Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 24(1); 2011 > Article
-
Review Article from Symposium
- Treatment of Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures after Hip Arthroplasty
- Kyu-Tae Hwang, M.D., Young-Ho Kim, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2011;24(1):121-130.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.1.121
Published online: January 21, 2011
- Address reprint requests to: Young-Ho Kim, M.D. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Guri Hospital, Hanyang University, College of Medicine, 249-1, Gyomun-dong, Guri 471-701, Korea. Tel: 82-31-560-2316·Fax: 82-31-557-8781, kimyh1@hanyang.ac.kr
Copyright © 2011 The Korean Fracture Society
- 670 Views
- 5 Download
- 3 Crossref
- 1. Amstutz HC, Thomas BJ, Jinnah R, Kim W, Grogan T, Yale C. Treatment of primary osteoarthritis of the hip. A comparison of total joint and surface replacement arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1984;66:228-241.Article
- 2. Beals RK, Tower SS. Periprosthetic fractures of the femur. An analysis of 93 fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1996;327:238-246.
- 3. Berry DJ. Epidemiology: hip and knee. Orthop Clin North Am, 1999;30:183-290.
- 4. Berry DJ, Harmsen WS, Ilstrup D, Lewallen DG, Cabanela ME. Survivorship of uncemented proximally porous-coated femoral components. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1995;319:168-177.
- 5. Bethea JS 3rd, DeAndrade JR, Fleming LL, Lindenbaum SD, Welch RB. Proximal femoral fractures following total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1982;170:95-106.
- 6. Brady OH, Garbuz DS, Masri BA, Duncan CP. Classification of the hip. Orthop Clin North Am, 1999;30:215-220.
- 7. Brady OH, Garbuz DS, Masri BA, Duncan CP. The reliability and validity of the Vancouver classification of femoral fractures after hip replacement. J Arthroplasty, 2000;15:59-62.
- 8. Campbell P, McWilliams TG. Periprosthetic femoral fractures. Curr Orthop, 2002;16:126-132.
- 9. Chandler HP, Tigges RG. The role of allografts in the treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures. Instr Course Lect, 1998;47:257-264.
- 10. Christensen CM, Seger BM, Schultz RB. Management of intraoperative femur fractures associated with revision hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1989;248:177-180.
- 11. Claus AM, Hopper RH Jr, Engh CA. Fractures of the greater trochanter induced by osteolysis with the anatomic medullary locking prosthesis. J Arthroplasty, 2002;17:706-712.
- 12. Cofield RH, Sperling JW, Morrey BF, O'Driscoll SW, Mabrey JD. Bucholz RW, Heckman JD, Court-Brown C. periprosthetic fracture. In: Rockwood and Green's Fractures in Adults, 2006;6th ed. Philadelphia, PA, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins Inc. 681-737.
- 13. Cooke PH, Newman JH. Fractures of the femur in relation to cemented hip prostheses. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1988;70:386-389.
- 14. Crockarell JR Jr, Berry DJ, Lewallen DG. Nonunion after periprosthetic femoral fracture associated with total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1999;81:1073-1079.
- 15. Dennis MG, Simon JA, Kummer FJ, Koval KJ, DiCesare PE. Fixation of periprosthetic femoral shaft fractures occurring at the tip of the stem: a biomechanical study of 5 techniques. J Arthroplasty, 2000;15:523-528.
- 16. Duncan CP, Masri BA. Fractures of the femur after hip replacement. Instr Course Lect, 1995;44:293-304.
- 17. Engh CA, Massin P. Cementless total hip arthroplasty using the anatomic medullary locking stem. Results using a survivorship analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1989;249:141-158.
- 18. Garbuz DS, Masri BA, Duncan CP. Periprosthetic fractures of the femur: principles of prevention and management. Instr Course Lect, 1998;47:237-242.
- 19. Giannoudis PV, Kanakaris NK, Tsiridis E. Principles of internal fixation and selection of implants for periprosthetic femoral fractures. Injury, 2007;38:669-687.
- 20. Haddad FS, Duncan CP, Berry DJ, Lewallen DG, Gross AE, Chandler HP. Periprosthetic femoral fractures around well-fixed implants: use of cortical onlay allografts with or without a plate. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2002;84:945-950.
- 21. Haddad FS, Masri BA, Garbuz DS, Duncan CP. The prevention of periprosthetic fractures in total hip and knee arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am, 1999;30:191-207.
- 22. Herzwurm PJ, Walsh J, Pettine KA, Ebert FR. Prophylactic cerclage: a method of preventing femur fracture in uncemented total hip arthroplasty. Orthopedics, 1992;15:143-146.
- 23. Incavo SJ, Beard DM, Pupparo F, Ries M, Wiedel J. One-stage revision of periprosthetic fractures around loose cemented total hip arthroplasty. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ), 1998;27:35-41.
- 24. Incavo SJ, DiFazio F, Wilder D, Howe JG, Pope M. Longitudinal crack propagation in bone around femoral prosthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1991;272:175-180.
- 25. Jensen JS, Barfod G, Hansen D, et al. Femoral shaft fracture after hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Scand, 1988;59:9-13.
- 26. Johansson JE, McBroom R, Barrington TW, Hunter GA. Fracture of the ipsilateral femur in patients wih total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1981;63:1435-1442.
- 27. Kavanagh BF. Femoral fractures associated with total hip arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am, 1992;23:249-257.
- 28. Kelley SS. Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg, 1994;2:164-172.
- 29. Kolstad K. Revision THR after periprosthetic femoral fractures. An analysis of 23 cases. Acta Orthop Scand, 1994;65:505-508.
- 30. Learmonth ID. The management of periprosthetic fractures around the femoral stem. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2004;86:13-19.
- 31. Lewallen DG, Berry DJ. Periprosthetic fracture of the femur after total hip arthroplasty: treatment and results to date. Instr Course Lect, 1998;47:243-249.
- 32. Macdonald SJ, Paprosky WG, Jablonsky WS, Magnus RG. Periprosthetic femoral fractures treated with a long-stem cementless component. J Arthroplasty, 2001;16:379-383.
- 33. Malkani AL, Lewallen DG, Cabanela ME, Wallrichs SL. Femoral component revision using an uncemented, proximally coated, long-stem prosthesis. J Arthroplasty, 1996;11:411-418.
- 34. Mallory TH, Kraus TJ, Vaughn BK. Intraoperative femoral fractures associated with cementless total hip arthroplasty. Orthopedics, 1989;12:231-239.
- 35. McElfresh EC, Coventry MB. Femoral and pelvic fractures after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1974;56:483-492.
- 36. McLauchlan GJ, Robinson CM, Singer BR, Christie J. Results of an operative policy in the treatment of periprosthetic femoral fracture. J Orthop Trauma, 1997;11:170-179.
- 37. Moran MC. Treatment of periprosthetic fractures around total hip arthroplasty with an extensively coated femoral component. J Arthroplasty, 1996;11:981-988.
- 38. Mont MA, Maar DC. Fractures of the ipsilateral femur after hip arthroplasty. A statistical analysis of outcome based on 487 patients. J Arthroplasty, 1994;9:511-519.
- 39. Ries MD. Periprosthetic fractures: early and late. Orthopedics, 1997;20:798-800.
- 40. Schmidt AH, Kyle RF. Periprosthetic fractures of the femur. Orthop Clin North Am, 2002;33:143-152.
- 41. Schwartz JT Jr, Mayer JG, Engh CA. Femoral fracture during non-cemented total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1989;71:1135-1142.
- 42. Scott RD, Turner RH, Leitzes SM, Aufranc OE. Femoral fractures in conjunction with total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1975;57:494-501.
- 43. Serocki JH, Chandler RW, Dorr LD. Treatment of fractures about hip prostheses with compression plating. J Arthroplasty, 1992;7:129-135.
- 44. Springer BD, Berry DJ, Lewallen DG. Treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures following total hip arthroplasty with femoral component revision. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2003;85:2156-2162.
- 45. Stuchin SA. Femoral shaft fracture in porous and press-fit total hip arthroplasty. Orthop Rev, 1990;19:153-159.
- 46. Tadross TS, Nanu AM, Buchanan MJ, Checketts RG. Dall-Miles plating for periprosthetic B1 fractures of the femur. J Arthroplasty, 2000;15:47-51.
- 47. Tower SS, Beals RK. Fractures of the femur after hip replacement: the Oregon experience. Orthop Clin North Am, 1999;30:235-247.
- 48. Tsiridis E, Haddad FS, Gie GA. The management of periprosthetic femoral fractures around hip replacements. Injury, 2003;34:95-105.
- 49. Tsiridis E, Narvani AA, Haddad FS, Timperley JA, Gie GA. Impaction femoral allografting and cemented revision for periprosthetic femoral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2004;86:1124-1132.
- 50. Wilson D, Masri BA, Duncan CP. Periprosthetic fractures: an operative algorithm. Orthopedics, 2001;24:869-870.
- 51. Wong P, Gross AE. The use of structural allografts for treating periprosthetic fractures about the hip and knee. Orthop Clin North Am, 1999;30:259-264.
- 52. Younger AS, Dunwoody I, Duncan CP. Periprosthetic hip and knee fractures: the scope of the problem. Instr Course Lect, 1998;47:251-256.
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
(A) This patient suffered from left hip pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis showing severe osteoporosis with wide medullary
canal.
(B) Prophylactic cerclage band and wires were used to prevent the intraoperative periprosthetic femoral fracture.
(C) Postoperative radiograph at six months shows stably fixed prosthesis in medullary canal.
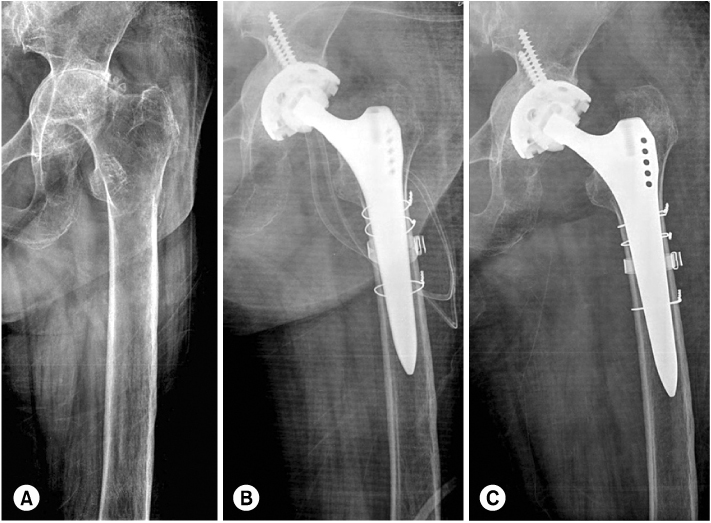

Fig. 2
(A) Preoperative radiograph showed loosening of cemented stem and massive osteolysis combined with severe osteopenic femur.
(B) Type C3 fracture occurred during insertion of provisional prosthesis intraoperatively.
(C) The fracture fixed with wires and bands with uncemented long stem prosthesis was united.


Fig. 5
(A) A type B1 fracture.
(B) The fracture was treated using plate with proximal cables and distal bicortical screws. The radiograph shows fracture united and a stable prosthesis.
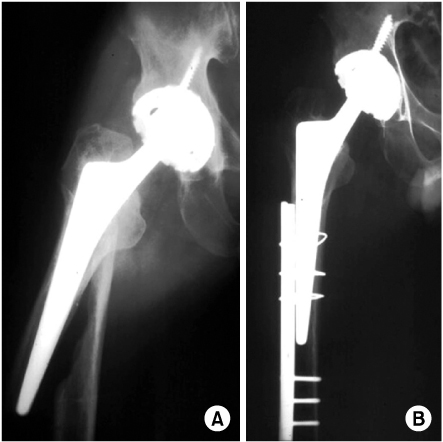

Fig. 6
(A) A type B2 fracture.
(B) The fracture was treated with an uncemented long-stem prosthesis 3 bandages and 1 wires. The radiograph demonstrates good healing of fracture with stable prosthesis.
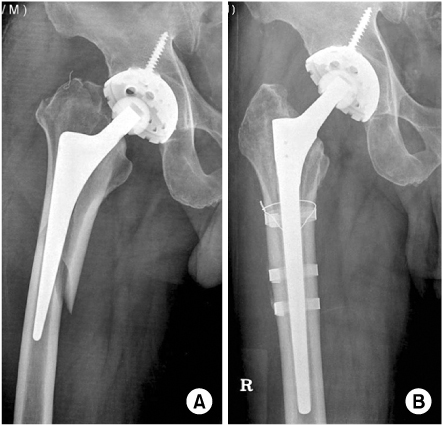

Fig. 7
(A) The anteroposterior radiograph of type B3 fracture reveals a loose prosthesis associated with deficient proximal lateral cortex.
(B) The fracture was treated with an uncemented long-stem prosthesis and plate with 4 cables with allograft. The radiograph demonstrates good healing with graft incorporation.
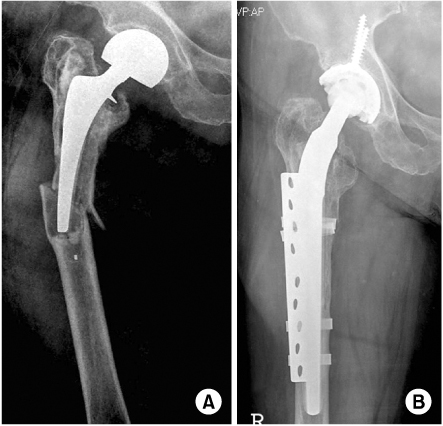

Fig. 8
(A) The AP radiograph shows type B3 fracture with severe proximal bone loss.
(B) Postoperative radiograph at second week shows that fracture is reduced and fixed with plate (supplementary fixation and additional allograft), but does not show fully restored bone stock.
(C) Postoperative radiograph at 26 months shows varus shift of stem.
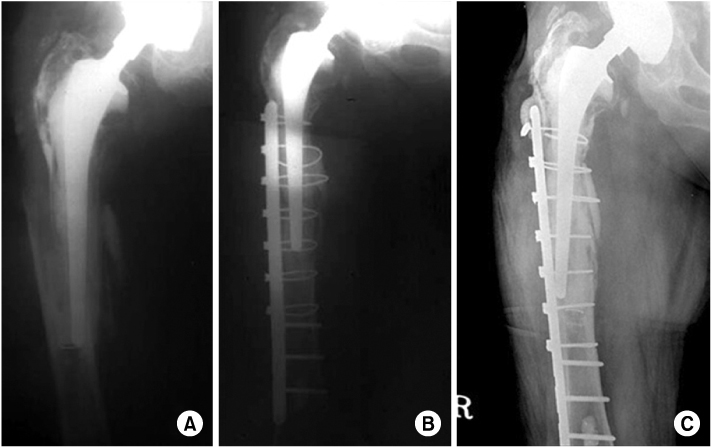

Fig. 9
(A) The anteroposteriorradiograph shows type B3 fracture.
(B) Postoperative radiograph at second week shows that fracture is stably fixed with plate, screws and cerclage wire, and remaining stem is stably fixed as well.
(C) Postoperative radiograph at one year shows good healing of fracture with stable prosthesis.


Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Recurrent Treatment Failure in Vancouver Classification Type C Periprosthetic Fractures around a Well Fixed Short Femoral Stem: A Case Report
Byeong Yeol Choi, Hong-Man Cho, Jiyeon Park
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2022; 35(1): 16. CrossRef - Decision-Making and Principle of Management in Periprosthetic Femoral Fracture after Total Hip Arthroplasty
Beom-Soo Kim, Kyung-Jae Lee, Byung-Woo Min
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2021; 56(3): 200. CrossRef - Treatment of Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures after Hip Arthroplasty
Jung-Hoon Choi, Jong-Hyuk Jeon, Kyung-Jae Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2020; 33(1): 43. CrossRef
Treatment of Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures after Hip Arthroplasty
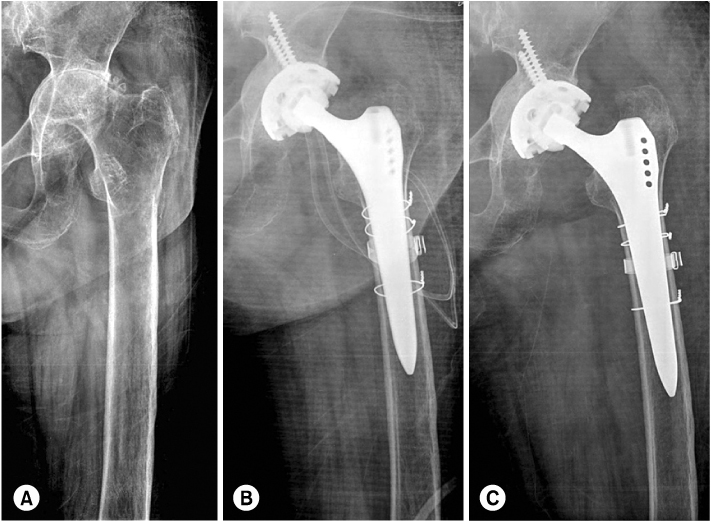
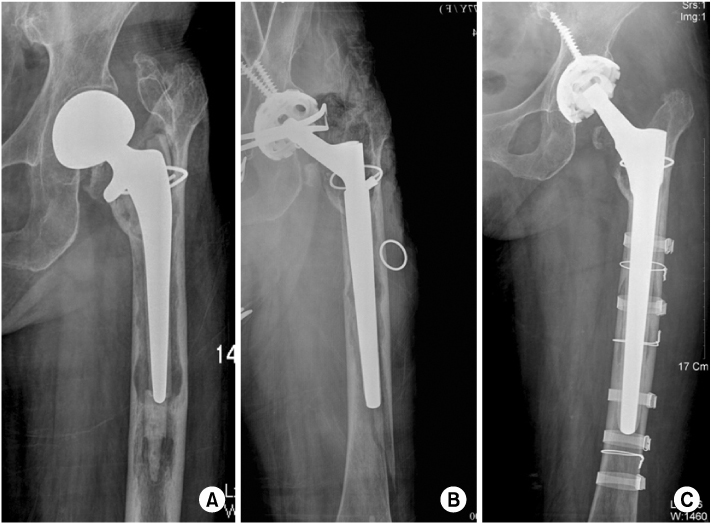
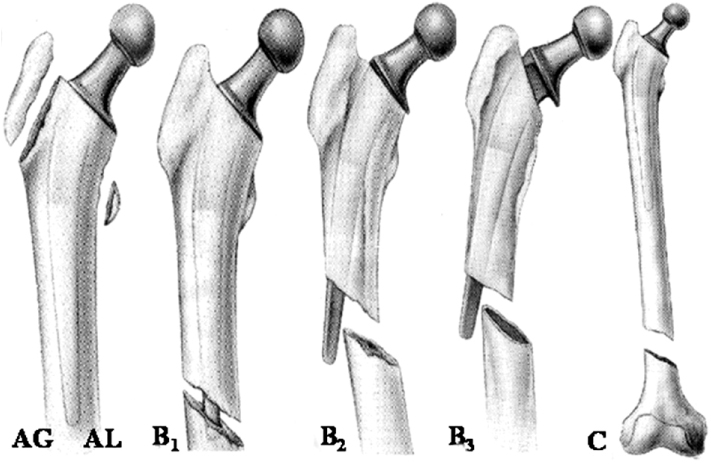
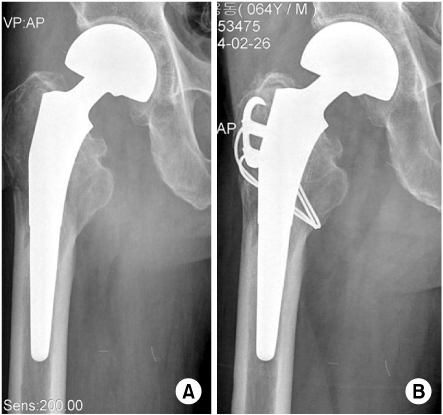

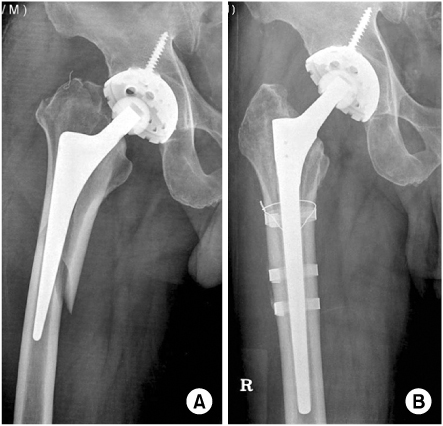
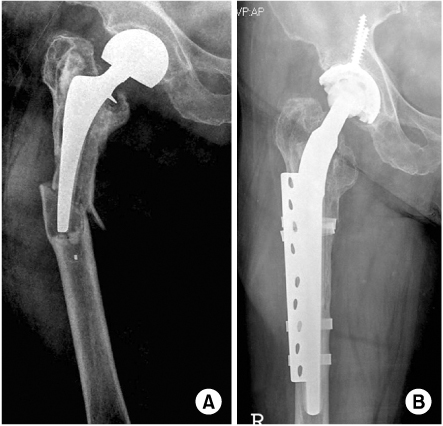
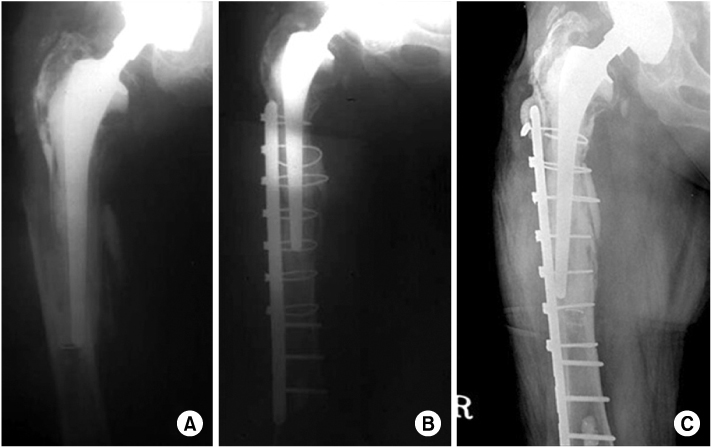
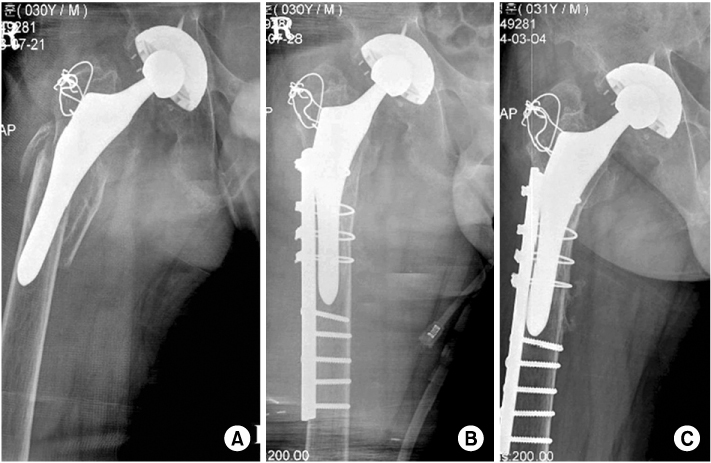
Fig. 1
(A) This patient suffered from left hip pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis showing severe osteoporosis with wide medullary
canal.
(B) Prophylactic cerclage band and wires were used to prevent the intraoperative periprosthetic femoral fracture.
(C) Postoperative radiograph at six months shows stably fixed prosthesis in medullary canal.
Fig. 2
(A) Preoperative radiograph showed loosening of cemented stem and massive osteolysis combined with severe osteopenic femur.
(B) Type C3 fracture occurred during insertion of provisional prosthesis intraoperatively.
(C) The fracture fixed with wires and bands with uncemented long stem prosthesis was united.
Fig. 3
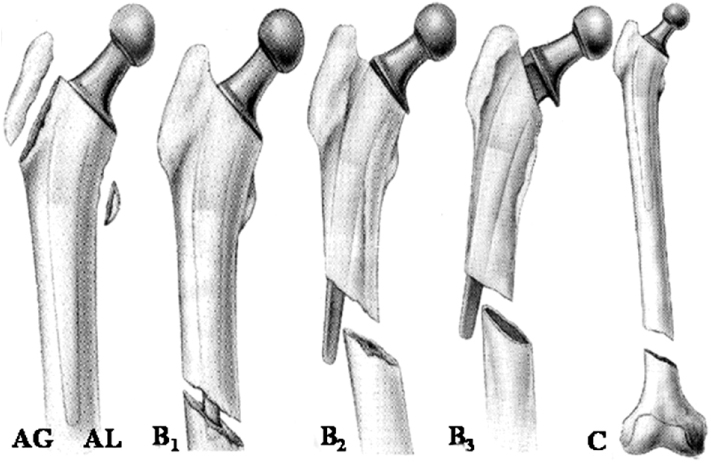
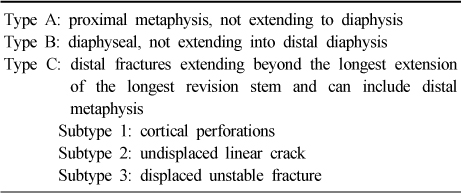
Vancouver classification of postoperative periprosthetic femoral fracture.
Fig. 4
(A) A type AG fracture.
(B) The fracture fixed with hook and cables was united.
Fig. 5
(A) A type B1 fracture.
(B) The fracture was treated using plate with proximal cables and distal bicortical screws. The radiograph shows fracture united and a stable prosthesis.
Fig. 6
(A) A type B2 fracture.
(B) The fracture was treated with an uncemented long-stem prosthesis 3 bandages and 1 wires. The radiograph demonstrates good healing of fracture with stable prosthesis.
Fig. 7
(A) The anteroposterior radiograph of type B3 fracture reveals a loose prosthesis associated with deficient proximal lateral cortex.
(B) The fracture was treated with an uncemented long-stem prosthesis and plate with 4 cables with allograft. The radiograph demonstrates good healing with graft incorporation.
Fig. 8
(A) The AP radiograph shows type B3 fracture with severe proximal bone loss.
(B) Postoperative radiograph at second week shows that fracture is reduced and fixed with plate (supplementary fixation and additional allograft), but does not show fully restored bone stock.
(C) Postoperative radiograph at 26 months shows varus shift of stem.
Fig. 9
(A) The anteroposteriorradiograph shows type B3 fracture.
(B) Postoperative radiograph at second week shows that fracture is stably fixed with plate, screws and cerclage wire, and remaining stem is stably fixed as well.
(C) Postoperative radiograph at one year shows good healing of fracture with stable prosthesis.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Fig. 6
Fig. 7
Fig. 8
Fig. 9
Treatment of Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures after Hip Arthroplasty
Vancouver classification of intraoperative periprosthetic femoral fracture
Table 1
Vancouver classification of intraoperative periprosthetic femoral fracture

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 Cite
Cite

