Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 29(3); 2016 > Article
-
Review Article
- Surgical Treatment for Displaced Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures
- Chul Hyun Park, M.D., Oog Jin Shon, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2016;29(3):221-231.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.3.221
Published online: July 21, 2016
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Oog Jin Shon, M.D. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yeungnam University Medical Center, 170 Hyeonchung-ro, Nam-gu, Daegu 42415, Korea. Tel: 82-53-620-3640, Fax: 82-53-628-4020, ossoj@med.yu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2016 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 1,257 Views
- 15 Download
- 1 Crossref
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Current Treatment of Calcaneal Fractures and Dislocation
Dae Jin Nam, Sung Hyun Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2022; 35(2): 74. CrossRef
Surgical Treatment for Displaced Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures
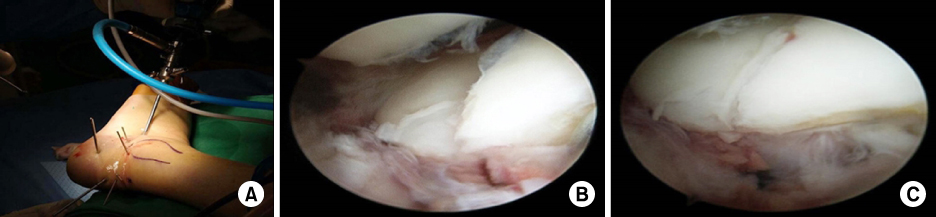
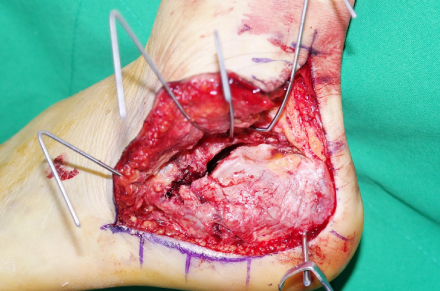
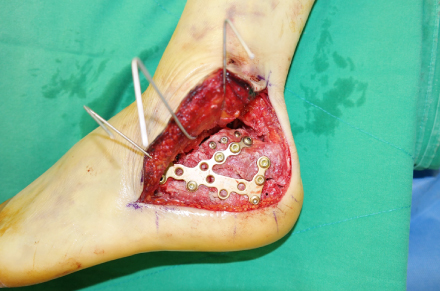
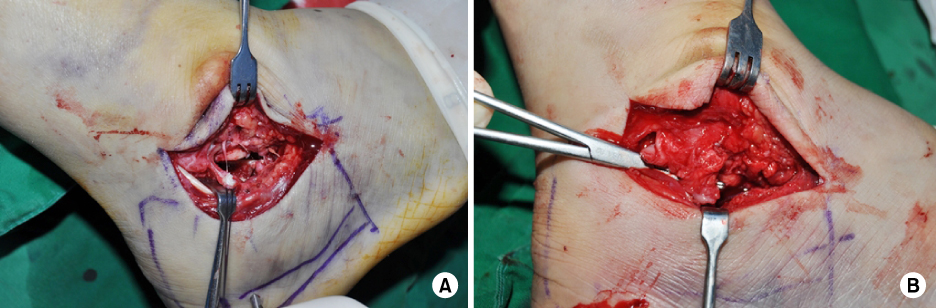
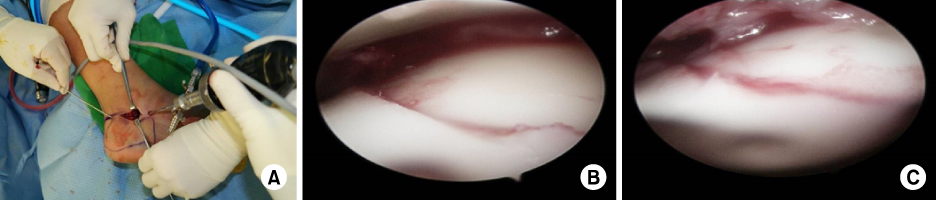
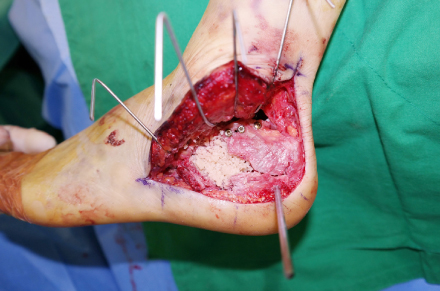
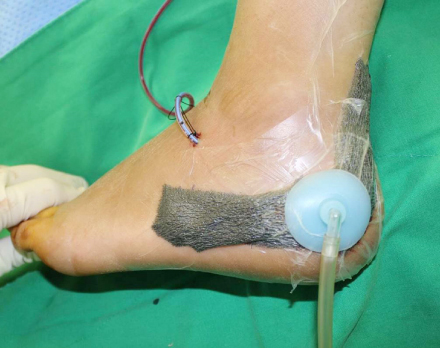
Fig. 1
(A) Arthroscopically guided reduction of the calcaneus fracture. Arthroscopic procedures are performed using the anterolateral and central portals. (B) Arthroscopic checking of the posterior facet. The intra-articular step is checked on the posterior facet. (C) The step is reduced with percutaneous leverage of the tuberosity fragment.
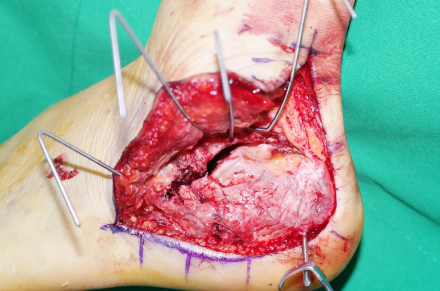
Fig. 2
Whole subtalar joint is exposed using the extensile lateral approach.
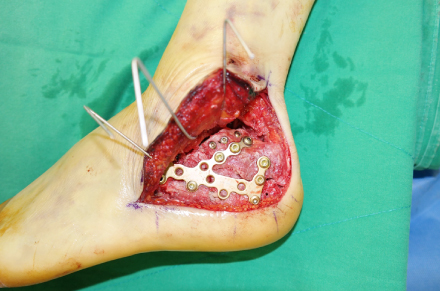
Fig. 3
Anatomical low-profile plate is placed after reduction of the posterior facet using the extensile lateral approach.
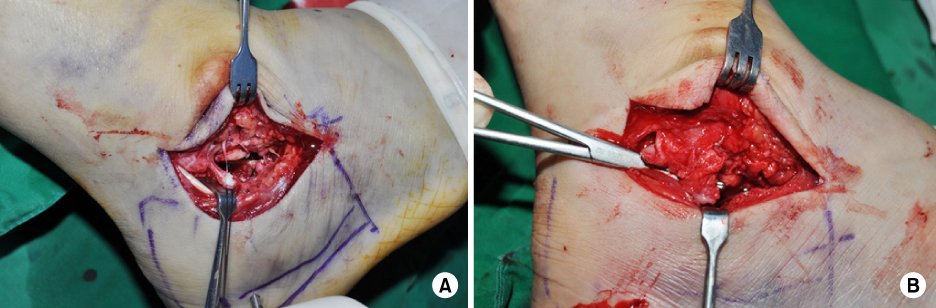
Fig. 4
Extended sinus tarsi approach. (A) After incision of the calcaneofibular ligament (CFL) at the fibular attachment, the subtalar joint is widely exposed. (B) A incised CFL is repaired using a 2.7-mm suture anchor.
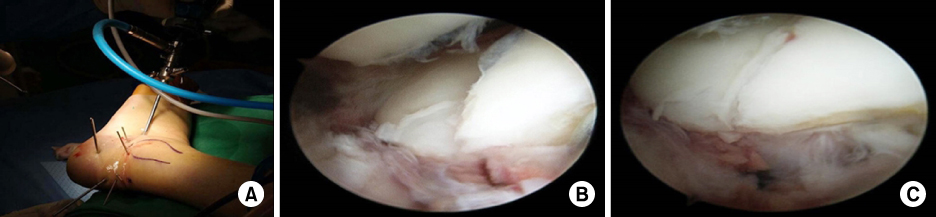
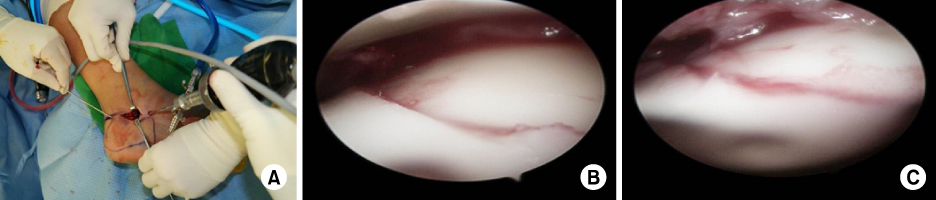
Fig. 5
(A) Open subtalar arthroscopy is performed after reduction and temporary K-wire fixation of the fragments using a sinus tarsi approach. (B) The intra-articular step is checked on the posterior facet. (C) The step is reduced with percutaneous leverage of the tuberosity fragment.
Fig. 6
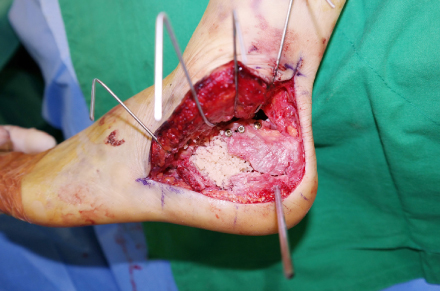
Allograft bone chips are inserted at the bone defect site after reduction of the posterior facet.
Fig. 7
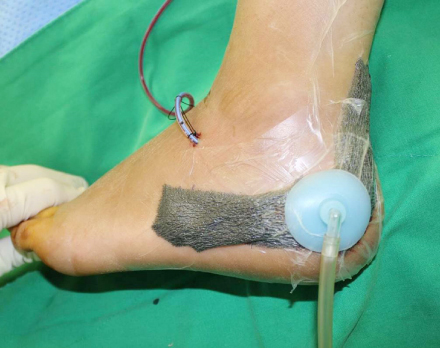
Negative pressure wound therapy is applied to assist wound healing after the extensile lateral approach.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Fig. 6
Fig. 7
Surgical Treatment for Displaced Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

