Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 32(1); 2019 > Article
- Original Article Use of a Distraction Dynamic External Fixator in the Treatment of Comminuted Middle Phalanx Base Fractures
- Sang Woo Kim, Chae Chil Lee, Sang Hun Ko, Il Yeong Hwang, Min Seok Kim, Woo Young Jin
-
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma 2019;32(1):1-5.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.1
Published online: January 31, 2019

- 865 Views
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
Abstract
PURPOSE
This paper suggests the use of distraction dynamic external fixators (DDEF) for the treatment of proximal middle phalanx fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Seven patients, who were diagnosed with comminuted intra-articular fractures at the base of the middle phalanx from February 2014 to November 2016, were enrolled in this study (volar aspect 6 cases, dorsal aspect 1 case). They underwent a closed reduction under a C-arm image intensifier, and DDEF was applied with general anesthesia. Range of motion (ROM) exercise was encouraged after 3 to 5 days postoperatively, and DDEF was removed after 5 weeks. Subluxation, angulation and displacement were evaluated 6 weeks postoperatively.
RESULTS
The patients who were treated with DDEF showed a normal proximal interphalangeal joint ROM (100°), and there was no subluxation or displacement on the X-ray film 6 weeks postoperatively. In addition, there were no signs of infection, such as local heat, redness, and pus-like discharge.
CONCLUSION
DDEF helps maintain the reduction and reducing forces through the ligamentotaxis. The joint stiffness is reduced, which it makes early return to daily life easier.
Published online Jan 25, 2019.
https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.1
Use of a Distraction Dynamic External Fixator in the Treatment of Comminuted Middle Phalanx Base Fractures
 , M.D.,
Chae Chil Lee
, M.D.,
Chae Chil Lee , M.D.,
Sang-Hun Ko
, M.D.,
Sang-Hun Ko , M.D.,
Il-Yeong Hwang
, M.D.,
Il-Yeong Hwang , M.D.,
Min-Seok Kim
, M.D.,
Min-Seok Kim , M.D.
and Woo Young Jin
, M.D.
and Woo Young Jin , M.D.
, M.D.
Abstract
Purpose
This paper suggests the use of distraction dynamic external fixators (DDEF) for the treatment of proximal middle phalanx fractures.
Materials and Methods
Seven patients, who were diagnosed with comminuted intra-articular fractures at the base of the middle phalanx from February 2014 to November 2016, were enrolled in this study (volar aspect 6 cases, dorsal aspect 1 case). They underwent a closed reduction under a C-arm image intensifier, and DDEF was applied with general anesthesia. Range of motion (ROM) exercise was encouraged after 3 to 5 days postoperatively, and DDEF was removed after 5 weeks. Subluxation, angulation and displacement were evaluated 6 weeks postoperatively.
Results
The patients who were treated with DDEF showed a normal proximal interphalangeal joint ROM (100°), and there was no subluxation or displacement on the X-ray film 6 weeks postoperatively. In addition, there were no signs of infection, such as local heat, redness, and pus-like discharge.
Conclusion
DDEF helps maintain the reduction and reducing forces through the ligamentotaxis. The joint stiffness is reduced, which it makes early return to daily life easier.
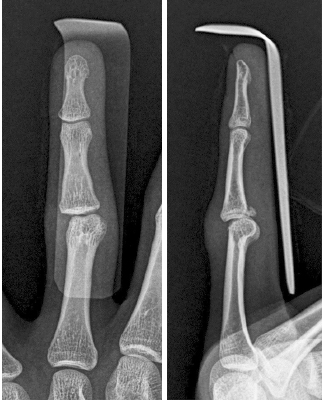
Fig. 1
Close-up X-ray image of the subluxation of proximal interphalangeal joint and suspected injury to the ulnar collateral ligament.
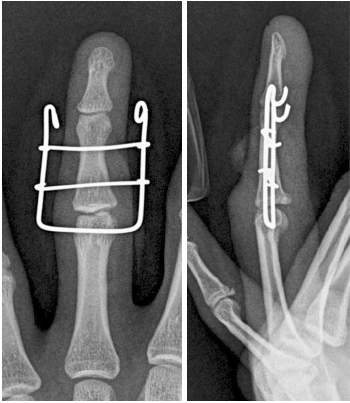
Fig. 2
Close-up X-ray image of distraction dynamic external fixator applied to subluxation of the proximal interphalangeal joint.
Fig. 3
Medical photograph of a patient who applied distraction dynamic external fixator at 3 days after operation.
Fig. 4
Medical photograph of a patient who applied distraction dynamic external fixator. Range of motion exercise was encouraged 3 to 5 days after surgery.
Fig. 5
Medical photograph of a patient applied distraction dynamic external fixator at 5 weeks after operation.
Fig. 6
Medical photograph of a patient applied distraction dynamic external fixator. The external fixator was removed after 5 weeks.
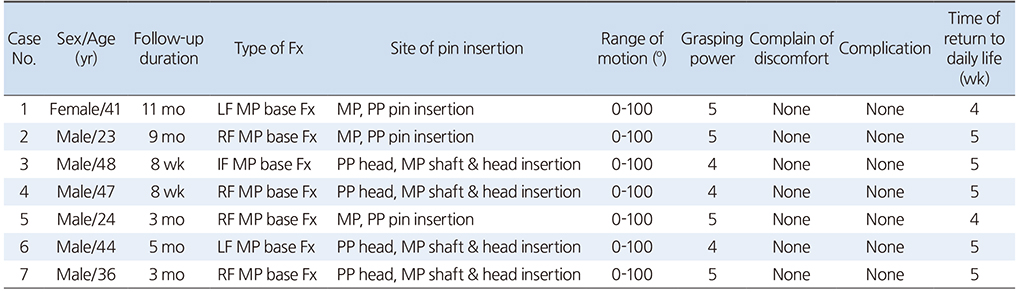
Table 1
Demographics and Summary of the Results
Financial support:None.
Conflict of interests:None.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS




 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite

