Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 22(2); 2009 > Article
-
Original Article
- Radiologic Analysis and Treatment of Posterior Malleolar Fractures of the Ankle
- Jae Sung Lee, M.D., Soo Yong Kang, M.D., Han Jun Lee, M.D., Young Bong Ko, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2009;22(2):98-103.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.2.98
Published online: April 30, 2009
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yong-San Hospital, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Soo Yong Kang, M.D. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yong-San Hospital, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, 65-207, Hangang-ro 3ga, Yongsan-gu, Seoul 140-757, Korea. Tel: 82-2-748-9848, Fax: 82-2-793-6634, sooykang@hitel.net
Copyright © 2009 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 632 Views
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to classify posterior malleolar fractures according to the position of fragments and to analyze radiologic features of each type.
-
Materials and Methods
- We analyzed forty-six patients of ankle fractures involving a posterior malleolus who were treated between January 2004 and December 2007. The posterior malleolar fractures were categorized into three types (posterolateral, posteromedial, shell) based on the major fracture line. In each type, we analyzed amount of displacement, involvement of articular surface, existence of subluxation and osteochondral impacted fragments.
-
Results
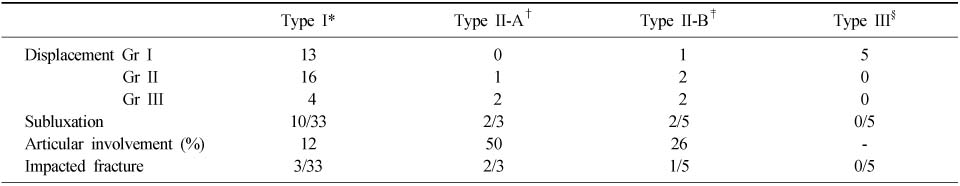
- The forty-six patients were categorized into three types: Posterolateral (PL) type (33 cases, 72%), Posteromedial (PM) type (8 cases, 17%), shell type (5 cases, 11%). Of the 8 cases with PM type, 7 cases showed displacement more than Grade II, 4 cases showed subluxation of ankle joint, and 3 cases showed osteochondral impacted fragment. Average involvement of articular surface of PM type is 35% (15~65%).
-
Conclusion
- Posterior malleolar fractures with medial extension tended to have adverse effect on ankle stability and Preoperative CT scan is essential for evaluation of fracture type and determination of appropriate surgical approach.
- 1. Bae SY, Sihn DH. The role of posterior malleolar frag ments in ankle pain after trimalleolar fractures. J Korean Soc Fract, 2003;16:59-66.
- 2. Boggs LR. Isolated posterior malleolar fractures. Am J Emerg Med, 1986;4:334-336.
- 3. Chung MY, Rhi WS, Song WC, Lee SM, Seo SD. Surgical treatment of fractures of the ankle. J Korean Orthop Assoc, 1997;32:741-748.PDF
- 4. Court-Brown CM, McBirnie J, Wilson G. Adult ankle fractures-an increasing problem? Acta Orthop Scand, 1998;69:43-47.
- 5. Ebraheim NA, Mekhail AO, Haman SP. External rotation-lateral view of the ankle in the assessment of the posterior malleolus. Foot Ankle Int, 1999;20:379-383.
- 6. Ebraheim NA, Wong FY. External rotation views in the diagnosis of posterior colliculus fracture of the medial malleolus. Am J Orthop, 1996;25:380-382.
- 7. Haraguchi N, Haruyama H, Toga H, Kato F. Pathoanatomy of posterior malleolar fractures of the ankle. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2006;88:1085-1092.
- 8. Harper MC, Hardin G. Posterior malleolar fractures of the ankle associated with external rotation-abduction injuries. Results with and without internal fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1988;70:1348-1356.
- 9. Jaskulka RA, Ittner G, Schedl R. Fractures of the posterior tibial margin: their role in the prognosis of malleolar fractures. J Trauma, 1989;29:1565-1570.
- 10. Jeong HJ, Kim KC, Chung SW. Treatment of the posterior malleolar fracture. J Korean Soc Fract, 1998;11:924-931.
- 11. Kang CN, Kim JO, Lee SB, Kang OY, Shin MS. Treatment of the posterior lip fracture of distal tibia using posteromedial approach. J Korean Soc Fract, 1995;8:594-599.
- 12. Katioz H, Bombaci H, Görgec M. Treatment of trimalleolar fractures. Is osteosynthesis needed in posterior malleolar fractures measuring less than 25% of the joint surface? Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc, 2003;37:299-303.
- 13. Lee CS, Suh JS, Yi JW. Comparative study for the results of ankle fracture depending on the extension of the posterior malleolus fracture. J Korean Orthop Assoc, 2007;42:470-474.
- 14. McDaniel WJ, Wilson FC. Trimalleolar fractures of the ankle. An end result study. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1977;122:37-45.
- 15. Neumaier Probst E, Maas R, Meenen NM. Isolated fracture of the posterolateral tibial lip (Volkmann's triangle). Acta Radiol, 1997;38:359-362.
- 16. Nugent JF, Gale BD. Isolated posterior malleolar ankle fractures. J Foot Surg, 1990;29:80-83.
- 17. Scheidt KB, Stiehl JB, Skrade DA, Barnhardt T. Posterior malleolar ankle fractures: an in vitro biomechanical analysis of stability in the loaded and unloaded states. J Orthop Trauma, 1992;6:96-101.
- 18. Talbot M, Steenblock TR, Cole PA. Posterolateral approach for open reduction and internal fixation of trimalleolar ankle fractures. Can J Surg, 2005;48:487-490.
- 19. Weber M. Trimalleolar fractures with impaction of the posteromedial tibial plafond: implications for talar stability. Foot Ankle Int, 2004;25:716-727.
REFERENCES
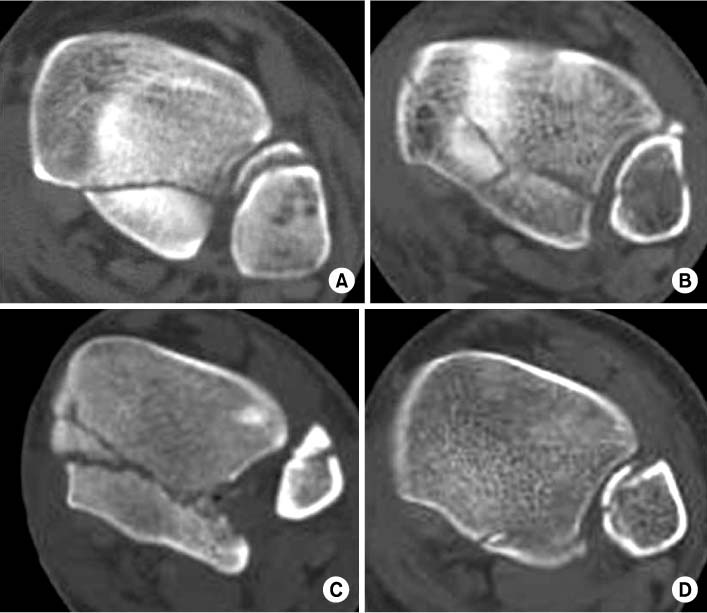
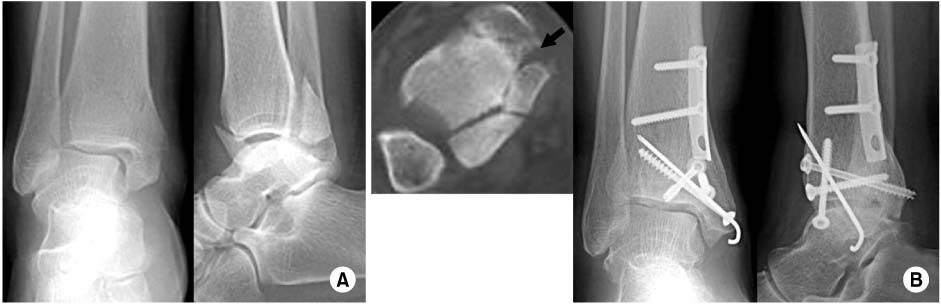
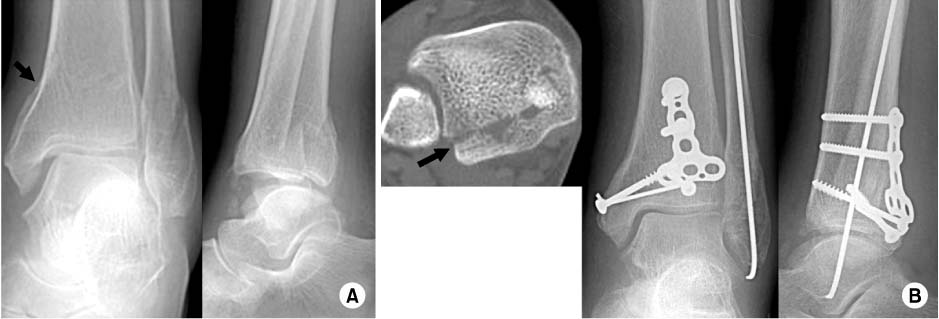
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Treatment of Isolated Posterior Malleolus Fracture in the Ankle
Ji Hoon Kim, Seong Mu Cha, Dae Yeon Jo, Jin Soo Suh
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2014; 49(1): 29. CrossRef
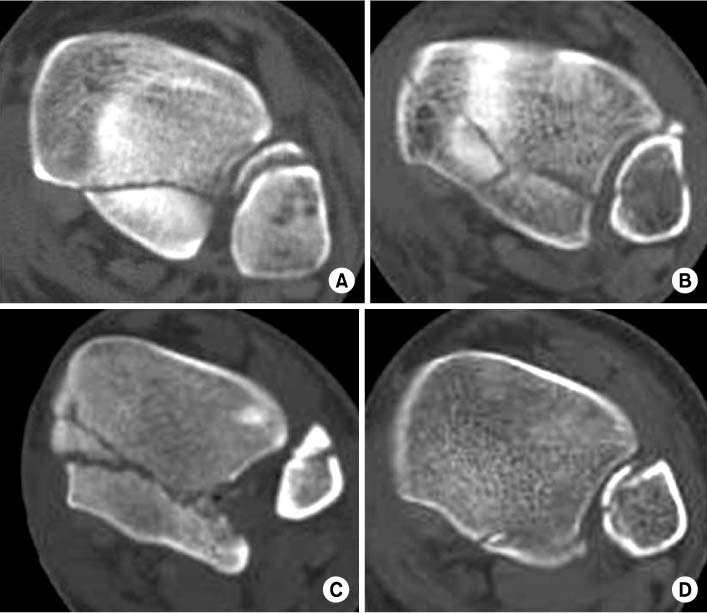
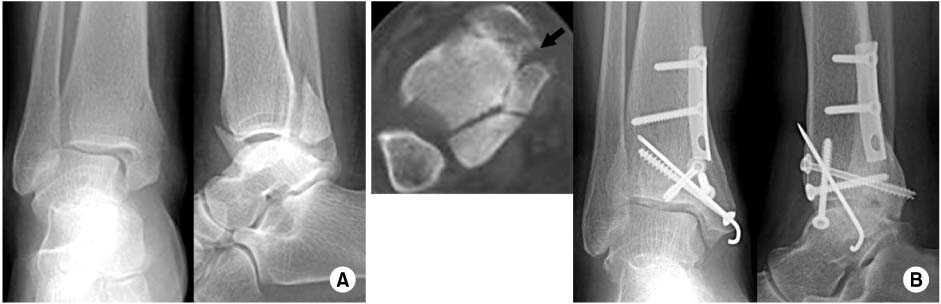
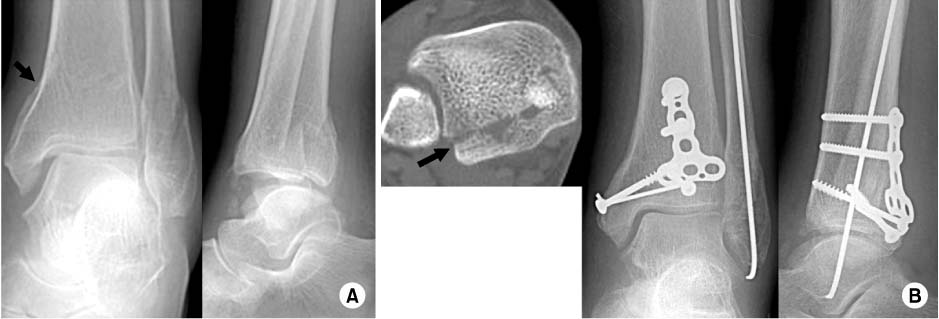
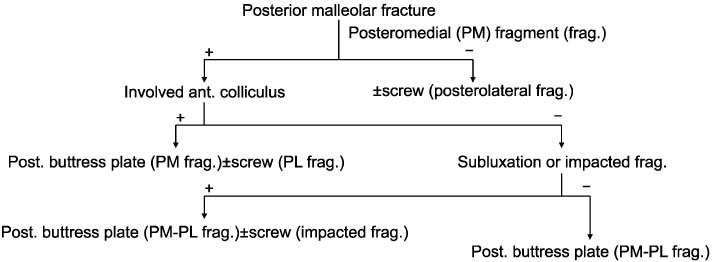
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
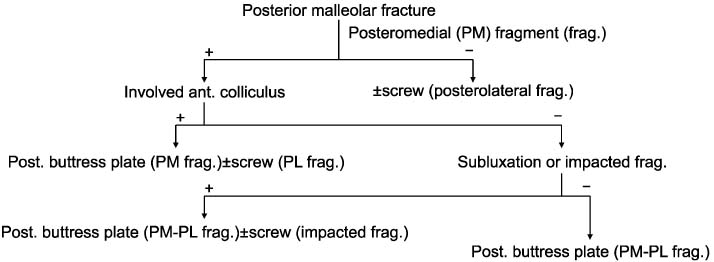
Fig. 4
Summary of results
*Type I: Posterolateral type, †Type II-A: Posteromedial type (involved to anterior colliculus), ‡Type II-B: Posteromedial type (involved to posterior colliculus), §Type III: Shell type
*Type I: Posterolateral type, †Type II-A: Posteromedial type (involved to anterior colliculus), ‡Type II-B: Posteromedial type (involved to posterior colliculus), §Type III: Shell type

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

