Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Articles
- Treatment of avulsion fractures around the knee
- Jeong-Hyun Koh, Hyung Keun Song, Won-Tae Cho, Seungyeob Sakong, Sumin Lim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):63-73. Published online March 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00073

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Avulsion fractures of the knee occur when tensile forces cause a bone fragment to separate at the site of soft tissue attachment. These injuries, which frequently affect adolescent athletes, can involve the cruciate and collateral ligaments, arcuate complex, iliotibial band, and patellar and quadriceps tendons. Radiographs aid in the initial diagnosis, while computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging facilitate a comprehensive evaluation of injury severity and concomitant damage. Specific avulsion fracture types include: anterior cruciate ligament avulsions (tibial site, Meyers and McKeever classification), posterior cruciate ligament avulsions (tibial attachment, Griffith's classification), Segond fractures (anterolateral complex injury), iliotibial band avulsions, medial collateral ligament avulsions (reverse Segond, Stieda fractures), arcuate complex avulsions ("arcuate sign"), medial patellofemoral avulsions (patellar dislocations), and patellar/quadriceps tendon avulsions. The treatment depends on the fracture location, displacement, and associated injuries. Non-displaced fractures can be managed conservatively, while displaced fractures or those with instability require surgical reduction and fixation. Prompt recognition and appropriate intervention prevent complications such as deformity, nonunion, malunion, and residual instability. This review provides an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management of knee avulsion fractures to guide clinical decision-making.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lateral marginal fractures of the patella and patellofemoral pain
Jae-Ang Sim, Chul-Ho Kim, Ji Wan Kim
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(3): 152. CrossRef
- Lateral marginal fractures of the patella and patellofemoral pain
- 16,883 View
- 184 Download
- 1 Crossref

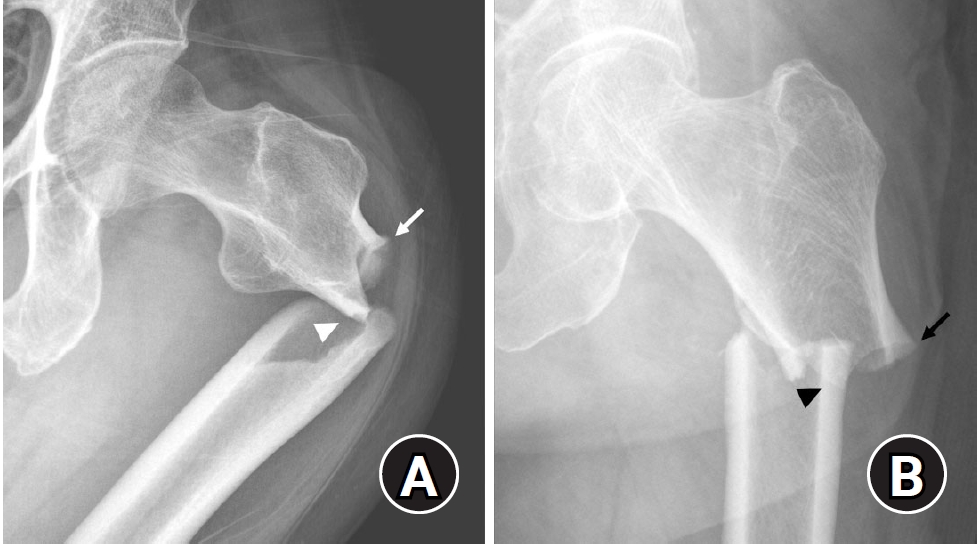
- Atypical femoral fractures: an update
- Won-Tae Cho, Jeong-Hyun Koh, Seungyeob Sakong, Jung-Taek Kim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):41-52. Published online March 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00031
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This narrative review provides an up-to-date overview of atypical femoral fractures (AFFs), emphasizing diagnostic criteria, epidemiology, pathophysiology, risk factors, and evaluation with screening strategies. AFFs are rare but significant complications associated with prolonged bisphosphonate (BP) therapy for osteoporosis. Although the pathogenesis of AFFs has not been fully elucidated, its primary mechanism is thought to involve impaired bone remodeling, leading to unhealed microfractures that progress to stress fractures under repetitive loading. AFFs can occur in various regions of the femur, influenced by femoral geometry and the lower limb axis. Other risk factors include prolonged steroid use, arthroplasty, genetic predispositions, and metabolic bone disorders. The diagnosis of AFFs is based on criteria established by the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. Key radiographic features include lateral cortical transverse fracture lines and localized cortical thickening, typically with minimal or no comminution on the medial cortex. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for screening tests and magnetic resonance imaging as an advanced imaging modality enable the early detection of incomplete fractures. This multi-modal approach facilitates the prompt identification of prodromal cortical changes, reducing the risk of complete fractures in high-risk populations, particularly patients undergoing prolonged BP therapy. Level of Evidence: V
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Atypical Femur Fractures Without Bisphosphonate Exposure (AFFwB): A Retrospective Report of 21 Cases
Lorenzo Lucchetta, Carmelinda Ruggiero, Samuele Berardi, Alice Franceschi, Michele Bisaccia, Giuseppe Rinonapoli
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 15(1): 25. CrossRef
- Atypical Femur Fractures Without Bisphosphonate Exposure (AFFwB): A Retrospective Report of 21 Cases
- 13,393 View
- 379 Download
- 1 Crossref


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


