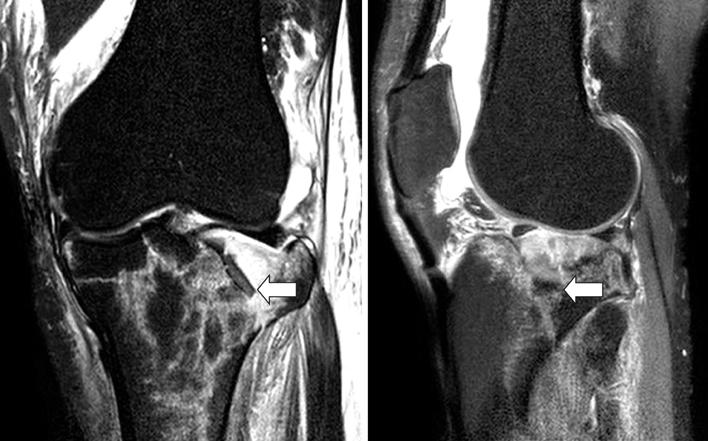
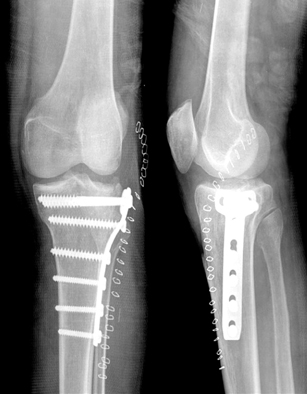
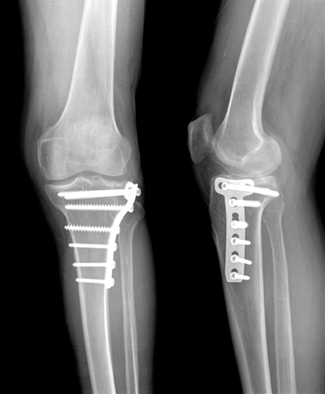
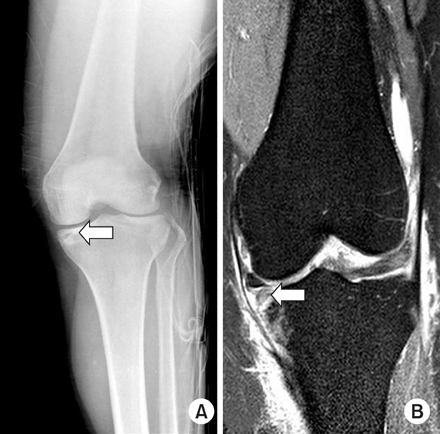
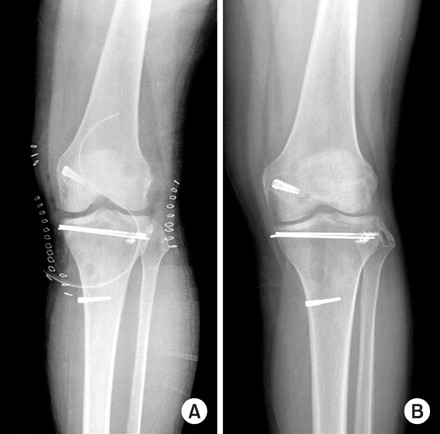
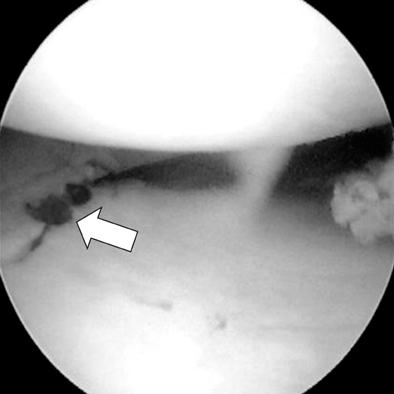
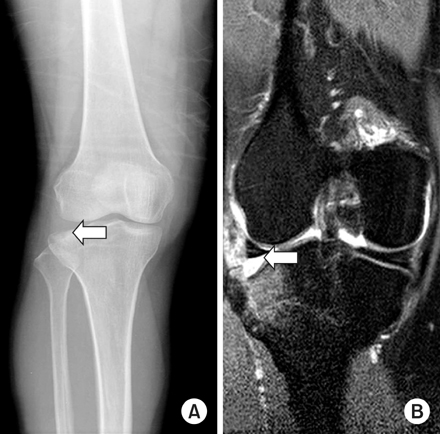
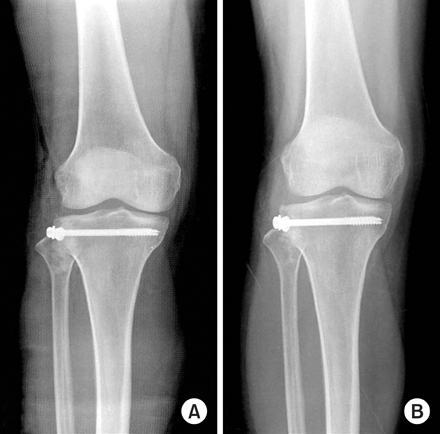
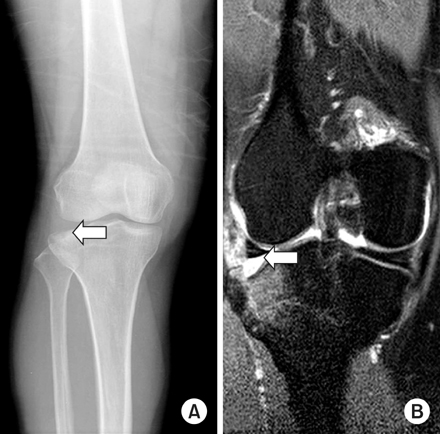
Fig. 1
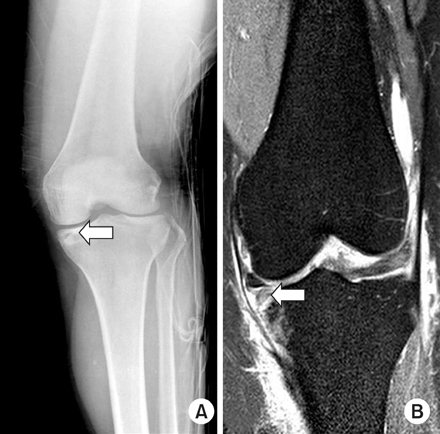
Preoperative anteroposterior and lateral radiograph of 65-year old male patient with Schatzker type II depressed lateral tibial plateau fracture (arrow).
Fig. 2
Preoperative MRI (arrow) showed the more depression of lateral tibial plateau.
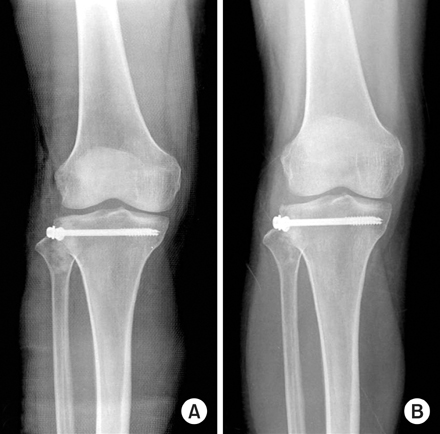
Fig. 3
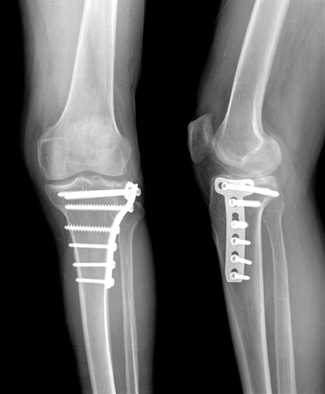
Postoperative radiograph showed the fixed T-plate after open reduction and cancellous impacted allogenous bone graft.
Fig. 4
The last follow-up radiograph showed the complete bone union and no depression of tibial plateau.
Fig. 5
Preoperative anteroposterior radiograph (A) and MRI image (B) of 47-year old female patient with Schatzker type IV depressed medial tibial plateau fracture (arrow).
Fig. 6
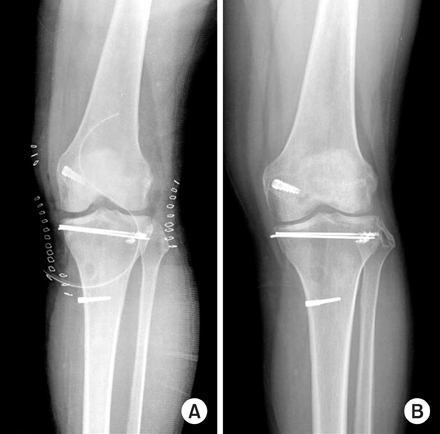
(A) The postoperative radiograph showed the 2 K-wires after open reduction and cancellous impacted allogenous bone graft, posterior cruciate ligament reconstruction and repair of posterolateral capsule.
(B) The last follow-up radiograph showed the complete bone union and no depression of tibial plateau.
Fig. 7
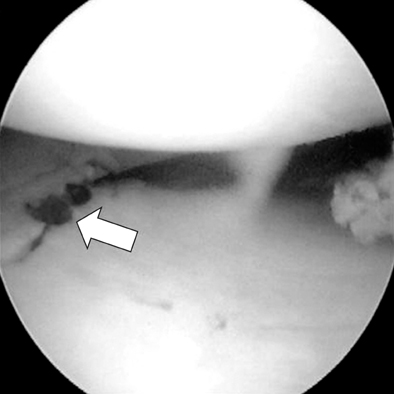
Arthroscopic finding (arrow) after anatomical reduction of medial tibial plateau.
Fig. 8
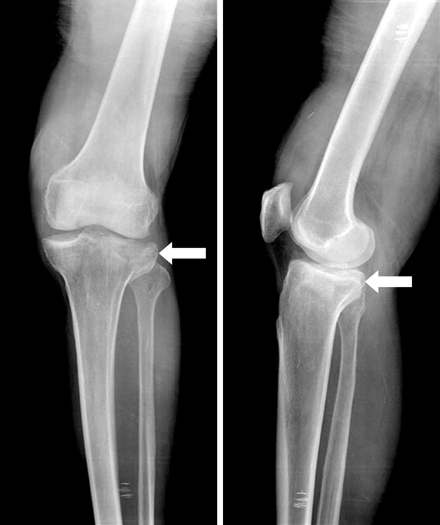
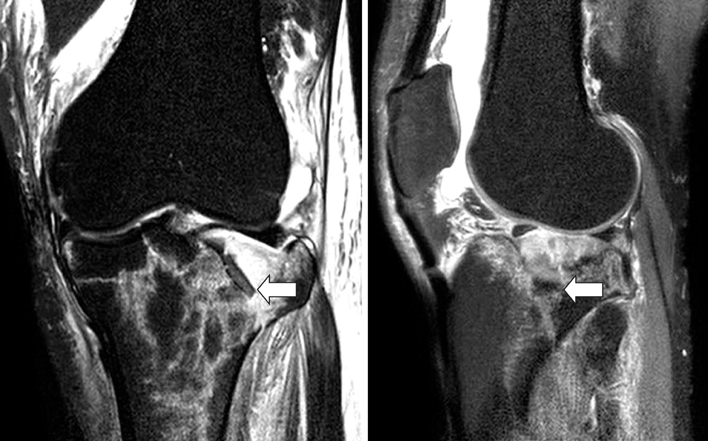
Preoperative anteroposterior radiograph (A) and MRI image (B) of 58-year old female patient with Schatzker type II depressed lateral tibial plateau fracture (arrow).
Fig. 9
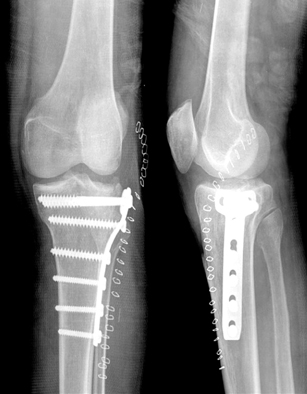
The postoperative (A) and last follow-up (B) radiograph showed the complete bone union and no depression of tibial plateau.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Fig. 6
Fig. 7
Fig. 8
Fig. 9
The Use of Fresh Frozen Allogenic Bone Graft in the Impacted Tibial Plateau Fractures
Modified Rasmussen's system
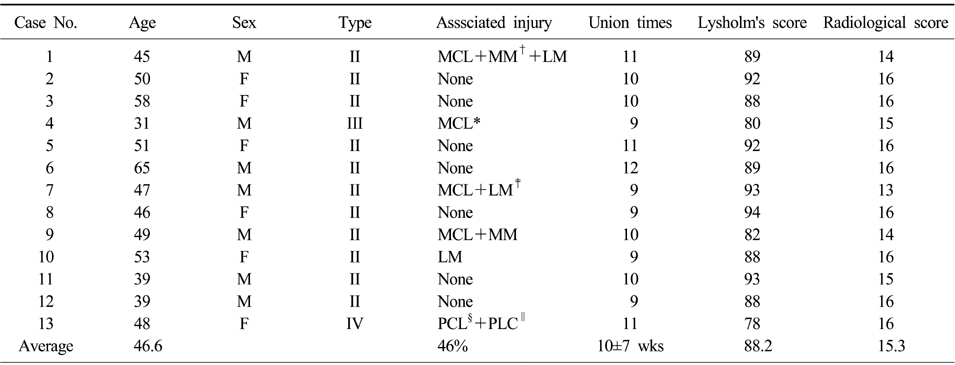
Charateristics of the group in details (clinical score, radiological union times as assessed at the time of the final follow-up)
*Medial collateral ligament, †Medial meniscus, ‡Lateral meniscus, §Posterior cruciate ligament, ∥Posterolateral capsule.
Table 1
Modified Rasmussen's system
Table 2
Charateristics of the group in details (clinical score, radiological union times as assessed at the time of the final follow-up)
*Medial collateral ligament, †Medial meniscus, ‡Lateral meniscus, §Posterior cruciate ligament, ∥Posterolateral capsule.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 Cite
Cite

