Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 20(2); 2007 > Article
-
Original Article
- Joint Depression Type of Intraarticular Calcaneal Fractures Treated with Essex-Lopresti Method
- Gyu Min Kong, M.D., Byoung Ho Suh, M.D., Dong Joon Kim, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2007;20(2):178-183.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.2.178
Published online: June 14, 2016
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Handong University Sunlin Hospital, Pohang, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Dong Joon Kim, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Handong University Sunlin Hospital, 69-7, Daesin-dong, Buk-gu, Pohang 791-704, Korea. Tel: 82-54-245-5164, Fax: 82-54-245-5345, docos@naver.com
Copyright © The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved
- 804 Views
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- To evaluate the result of joint depression type of intraarticular calcaneal fractures treated with Essex-Lopresti method.
-
Materials and Methods
- From March 2001 to February 2005, Thirty two patients' joint depression type of intraarticular calcaneal fractures which treated with Essex-Lopresti method were clinically and radiographically evaluated retrospectively.
-
Results
- According to Creighton-Nebraska Health Foundation Assessment Score (C-N score), there were 5 excellent, 11 good, 6 fair and 10 poor results. Böhler angle was corrected from 10.3 degrees to 24.5 degrees. There was a positive correlation between size of depressed fragment and C-N score (p<0.01).
-
Conclusion
- Essex-Lopresti method can substitute open reduction methods in joint depression type of intraarticular calcaneal fractures which have relatively large depressed joint fragments.
- 1. Bernstein SA. Late sequelae of calcaneal fractures. Clin Podiatr Med Surg, 2000;17:81-96.Article
- 2. Crosby LA, Fitzgibbons T. Computerized tomography scanning of acute intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. A new classification system. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1990;72:852-859.Article
- 3. Crosby LA, Fitzgibbons T. Intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Results of closed treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1993;290:47-54.Article
- 4. Essex-Lopresti P. The mechanism, reduction technique and results of os calcis. Br J Surg, 1952;39:395-419.
- 5. Kwak KD, Cho HO, Lim DH, Ahn SM, Jang JH. Modified Essex-Lopresti reduction for the displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures. J Korean Soc Foot Surg, 2003;7:109-114.
- 6. Lance EM, Carey EJ Jr, Wade PA. Fractures of the os calcis treatment by early mobilization. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1963;30:76-90.
- 7. Miller WE. Pain and impairment considerations following treatment of disruptive os calcis fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1983;(177):82-86.
- 8. Myerson M, Quill GE Jr. Late complications of fractures of the calcaneus. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1993;75:331-341.
- 9. Pozo JL, Kirwan EO, Jackson AM. The long-term results of conservative management of the severely displaced fractures of the calcaneus. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1984;66:386-390.
- 10. Ross SD, Sowerby MR. The operative treatment of fractures of the os calcis. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1985;199:132-143.
- 11. Sanders R. Displaced intraarticular fractures of the calcaneus. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2000;82:225-250.
- 12. Sanders R, Fortin P, DiPasquale T, Walling A. Operative treatment in 120 displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Results using a prognostic computed tomography scan classification. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1993;290:87-95.
- 13. Sung CH, Park BM, Song KS, Kim HG, Kim JM, Kim TE. Operative treatment of intraarticular calcaneal fractures-comparison of outcomes between open reduction and closed reduction. J Korean Fract Soc, 2005;18:170-175.
- 14. Tornetta P 3rd. The Essex-Lopresti reduction for calcaneal fractures revisited. J Orthop Trauma, 1998;12:469-473.
- 15. Yoon HK, Jeon KP, Kang KH, Kim JI, Kim DS, Song KS. Essex-Loprestis axial pinning in the treatment of intraarticular calcaneal fracture. J Korean Soc Fract, 1999;12:344-350.
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
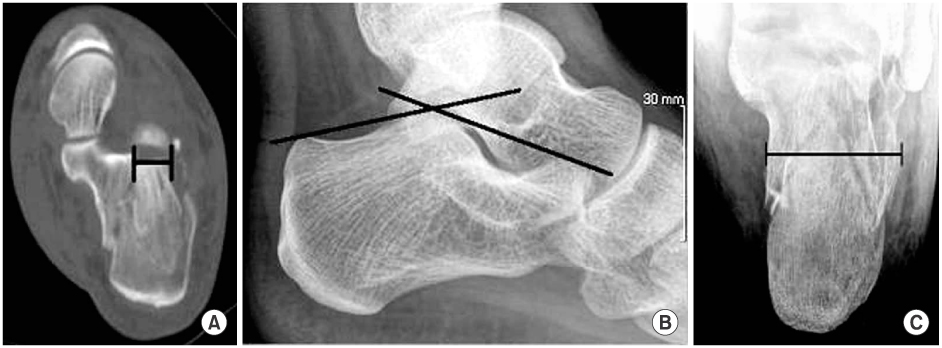
These photographs show methods of measurement of the size of depressed fragment (A), Böhler angle (B) and calcaneal width (C).

Fig. 2
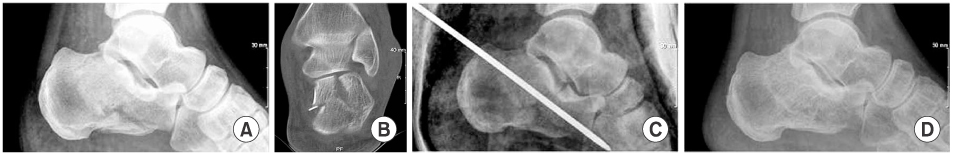
Preoperative lateral radiograph (A) and CT scan (B) of a 43 year-old male patient show joint depression type of intraarticular calcaneal fracture. Preoperative Böhler angle is 11.6 degrees and the size of depressed joint fragment is 13.5 mm. Postopertive radiograph (C) shows increased Böhler angle to 30.5 degrees. Nineteen month follow-up radiogragh (D) shows good alignment of subtalar joint and 30 degrees of Böhler angle. Final C-N score is 85 points.

Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Treatment of Calcaneus Fractures: Recent Trend for Acute Fractures and Complications
Woo-Chun Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2007; 20(4): 361. CrossRef
Joint Depression Type of Intraarticular Calcaneal Fractures Treated with Essex-Lopresti Method
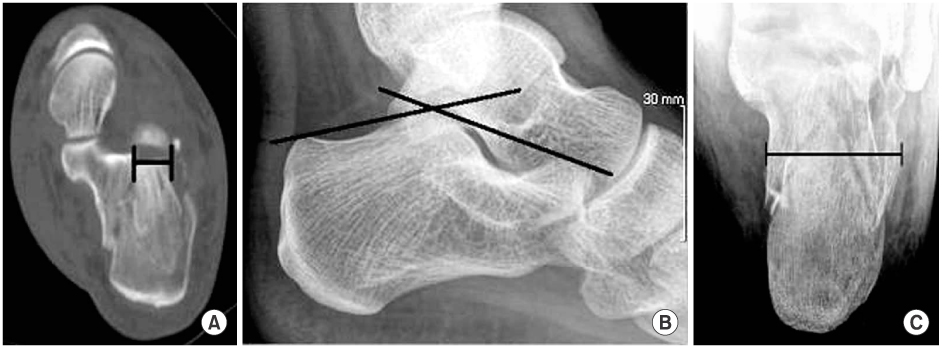
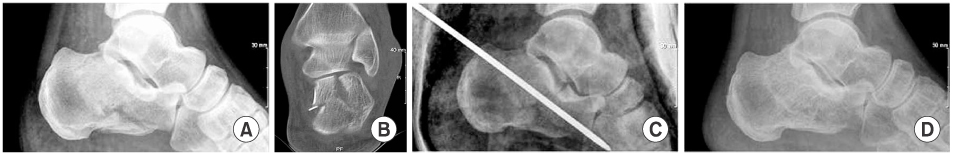
Fig. 1
These photographs show methods of measurement of the size of depressed fragment (A), Böhler angle (B) and calcaneal width (C).
Fig. 2
Preoperative lateral radiograph (A) and CT scan (B) of a 43 year-old male patient show joint depression type of intraarticular calcaneal fracture. Preoperative Böhler angle is 11.6 degrees and the size of depressed joint fragment is 13.5 mm. Postopertive radiograph (C) shows increased Böhler angle to 30.5 degrees. Nineteen month follow-up radiogragh (D) shows good alignment of subtalar joint and 30 degrees of Böhler angle. Final C-N score is 85 points.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Joint Depression Type of Intraarticular Calcaneal Fractures Treated with Essex-Lopresti Method
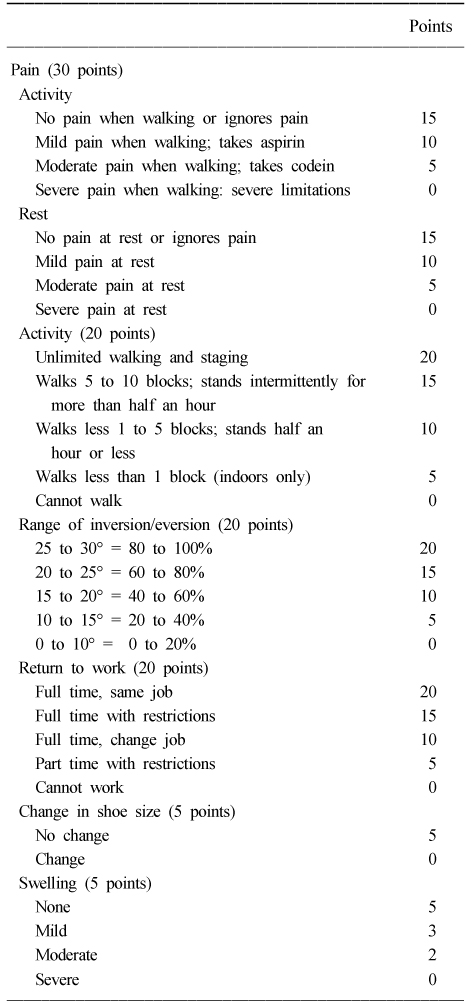
Creighton-Nebraska health foundation assessment scale for fractures of the calcaneus*
*90 to 100 points is an excellent result; 80 to 89 a good result; 65 to 79 a fair result; and 64 or less a poor result.
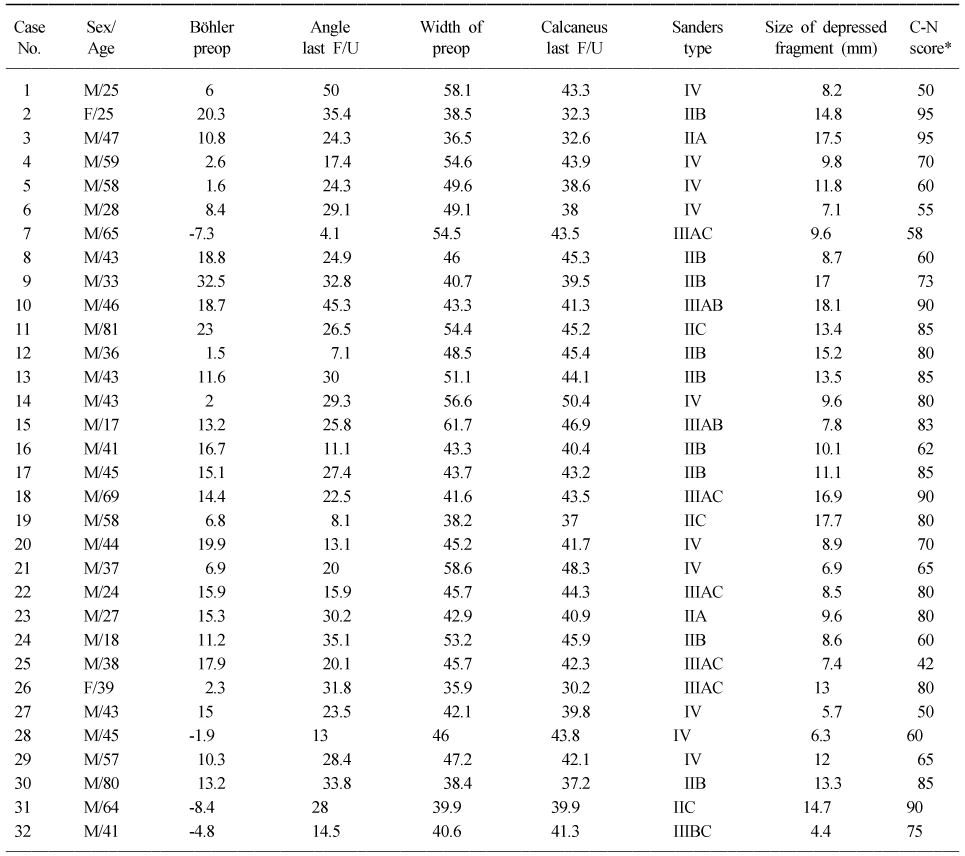
Radiographic and clinical results of the joint depression type of intraarticular calcaneal fractures
*Creighton-Nebraska health foundation assessment score.
Table 1
Creighton-Nebraska health foundation assessment scale for fractures of the calcaneus*
*90 to 100 points is an excellent result; 80 to 89 a good result; 65 to 79 a fair result; and 64 or less a poor result.
Table 2
Radiographic and clinical results of the joint depression type of intraarticular calcaneal fractures
*Creighton-Nebraska health foundation assessment score.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

