Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Case Reports
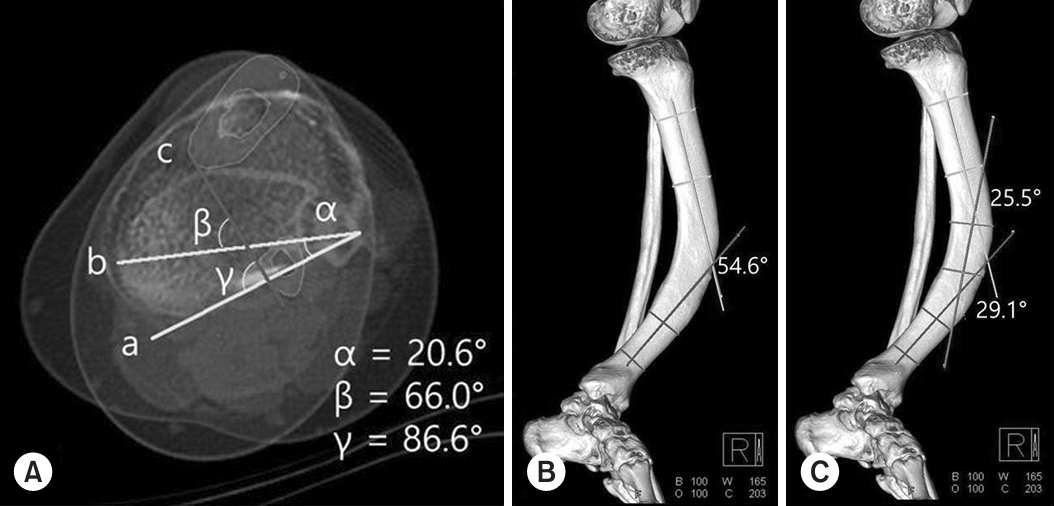
- Acute on Chronic Stress Fracture of a Varus Deformed Distal Tibia - A Case Report -
- Seong Kee Shin, Ki Chun Kim, Eli Schmidt, Seung Yeon Cho, Ki Chul Park
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2024;37(4):184-189. Published online October 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2024.37.4.184
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A severe post-traumatic distal tibia vara deformity is an uncommon condition in orthopedics. Typical symptoms include intractable recurrent pain, fragility related to stress fractures over the tensile area, and a limping gait caused by leg length discrepancy. Surgical management should be performed on acute fractures extending from a stress fracture gap. For successful surgical results, deformity correction is important for sustaining axial load bearing for standing and walking. Procedures to manage this condition have been proposed, but there is a high risk of complications, including metal failure, nonunion, and weakness caused by a long period of rehabilitation. In this case, the authors report a successful result using a modified clamshell osteotomy combined with a proximal and distal wedge bone resection in a single stage.
- 496 View
- 22 Download

- Clay-Shoveler's Fracture in an 18-Year-Old Cheerleader: A Case Report
- Il Yeong Hwang, Sun Jae Park, Jae Ryong Cha
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(2):57-60. Published online April 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.2.57
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Clay-Shoveler's fracture refers to a fracture that is solely developed on the spinous process of the cervical spine or the thoracic vertebrae. This fracture rarely occurs during sporting activities. In this case, an 18-year-old female developed the fracture on the spinous process of the 7th cervical spine and 1st thoracic vertebrae due to the repetitive practice of cheerleading. The patient's pain was improved by wearing a support device and taking an anti-inflammatory analgesic drug and muscle relaxant. Her case is being followed-up at the outpatient department.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clay-Shoveler’s Fracture on the Baseball Diamond: A Case of Noncontact Thoracic Spine Pain in an Adolescent Athlete
Jason S. Silver, Jordan Bork, Charles D. Kenyon
Current Sports Medicine Reports.2025; 24(6): 140. CrossRef - An unusual cause of neck pain in the physiotherapy clinic: Neglected clay-shoveler's fracture
GaneshSingh Dharmshaktu
Indian Journal of Physical Therapy and Research.2020; 2(2): 147. CrossRef
- Clay-Shoveler’s Fracture on the Baseball Diamond: A Case of Noncontact Thoracic Spine Pain in an Adolescent Athlete
- 842 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Multiple Stress Fractures Related to Low-dose Adefovir Dipivoxil Treatment in a Patient with Chronic Hepatitis B: A Case Report
- Chul Hyun Park, Hyo Sae Ahn, Dong Chul Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(4):327-331. Published online October 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.4.327
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Stress fractures typically result from repeated abnormal mechanical loading to the bones. In particular, multiple stress fractures may occur in patients with systemic disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis, osteoporosis, or osteoarthritis. Adefovir dipivoxil (ADV), a nucleotide analogue of adenosine monophosphate, very rarely causes severe hypophosphatemia when using a low dosage of 10 mg daily for treatment of chronic hepatitis B. To the best of our knowledge, in English literature, this is the first report of multiple stress fractures in a chronic hepatitis B patient who has been treated with a low dosage of ADV. We think it is important to consider that use of ADV in a patient with chronic hepatitis B could be a risk factor for stress fractures.
- 215 View
- 0 Download

- Tension Band Plating for a Stress Fracture of the Anterior Tibial Cortex in a Basketball Player: A Case Report
- Chul Hyun Park, Woo Chun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(4):323-326. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.4.323
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Stress fractures of the anterior tibial cortex are prone to complete fracture because these stress fractures occur on the tension side of the bone. Recently, surgical treatments are preferred in high-performance athletes requiring rapid return to sports. We report our experience of a case in which stress fracture of the anterior tibial cortex was treated using anterior tension band plating in a male athlete and successful bony union and rapid return to sports were achieved.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Stress fractures of the tibia
Jung Min Park, Ki Sun Sung
Arthroscopy and Orthopedic Sports Medicine.2015; 2(2): 95. CrossRef
- Stress fractures of the tibia
- 391 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Stress Fracture on the 4th Metatarsal Bone after Treatment of Stress Fracture on the 5th Metatarsal Bone: A Case Report
- Kyung Tai Lee, Ki Won Yong, Jae Young Kim, Hui Dong Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(3):261-264. Published online July 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.3.261
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A stress fracture that occurs in the player such as soccer player etc is localized most often in 5th metatarsal bone and has been reported frequently about it. But rarely stress fracture on other metatarsal bone has been reported. So we report a stress fracture on 4th metatarsal bone, that occurred after stress fracture on 5th metatarsal base which had been treated by bone graft and fixation with intramedullary compression screw, was successfully treated with non-weight bearing and custom molded shoes.
- 274 View
- 2 Download

Original Articles
- Stress Fracture of the Femoral shaft
- Sung Ho Hahn, Bo Kyu Yang, Seung Rim Yi, Shun Wook Chung, Hyoung Sik Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2001;14(2):200-207. Published online April 30, 2001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2001.14.2.200
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study was evaluated to find the aspect of the femoral shaft stress fracture. MATERIAL AND METHOD: From Jan. 1990 to May. 1999, this study included 8 cases diagnosed as stress fracture of the femoral shaft that were proved by clinical & radiologic findings in our hospital. Patients with undisplaced femoral shaft stress fracture were treated conservatively and patients with displaced ones were treated with open reduction and internal fixation.
RESULT
5 of 8 fractures were located in the distal shaft and 3 were in the middle shaft. 5 of 8 fractures were undisplaced and 3 were displaced. These 3 displaced fractures were located in the distal shaft.
CONCLUSION
According to our experience, femoral distal shaft stress fracture which is rare, has a high tendency to displace. Therefore, the early diagnosis and prevention of femoral distal shaft fracture is important to prevent progression to displaced fracture.
- 191 View
- 0 Download

- MRI Findings of Stress Fracture in Long Bone
- Sung Ho Hahn, Bo Kyu Yang, Seung Rim Yi, Shun Wook Chung, Yang Hee Park, Dong Oh Ko
- J Korean Soc Fract 2001;14(2):145-151. Published online April 30, 2001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2001.14.2.145
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The goal of our study was to evaluate diagnosis and management of stress fracture in long bones using MRI findings. MATERIAL & METHOD: Between May 1995 to May 1999, 40 patients( 45 cases ) were confirmed to have a stress fracture by clinical and radiological findings. All patients were evaluated with clinical, X-ray, bone scan, and MRI findings. The patient was 21 years in average( range from 18 to 23 years ). All were males and soldiers. The evaluation was made by comparison of MRI and plain radiograph, and duration of symptom was evaluated with MRI grading by Fredericson et al.
RESULT
The locations of stress fracture of long bones were tibia(n=25), fibula(n=14), and femur(n=6). MRI findings were bone marrow edema in 38(84.4%)cases, intramedullary low signal intensity band in 19(42.2%)cases which was continuous with cortex and cortical fracture line. Periosteal reaction was seen in 45(100%)cases and surrounding soft tissue edema in 20(44.4%)cases. Plain X-ray findings were peristeal reaction in 31( 68.9%)cases, medullary sclerosis in 10(22.2%)cases, and cortical fracture line in 8(17.8%) cases. Duration of symptom was longer in higher MRI grade.
CONCLUSION
MRI was more useful in early diagnosis and differential diagnosis of stress fracture, showing various findings than plain radiograph. MRI grading was helpful in planning tlhe therapy of stress fracture.
- 191 View
- 0 Download

Case Reports
- Stress fractures in calcaneus and juxtatectal region of the acetabulum : case report
- Soon Man Hong, Hong Tae Kim, Young Soo Byun, Sang Chul Shin, Kyoung Hoon Hyun, Soo Yeol Jeon
- J Korean Soc Fract 1999;12(4):749-753. Published online October 31, 1999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1999.12.4.749
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We have experienced a fatigue fracture occurred in the calcaneus of 49-year-old man and an insufficiency fracture occurred in the juxtatectal region of acetabulum in 70 -year-old woman. Both cases healed successively after rest. We suggest these fractures must be considered in differential diagnosis.
- 189 View
- 0 Download

- Femoral Stress Fractures in Civilians who are not military recruits and athlethes :Two cases report
- Myung Ku Kim, Suk Myun Ko, Kyung Ho Mun
- J Korean Soc Fract 1998;11(4):784-789. Published online October 31, 1998
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1998.11.4.784
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We reports two cases of femoral stress fractures, one at femoral neck, the other at distal femur. Femoral stress fracture is not uncommon in reported literature, but most of reported cases limited in military recruits and athlethes. There are few reports about femoral stress fractures of civilians. Early dignosis is difficult because complaints are vague and poorly localized, so displacement occurs and misdiagnosis is made. The purpose of this report is to call attention to the importance of early diagnosis of stress fracture of the femur so that displacement and misdiagnosis, which may lead to prolonged in capacitation or to the necessity for surgical intervention, may be prevented.
- 244 View
- 0 Download

Original Article
- A Case Report of Stress Fracture of the Suparcondyle of the Femur
- Kwon Ick Ha, Sung Ho Hahn, Minyoung Chung, Bo Kyu Yang, Seung Rim Yi
- J Korean Soc Fract 1990;3(2):197-201. Published online November 30, 1990
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1990.3.2.197
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The stress fracture is a disease which results from the application of an abnormal stress to the normal bone by the action of the constant and repeated muscular pull. prior to the early 1960s, most reports of stress fractures were from military installation, however, with the recent increase in participation in leisure and professional athetic activities such fractures have vecome more common among civilians. We treated two cases of stress fractures of the supracondylar region of the femur in runners. One patient was treated conservatively, but the other with displacement was treated operatively. To our knowledge, no previous cases of this nature have been reported.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Trochanteric Stress Fracture in a Female Window Cleaner
Bong-Jin Lee, Jyewon Song
Hip & Pelvis.2016; 28(1): 60. CrossRef
- Trochanteric Stress Fracture in a Female Window Cleaner
- 317 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA

 First
First Prev
Prev


