Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Biomechanical finite element analysis of a femoral neck system fixation construct for femur neck fractures and clinical implications
- Hoon-Sang Sohn, Se-Lin Jeong, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):133-142. Published online July 22, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00108
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
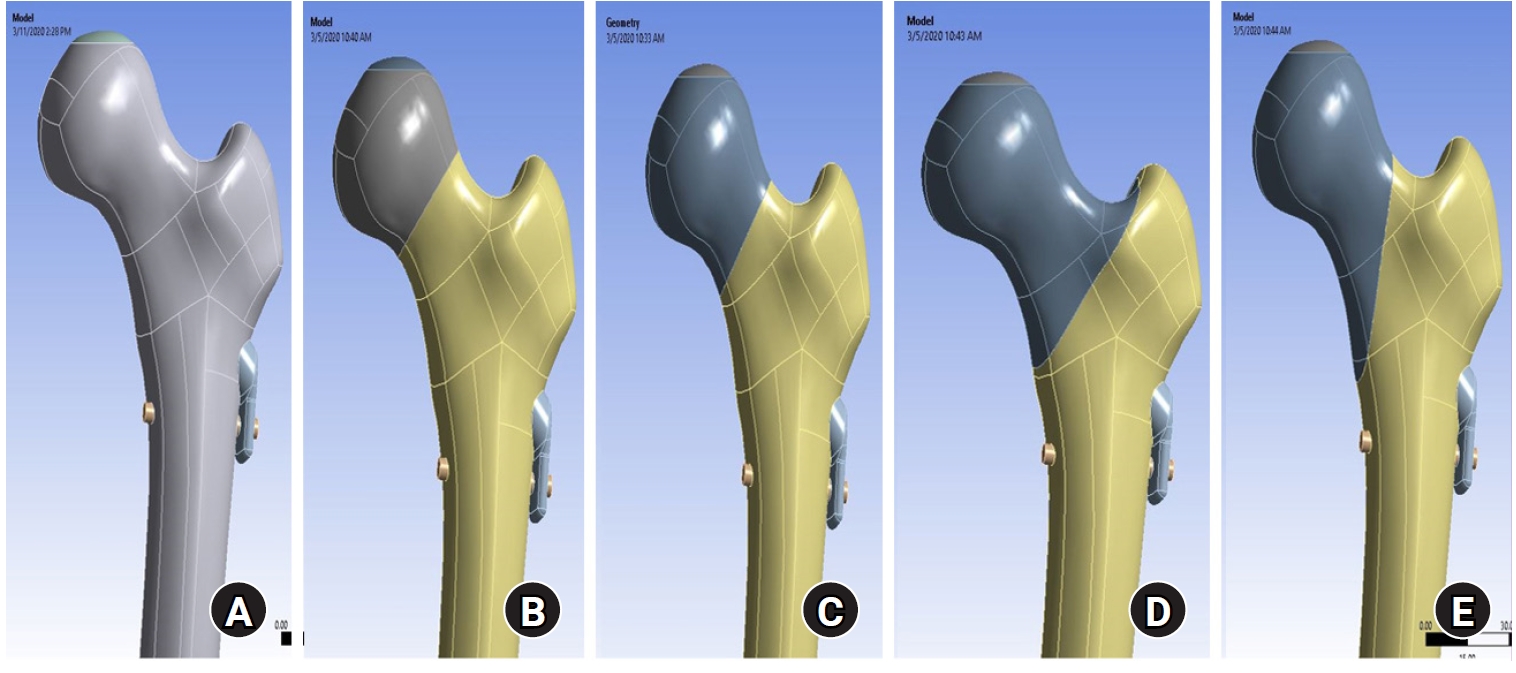
This study assessed the structural/mechanical stability of fixation constructs with a femoral neck system (FNS) via finite element analysis after simulating femoral neck fractures and explored the clinical implications.
Methods
We simulated subcapital, transcervical, basicervical, and vertical fracture models using a right femur (SAWBONES) and imported the implant model of FNS to Ansys (Ansys 19.0, Ansys Inc.) to place the implant in the optimal position. The distal end of the femur model was completely fixed and was abducted 7°. The force vector was set laterally at an angle of 3° and posteriorly at an angle of 15° in the vertical ground. The analysis was conducted using Ansys software with the von Mises stress (VMS) in megapascals (MPa).
Results
The maximum VMS of the fracture site was 67.01 MPa for a subcapital, 68.56 MPa for a transcervical, 344.54 MPa for a basicervical, and 130.59 MPa for a vertical model. The maximum VMS of FNS was 840.34 MPa for a subcapital, 637.37 MPa for a transcervical, 464.07 MPa for a basicervical, and 421.01 MPa for a vertical model. The stress distribution of basicervical and vertical fractures differed significantly, and the basicervical fracture had higher VMS at the bone, implant, and fracture sites.
Conclusions
FNS fixation should be performed with consideration the osseous anchorage in the femoral head, and this technique might be appropriate for vertical fractures. Regarding the VMS at the fracture site, FNS might be applied cautiously only to basicervical fractures with anatomical reduction without a gap or comminution. Level of evidence: IV. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Finite element analysis of screw thread geometry and titanium plate materials in internal fixation of the human femur
Abdessamed Bachiri, Mustapha Amine Arab, Nadia Kadouri
Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering.2026; : 1. CrossRef
- Finite element analysis of screw thread geometry and titanium plate materials in internal fixation of the human femur
- 1,948 View
- 82 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Report
- Recurrent Treatment Failure in Vancouver Classification Type C Periprosthetic Fractures around a Well Fixed Short Femoral Stem
- Byeong Yeol Choi, Hong-Man Cho, Jiyeon Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(1):16-20. Published online January 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.1.16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A short femoral stem (type 1 cementless stem) is being increasingly used to perform total hip arthroplasty; however, various types of intra- or postoperative periprosthetic fractures have been reported in recent times. A 66-year-old woman with a history of bilateral total hip arthroplasties using a type 1B femoral stem was admitted 2 months post-operation for a Vancouver type C periprosthetic fracture. She underwent open reduction and internal fixation; however, we observed recurrent non-union and plate breakage at the same site. In this case report, we discuss the factors associated with treatment failure in patients with a Vancouver type C periprosthetic fracture following type 1 femoral stem im-plantation.
- 381 View
- 0 Download

Original Articles
- Comparing Outcomes of Retrograde Intramedullary Nail and Locking Plate Fixation in Distal Femoral Fractures
- Byung-Ho Yoon, Bo Kwon Hwang, Hyoung-Keun Oh, Suk Kyu Choo, Jong Min Sohn, Yerl-Bo Sung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2021;34(4):131-136. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.4.131
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
We compared the radiological and clinical results of fixation for distal femoral fracture (DFF) using a locking compression plate (LCP) or a retrograde intramedullary nail (RIN).
Materials and Methods
From October 2003 to February 2020, 52 cases of DFF with a minimum 1-year follow-up (with a mean follow-up of 19.1 months) were included: 31 were treated with LCP and 21 with RIN. The operation time, blood loss, and hospitalization period were compared, and the incidence of postoperative nonunion, malunion, delayed union and metal failure and other post-operative complications were evaluated and compared.
Results
There was no significant difference in the operating time between the two groups, but the mean blood loss was significantly higher in the LCP group (LCP 683.5 ml vs RIN; 134.9 ml; p=0.015). In 49 out of 52 cases, bone union was achieved without additional surgery in an average of 6.8 months, and a complete union was achieved after additional surgery in three cases of nonunion (LCP 2 cases vs RIN 1 case; p=0.065). One case of malunion and superficial infection was confirmed in each group.
Conclusion
Internal fixation using LCP and RIN give good outcomes with a low complication rate and can therefore be considered useful surgical treatments for DFF.
- 483 View
- 6 Download

- Treatment of Proximal Femur Fracture with a Newly Designed Nail: Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced (TFNA)
- Jae Youn Yoon, Ji Wan Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(4):189-195. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.4.189
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study evaluated the clinical results and implant safety of a newly developed implant, Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced (TFNA; DePuy Synthes), in the treatment of proximal femur fractures.
Materials and Methods
This was a retrospective cohort study of 26 patients diagnosed with proximal femur fracture and treated surgically with TFNA. The patients’ demographic data, surgical data, radiologic findings, and functional outcomes, including complications, were evaluated.
Results
The mean age of the patients was 71.2 years (95% confidence interval [CI], 68.2-74.2); 65.4% were female. The mean Carlson comorbidity index score was 5.4, and the mean Koval grade before fracture was 2.1. Fracture classification included four cases of AO/OTA 31.A1, nine cases of A2, six cases of A3, and seven cases of 32A including six cases of atypical femoral fractures. The mean operating time was 53.3 minutes (95% CI, 43.6-63.1). There were no early postoperative complications, such as postoperative infection, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, or in-hospital death, except one case of pneumonia. The mean Koval score at the postoperative six-month follow-up was 2.9. EuroQol-5 Dimension (EQ-5D) increased from 0.05 to 0.54 after three months and 0.72 at six months postoperatively. Bone union was observed in all cases with a mean union time of 12.9 weeks. No implant failure occurred, and no cases required secondary revision surgery.
Conclusion
A new intramedullary nail system, TFNA, showed excellent outcomes and safety in the surgical treatment of proximal femur fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intermediate Length Cephalomedullary Nails in Proximal Femoral Fractures: Review of Indications and Outcomes
Daniel Scott Horwitz, Ahmed Nageeb Mahmoud, Michael Suk
Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.2025; 33(19): 1071. CrossRef - Outcomes of Intertrochanteric Fracture Fixation Using the Trochanteric Fixation Nail Advanced (TFNA): A Retrospective Analysis
Ramprasad Jasti, Prithvi Mohandas, Mahesh K Ragavan, Sunil D Magadam, Umesh Kannadasan
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures Treated with Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced and Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation-II: Correlation between Lateral Sliding of the Helical Blade and Lateral Trochanteric Pain
Sung Yoon Jung, Myoung Jin Lee, Lih Wang, Hyeon Jun Kim, Dong Hoon Sung, Jun Ha Park
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2024; 59(3): 208. CrossRef - Prospective randomized multicenter noninferiority clinical trial evaluating the use of TFN-advancedTM proximal femoral nailing system (TFNA) for the treatment of proximal femur fracture in a Chinese population
Lidan Zhang, Zhijun Pan, Xiaohui Zheng, Qiugen Wang, Peifu Tang, Fang Zhou, Fan Liu, Bin Yu, Frankie K. L. Leung, Alex Wu, Suzanne Hughson, Zhuo Chen, Michael Blauth, Anthony Rosner, Charisse Sparks, Manyi Wang
European Journal of Trauma and Emergency Surgery.2023; 49(3): 1561. CrossRef - Risk of shortening in operatively treated proximal femur fractures with cephalomedullary nails with dynamically versus statically locked helical blades
Nathan Cherian, Lasun Oladeji, Cole Ohnoutka, Dan Touhey, Madeline Sauer, Kyle A. Schweser, Mauricio Kfuri, James L. Cook, Gregory J. Della Rocca, Brett D. Crist
Injury.2023; 54(2): 669. CrossRef - GS Hip Nail versus Affixus Hip Fracture Nail for the Intramedullary Nailing of Intertrochanteric Fractures
Seungcheol Kwon, Minjae Lee, Heeyeon Lee, Jihyo Hwang
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(21): 6720. CrossRef - Comparison of the Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of TFNA (Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced) and PFNA-II (Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation-II) Treatment in Elderly Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures
Min Sung Kwon, Young Bok Kim, Gyu Min Kong
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2022; 35(4): 162. CrossRef - Analysis of Clinical and Functional Outcomes according to the Blood Sugar Control Status at the Time of Ankle Fractures Resulting from Rotational Injuries
Jun Young Lee, Dong Seop Lim, Seung Hyun Lee, Seo Jin Park
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2022; 35(4): 135. CrossRef - Conventional versus helical blade screw insertion following the removal of the femoral head screw: a biomechanical evaluation using trochanteric gamma 3 locking nail versus PFN antirotation
Hong Man Cho, Kwang Min Park, Tae Gon Jung, Ji Yeon Park, Young Lee
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and Radiologic Outcome of Intertrochanteric Fracture Treatment Using TFNA (Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced)
Hyeon Joon Lee, Hyun Bai Choi, Ba Rom Kim, Seung Hwan Jo, Sang Hong Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2021; 34(3): 105. CrossRef
- Intermediate Length Cephalomedullary Nails in Proximal Femoral Fractures: Review of Indications and Outcomes
- 2,470 View
- 24 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Does the Use of a Silicone Ring Tourniquet Help Reduce Bleeding in the Minimally Invasive Internal Fixation with Locking Plate for Distal Femoral Fractures?
- Ki-Bong Park, Hong-Ki Jin, Il-Yeong Hwang, Sung-Who Chang, Sung-Cheon Na
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(3):148-153. Published online July 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.3.148
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study evaluated the usefulness of a silicone ring tourniquet by analyzing the changes in the perioperative hemoglobin (Hb) levels or amount of perioperative bleeding compared to those of a pneumatic tourniquet or no usage during minimally invasive plate fixation for distal femoral fractures.
Materials and Methods
From January 2017 to December 2019, 30 patients who underwent minimally invasive plate fixation using a locking compression plate for distal femoral fractures were evaluated and classified as a silicone ring tourniquet (Group 1), a pneumatic tourniquet (Group 2), and no usage (Group 3). The variables for analysis were age, sex, preoperative Hb (preHb), postoperative 72-hour Hb (postHb), differences between preHb and postHb (preHb-postHb), amount of intraoperative and overall transfusion, estimated unit of transfusion corrected by preHb-postHb and total transfusion (Hb-lost), amount of intraoperative and postoperative and total bleeding. One-way ANOVA was used to identify the differences between the groups.
Results
The age, sex, operation time, preHb, preHb-postHb, amount of intraoperative and overall transfusion and Hb-lost were similar in the two groups. The amount of intraoperative bleeding was significantly lower in Group 1 than Group 3 (p=0.004), but there was no difference in the amount of postoperative and total bleeding between the two groups.
Conclusion
The use of a silicone ring tourniquet in the minimally invasive plate fixation for distal femoral fractures decreased the amount of intraoperative bleeding compared to no use of a tourniquet. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Silicone ring tourniquet could be a substitute for a conventional tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty with a longer surgical field: a prospective comparative study in simultaneous total knee arthroplasty
Tae sung Lee, Kwan Kyu Park, Byung Woo Cho, Woo-Suk Lee, Hyuck Min Kwon
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Silicone ring tourniquet could be a substitute for a conventional tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty with a longer surgical field: a prospective comparative study in simultaneous total knee arthroplasty
- 971 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Failure of Intramedullary Nailing for Subtrochanteric Atypical Femoral Fractures Caused by Endosteal Cortical Thickening
- Young Ho Roh, Kimoon Kang, Hee Joong Kim, Kwang Woo Nam
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(4):211-221. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.4.211
- Correction in: J Musculoskelet Trauma 2020;33(1):63
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
Recent literature has noted incidences of subtrochanteric atypical femoral fractures (AFFs) in patients who have taken long-term bisphosphonates (BPs). Most cases of subtrochanteric AFFs have been treated with intramedullary nailing and cases of delayed union have been reported. On the other hand, there is no data available on the complications associated with endosteal thickening or cortical thickening. This study evaluated the results of surgical treatment according to the endosteal thickening of the lateral cortex in subtrochanteric AFFs.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Investigation was performed at the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Jeju National University Hospital. The study consisted of patients with subtrochanteric AFFs, defined by the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research (ASBMR) major criteria, who underwent intramedullary nailing from March 2012 to October 2014. The cases were categorized into two groups based on the presence of endosteal thickening. The evaluation included the demographic data, radiographic data of initial reduction state, and duration of BPs.
RESULTS
The demographic data and duration of BPs were similar in the two groups. On the other hand, varus reduction (Group I: 12.5% vs. Group II: 78.9%; p=0.001), delayed union (Group I: 0% vs. Group II: 70.0%; p=0.003), nonunion (Group I: 0% vs. Group II: 47.4%; p=0.017), and union time (Group I: 5.5 months vs. Group II: 8.3 months; p<0.001) were significantly different in the two groups.
CONCLUSION
Endosteal thickening of the lateral cortex in subtrochanteric AFFs was identified as an independent factor that decides the reduction of the fracture and nonunion. The endosteal thickening should be removed to obtain anatomical alignment for successful surgical results. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Controlled bending of proximal femoral nails used in fractures of bowed femurs: biomechanical study with clinical application
Hong Moon Sohn, Suenghwan Jo
Medical Biological Science and Engineering.2022; 5(2): 63. CrossRef
- Controlled bending of proximal femoral nails used in fractures of bowed femurs: biomechanical study with clinical application
- 1,162 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Treatment of the Proximal Femoral Fracture Using the New Design Cephalomedullary Nail: Prospective Outcomes Study
- Young Ho Roh, Joseph Rho, Kwang Woo Nam
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(1):35-42. Published online January 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.35
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The aim of this study is to investigate the clinical performance and safety of Zimmer® natural nail cephalomedullary nail (ZNN CM nail) in the treatment of proximal femur fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The following research was conducted as a prospective, non-comparative, single center outcome study. Upon providing written informed consent, enrolled patients' data were collected and analyzed. Postoperative follow-up visits were scheduled at 6 weeks, 3 months, 6 months, and 1 year. Follow-up evaluation included radiographic assessment, physical examination, and quality of life and adverse events reports.
RESULTS
Thirty-nine patients were available for evaluation at one year postoperative. The patients reported the mean EuroQol-5 Dimension score increased after surgery: from 0.4 points at discharge (n=49) to 0.6 points at 1-year post-surgery (n=39). The mean Harris hip score also increased after surgery: from 56.3 points at discharge (n=49) to 72.1 points at 1 year (n=12). Bone union was seen in 64% (n=16) in 6 months and 95% (n=37) in 1 year.
CONCLUSION
The results of this 1-year follow-up study affirmed the effectiveness and safety of the ZNN CM nail in the treatment of proximal femur fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical and Radiologic Outcome of Intertrochanteric Fracture Treatment Using TFNA (Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced)
Hyeon Joon Lee, Hyun Bai Choi, Ba Rom Kim, Seung Hwan Jo, Sang Hong Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2021; 34(3): 105. CrossRef - Treatment of Proximal Femur Fracture with a Newly Designed Nail: Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced (TFNA)
Jae Youn Yoon, Ji Wan Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2020; 33(4): 189. CrossRef
- Clinical and Radiologic Outcome of Intertrochanteric Fracture Treatment Using TFNA (Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced)
- 916 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Radiologic and Serologic Factors Associated with Bone Union at Femoral Atypical Fracture
- Suc Hyun Kweon, Byung Min Yoo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(1):27-34. Published online January 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.27
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to investigate the radiologic and serologic factors related to postoperative union using intramedullary (IM) internal fixation in atypical femoral fractures (AFF), which are closely related to bisphosphonates (BPs) for osteoporosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From February 2008 to December 2016, 65 patients (71 cases) who had undergone IM nail fixation after diagnosis of AFF were enrolled in this study. Patients were divided into group A, who experienced union within 6 months and group B, who did not experience union within 6 months. They were evaluated for duration of BPs use, radiologic factors and serological factors.
RESULTS
The mean duration of BPs use was 6.17 years in group A and 8.24 years in group B (p=0.039). In the subtrochanteric area, there were 14 cases (27.5%) in group A and 14 cases (70.0%) in group B. In the femoral shaft, there were 37 cases (72.5%) in group A and 6 cases (30.0%) in group B (p=0.001). On the preoperative, the flexion in the coronal plane was 5.9° (2.1°–9.2°) in group A and 8.0° (3.1°–12.1°) in group B (p=0.041). On the postoperative, conversion to valgus was 15 cases (29.4%), 8 cases (40.0%); conversion to neutral was 34 cases (66.7%) and 8 cases (40.0%); conversion to varus was 2 cases (3.9%) and 4 cases (20.0%), each (p=0.037). The fracture site gap was 1.5 mm (0–2.9 mm) on the front side and 1.2 mm (0–2.2 mm) on lateral side and 2.2 mm (0.9–4.7 mm) and 1.9 mm (0.5–3.5 mm), each (p=0.042, p=0.049). Among serological factors, there was no significant difference between the two groups.
CONCLUSION
Factors adversely affecting the union should be recognized before surgery, such as longterm BPs use or a severe degree of bending of the femur in the coronal plane. During surgery, proper reduction and spacing of the fracture site on the coronal plane should allow adequate reduction of the anterior and posterior surfaces. Obtaining anatomic reduction would be most beneficial for union, but if that is not possible, obtaining congenital valgus rather than varus on the coronal plane may be helpful for union. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Subtrochanteric Fracture Reduction during Intramedullary Nailing: Technical Note
Gyu Min Kong
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2019; 32(2): 107. CrossRef
- Subtrochanteric Fracture Reduction during Intramedullary Nailing: Technical Note
- 865 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Risk Factors for Knee Stiffness in Distal Femoral Fractures
- Dong Wook Son, Hyoung Soo Kim, Woo Young Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(4):123-131. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.4.123
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The aims of this study were to evaluate risk factors for knee stiffness after the fixation of distal femoral fractures, and to analyze the clinical and radiologic outcomes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This is a retrospective case control study of 104 consecutive patients who have a distal femoral fracture and were treated with a submuscular locking plate. The case group comprised of patients with 12-month postoperative range of motion (ROM) ≤90° or a history of manipulation under anesthesia. The case group was compared with the control group of patients with a 12-month postoperative ROM >90°. The possible risk factors were evaluated by univariate and logistic regression analysis. The postoperative ROM and Knee Society clinical rating system was evaluated for the clinical assessment and the distal femoral angle on a whole-extremity scanogram was measured for radiologic assessments.
RESULTS
Fifty-four patients were included in the study (14 in the case group, 40 in the control group). Univariate analysis showed that comminuted fracture, intra-articular fracture, open fracture, temporary external fixation, severe osteoarthritis, and prolonged immobilization placed patients at an increased risk for knee stiffness. On the other hand, multivariate logistic regression showed that an extensor mechanism injury was the only significant predictor (p=0.001; odds ratio, 42.0; 95% confidence interval, 5.0–350.7). The ROM and Knee Society score were significantly lower in the case group; however, the coronal alignment was similar in the case and control group.
CONCLUSION
Various factors that delay postoperative knee motion place patients at increased risk of knee stiffness. Understanding these risk factors may help surgeons prevent postoperative knee stiffness after distal femoral fractures. In particular, extensor mechanism injury, such as patella fracture or open quadriceps injury, was found to be an independent predictable factor associated with knee stiffness. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comprehensive Approach to Stiffness in Total Knee Arthroplasty
Brian P. Chalmers, Linda I. Suleiman, Peter K. Sculco, Matthew P. Abdel
The Journal of Arthroplasty.2025; 40(9): S59. CrossRef - Staged Management for Distal Femur Fractures: Impacts on Reoperation, Stiffness, and Overall Outcomes
Matthew T. Yeager, Robert W. Rutz, Alex Roszman, Gerald McGwin, James E. Darnley, Joseph P. Johnson, Clay A. Spitler
Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma.2024; 38(11): 577. CrossRef - Outcome of the Masquelet Technique for Complex Bilateral Distal Femoral Bone Defects
Ziad A Aljaafri, Abdullah Alzahrani, Ali Alshehri, Ahmed AlHussain, Faisal Alzahrani, Khalid Alsheikh
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of non-operative treatment of patients with knee arthrofibrosis using high-intensity home mechanical therapy: a retrospective review of 11,000+ patients
Shaun K. Stinton, Samantha J. Beckley, Thomas P. Branch
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Distal Femoral Replacement and Extensor Mechanism Repair Reinforced With Synthetic Mesh for Distal Femur Fracture With Patellar Ligament Avulsion
Charles Powell, Kristopher Sanders, Neal Huang, Luis Felipe Colón, Colton Norton
Arthroplasty Today.2022; 16: 31. CrossRef - The fragility of statistical significance in distal femur fractures: systematic review of randomized controlled trials
Michael Megafu, Hassan Mian, Emmanuel Megafu, Sulabh Singhal, Alexander Lee, Richawna Cassie, Paul Tornetta, Robert Parisien
European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology.2022; 33(6): 2411. CrossRef - Association Between Femoral “Spike” Size After Intramedullary Nailing and Subsequent Knee Motion Surgery
Michael G. Schloss, Nathan N. O'Hara, Syed M. R. Zaidi, Zachary D. Hannan, Dimitrius Marinos, Jared Atchison, Alexandra Mulliken, Jason W. Nascone, Robert V. O'Toole
Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma.2021; 35(2): 100. CrossRef - Distal Femur Replacement Versus Surgical Fixation for the Treatment of Geriatric Distal Femur Fractures: A Systematic Review
Brett P. Salazar, Aaron R. Babian, Malcolm R. DeBaun, Michael F. Githens, Gustavo A. Chavez, L. Henry Goodnough, Michael J. Gardner, Julius A. Bishop
Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma.2021; 35(1): 2. CrossRef
- A Comprehensive Approach to Stiffness in Total Knee Arthroplasty
- 693 View
- 10 Download
- 8 Crossref

- The Treatment of Subtrochanteric Fracture with Cephallomedually Nail: Minimal Incision and Lowman Clamp Assisted Reduction
- Jang Seok Choi, Do Hyun Moon, Young Tae Noh
- J Korean Fract Soc 2011;24(4):301-306. Published online October 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.4.301
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the radiographic results of patients with subtrochanteric femoral fracture using minimal incision and cephalomedullary nail technique.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study was performed on 54 patients, 54 cases of hip, recruited among patients who underwent minimal incision and Cephalomedullary nail from September 2005 to August 2008 and were available for 1-year or longer follow up. The gender ratio was 37 males and 17 females, and the mean age at the time of surgery was 57.4 years (range; 16~81 years). According to injury mechanism, traffic accident was 29 cases, fall down form high height was 18 cases, slip down was 7 cases. In classification by Seinsheimer, type II was 23 cases (m/c), type III was 18 cases, type IV was 13 cases. Average follow up period was 14 months (12~18). Radiographic evaluation was performed for time taking union, mal-union and complication.
RESULTS
53 of the 54 cases united. 39 of 54 reductions were anatomic. 19 fractures had a monir varus deformity of proximal fragment (between 2degrees and 5degrees). There was no varus deformity of more than 5degrees. 1 case that had been treated with PFN had nail breakage without trauma. There were no other complications.
CONCLUSION
Surgical treatment of subtrochanteric fractures with minimal incision and Cephalomedullary nail technique can reslut in excellent reduction without complications including inflammation & malunion. Careful attention to detail for using Lowman clamp is demanding to decrease soft tissue injury. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Treatment of Subtrochanteric Fractures with Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation
Chi Hyoung Pak, Sang Hong Lee, Sang Ho Ha, Gwang Chul Lee, Kyoung Chul Song
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2013; 26(4): 284. CrossRef - Fixation of the Femoral Subtrochanteric Fracture with Minimally Invasive Reduction Techniques
Chul-Hyun Park, Chul-Wung Ha, Sang-Jin Park, Min-Su Ko, Oog-Jin Shon
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2013; 26(2): 112. CrossRef
- The Treatment of Subtrochanteric Fractures with Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation
- 746 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Surgical Treatment of AO Type C Distal Femoral Fractures Using Locking Compression Plate (LCP-DF, Synthes(R))
- Kap Jung Kim, Sang Ki Lee, Won Sik Choy, Won Cho Kwon, Do Hyun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2010;23(1):20-25. Published online January 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.1.20
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyze the surgical results of AO type C distal femoral fractures using locking compression plate.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From February 2006 to June 2008, 14 patients 15 cases were included. Injury mechanisms, combined injuries, radiologic and clinical results and postoperative complications were analyzed.
RESULTS
The mean age was 59.6 (30~77) years. The mean follow up period was 25 (12~40) months. AO types were 3 of C1, 5 of C2 and 7 of C3. Injury mechanisms were 9 of traffic accident, 5 of slip down and 1 of fall from a height. Four cases were combined with other extremity injuries or fractures. The mean radiologic union was obtained at postoperative 15 (13~20) weeks. The mean Neer's functional score was 74.2 (58~97); 3 of excellent, 5 of satisfactory and 7 of unsatisfactory. Postoperative complications were 2 of infection and 1 of nonunion. There were no mechanical failures or fixation loss with locking compression plate at the final follow up.
CONCLUSION
Internal fixation using locking compression plate for AO type C distal femoral fractures provided excellent fixations. At the final follow up, the clinical results were variable. The affecting factors on the final results seemed to be joint congruencies after anatomical reduction and active rehabilitation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Functional outcome of distal femoral fractures treated with distal femoral locking compression plate: a cross-sectional study
Sandeep Kumar Kumar Deep, Varun Phogat, Sankar Debroy
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics.2025; 11(5): 1089. CrossRef - A STUDY OF SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF DISTAL FEMORAL FRACTURES BY DISTAL FEMORAL LOCKING COMPRESSION PLATE OSTEOSYNTHESIS
Dema Rajaiah, Yerukala Ramana, Kuppa Srinivas, Venkateswar Reddy S
Journal of Evidence Based Medicine and Healthcare.2016; 3(66): 3584. CrossRef
- Functional outcome of distal femoral fractures treated with distal femoral locking compression plate: a cross-sectional study
- 840 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Comminuted Subtrochanteric Fracture of the Femur
- Chang Wug Oh, Jong Keon Oh, Sung Jung Kim, Shin Yoon Kim, Seung Hoon Baek, In Ho Jeon, Poong Taek Kim, Sang Won Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(4):407-411. Published online October 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.4.407
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the outcomes of patients with comminuted subtrochanteric femoral fractures using minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) technique.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twelve patients with a mean age of 38.2 years, who sustained comminuted subtrochanteric femoral fractures, were treated using MIPO technique. All patients suffered these fractures either from traffic accidents (6) or falls from height (6). Average follow-up was 4.3 years (range, 29~78 months). Patients were assessed radiographically and clinically with regards to time to union, malunion, and complications. According to the Seinsheimer's classification, there were 1 type III, 7 type IV, and 4 type V. Type C fractures were ten according to AO-OTA classification.
RESULTS
Union was achieved in 7 of 12 cases, in an average of 23.4 weeks (range, 12~42 weeks). Three definite non-unions with implant failures, needed the procedure of implant change and bone graft. In other two patients, early bone graft was performed for anticipated nonunion of comminuted area. The most common complication was metal failures (2 plate failures and 3 screw breakages). Limb length shortening of 1.5 cm occurred in one patient, and external rotation malunion of 15 degrees was noted in one patient. No patients developed infection.
CONCLUSION
Preserving biology of the fracture fragments, the use of MIPO technique using DCS has proven to be less successful in comminuted subtrochanteric fractures, comparing to fractures in other areas. To avoid mechanical failure, the careful and protective weight bearing is needed until the callus-bridging is seen in the commniuted area. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Femoral Mid-Diaphyseal Fractures
Hyoung-Keun Oh, Suk-Kyoo Choo, Jong-In Kim, Sung-Jong Woo
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2013; 26(2): 140. CrossRef - Fixation of the Femoral Subtrochanteric Fracture with Minimally Invasive Reduction Techniques
Chul-Hyun Park, Chul-Wung Ha, Sang-Jin Park, Min-Su Ko, Oog-Jin Shon
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2013; 26(2): 112. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis of Subtrochanteric Femoral Fractures
Chang-Wug Oh
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(2): 123. CrossRef - What is an Ideal Treatment?
Chang-Wug Oh
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2008; 21(4): 347. CrossRef
- Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Femoral Mid-Diaphyseal Fractures
- 648 View
- 0 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Retrograde Intramedullary Nail for Femoral Shaft Fracture with Limited Indications
- Sung Jung Kim, Chang Wug Oh, Joo Chul Ihn, Hee Soo Kim, In Ho Jeon, Hee Soo Kyung, Il Hyung Park, Kyung Hoon Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(1):45-51. Published online January 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.1.45
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This is a retrospective study to analyze the results after retrograde intramedullary(IM) nailing in femoral shaft fractures with limited indications.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty-four femoral shaft fractures(21 patients) were operated with unreamed IM nail(Unreamed femoral nail, SynthesR) in a retrograde method and were followed for more than 1 years. There were 16 men and 5 women, and the mean age at index operation was 41 years (range 18-76 years). In Winquist-Hansen classifications, there were 10 of type I, five of type II, three of type III, and six of type IV. All the patients had associated fractures or injuries, and there were eight ipsilateral tibia fractures, five ipsilateral proximal femoral fractures(including neck and trochanter), four ipsilateral pelvic or acetabular fracture, three bilateral femoral fractures, and one ipsilateral knee injury according to the used indications. In radiological study, we evaluated the time for union, non-unions and malunion, and clinical evaluation with Neer 's criteria was done.
RESULTS
Most fractures(87.5%) were primarily united cases, and the mean time for union was 15.8 weeks(range 12-20 weeks). Three cases of delayed union or nonunion were developed, but a shortening over 1cm or malunion over 10 degrees angular deformity were not found. Evaluating the knee functions, the Neer score was 86.9 in average and all the cases were above satisfactory grade. The average range of knee motion was 120.2 degrees, and the mild knee pain was developed in three cases.
CONCLUSION
The retrograde IM nailing can be a useful option for femoral shaft fractures with limited indications, including ipsilateral fractures of other areas or multiple fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Operative Methods between Retrograde and Antegrade Nailing for Ipsilateral Femoral Shaft and Neck Fracture
Chang-Wug Oh, Jong-Keon Oh, Woo-Kie Min, Shin-Yoon Kim, Seung-Hoon Baek, Byung-Chul Park, Hyung-Soo Ahn, Tae-Gong Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2007; 20(2): 135. CrossRef - Retrograde Intramedullary Nailing for the Treatment of Ipsilateral Femoral Shaft and Neck Fracture
Chang-Wug Oh, Jong-Keon Oh, Shin-Yoon Kim, Ki-Bong Cha, In-Ho Jeon, Byung-Chul Park, Woo-Kie Min, Tae-Gong Kim
The Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2007; 42(3): 380. CrossRef
- Comparison of Operative Methods between Retrograde and Antegrade Nailing for Ipsilateral Femoral Shaft and Neck Fracture
- 522 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Complications in the Use of Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing for the Femoral Fractures
- Sung Kwan Hwang, Jae Beum Han
- J Korean Soc Fract 1995;8(1):1-12. Published online January 31, 1995
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1995.8.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A retrospective review was undertaken in 31 patient with femoral fracture which had complication after undergoing the closed reduction and internal fixation using interlocking intramedullay nail. The technical complexity associated with the locking nail introduces a new set of complications. This article discusses these problems and suggests means to avoid certain difficulties. The results were as follws; 1 Intraoperative complications were new fracture near the original fracture site(3 cases), Iatrogenic femur neck fracture(1 case), pudendal nerve neuropraxia(1 case). 2. Postoperative complications were delayed union(13 cases), limb shortening(4 cases), nonunion(3 cases), infection(3 cases), distal screw breakage(3 cases), nail breakage(1 case), proximal screw breakage(1 case), and angulation(1 case). 3. At final follow up, the major complications were 11 cases(13.4%) but, bone union was achived in all cases except 3 case, union rate was 96.4%. 4. Highly developed operative technique and postoperative management were necessary to diminish complications.
- 750 View
- 7 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


