Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Risk factors for ankle fractures in older adults based on clinical components of the Fracture Risk Assessment (FRAX) tool and comorbidities in Korea: a retrospective case-control study
- Myeong Jun Song, Se Woong Jang, Jun Young Lee, Seojin Park
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):193-202. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Ankle fractures are common in older adults; however, their relationship with osteoporotic fractures remains unclear. This study aimed to evaluate potential risk factors for ankle fractures in older adults by analyzing individual clinical components of the Fracture Risk Assessment (FRAX) tool and comorbidities.
Methods
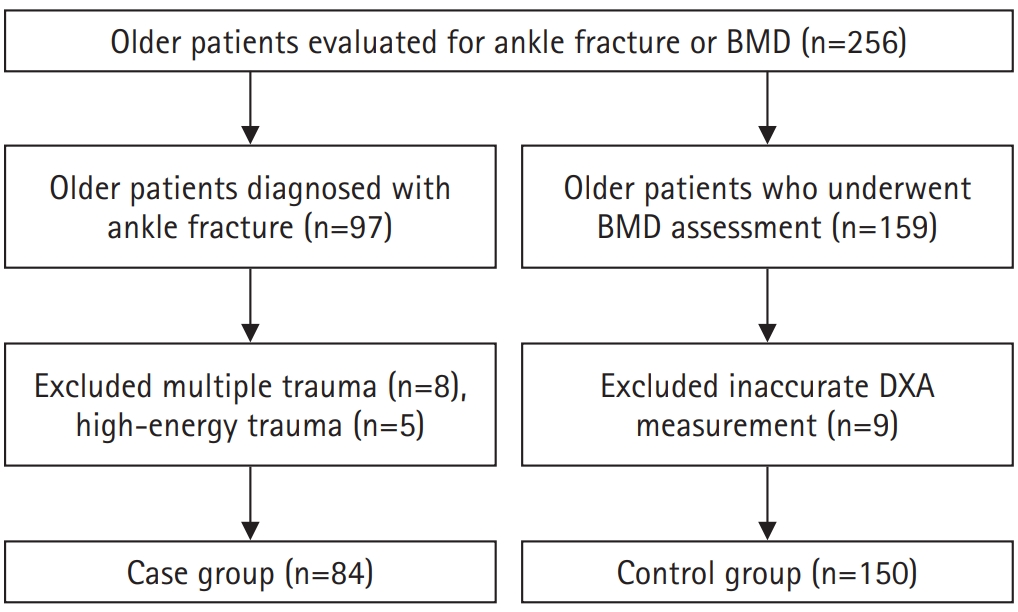
We conducted a retrospective case-control study including 84 patients aged ≥65 years with ankle fractures and 150 controls who underwent bone mineral density (BMD) testing without prior ankle fractures. The variables analyzed included age, sex, body mass index, smoking, alcohol consumption, prior fracture history, and comorbidities such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and dementia. BMD was measured at the spine, total hip, and femoral neck.
Results
Univariate analysis showed that alcohol consumption, diabetes mellitus, and total hip T-score categories were significantly associated with ankle fractures. In binary logistic regression, alcohol consumption remained significantly associated with higher ankle fracture risk (odds ratio [OR], 5.302; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.778–15.811; P=0.003), and both osteopenia and osteoporosis at the total hip were also associated with increased risk (OR, 3.260, P=0.049; OR, 3.561, P=0.031, respectively). Diabetes mellitus did not reach statistical significance in the adjusted model (P=0.074). Model fit was adequate (Hosmer-Lemeshow P=0.377), and post hoc power analysis confirmed sufficient sample size.
Conclusions
These findings suggest that lower total hip BMD and alcohol-related factors may be associated with ankle fracture risk in older adults. The FRAX score itself was not calculated; instead, this study focused on analyzing selected clinical components. Limitations include the retrospective design, lack of fall and medication data, and cross-sectional BMD assessment. Level of evidence: III.
- 1,121 View
- 21 Download

- Demographic and Radiographic Parameters as Predictors of Reduction Loss after Conservative Treatment of Distal Radius Fractures in Adults
- Kyu Jin Kim, Dae Won Shin, Seong Kee Shin
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(2):45-51. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.2.45
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the demographic and radiological risk factors for later reduction loss of distal radius fractures treated conservatively. Materials and Methods This study enrolled patients treated for distal radius fractures between January 2017 and December 2019. Seventy-eight patients were included in the analysis and divided into two groups. The patients who showed minimal reduction loss within an acceptable radiologic angle after initial manual reduction were classified as Group A. The patients who showed reduction loss out of an acceptable radiologic angle and finally malunited or converted to surgical treatments were classified as Group B. The patient’s age and bone marrow density were used as demographic data. The initial X-ray images were evaluated to determine the fracture type. Various radiological parameters were measured. Results The 78-patient study cohort consisted of nine men and 69 women with a mean age of 67 years. Forty-eight cases were sorted into Group A, and 30 cases into Group B. On logistic regression analysis, the age of 80 or older was a risk factor for later fracture displacement among the demographic factors (p=0.037, odds ratio=4.937). Among the radiographic factors, the presence of distal ulnar fracture and dorsal cortical comminution were disclosed as risk factors of later displacement (p=0.049, 0.003, odds ratio=3.429, 7.196). Conclusion When conservative management for distal radius fracture is decided in patients more than 80 years of age or accompanied by a distal ulnar fracture or with dorsal cortical comminution, the possibility of later displacement of the distal radius should be considered.
- 494 View
- 2 Download

- Perioperative Blood Loss in Intramedullary Hip Screw for Intertrochanteric Fracture: Analysis of Risk Factors
- Jai Hyung Park, Hwa Jae Jung, Hun Kyu Shin, Eugene Kim, Se Jin Park, Taeg Su Ko, Jong Hyon Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2015;28(1):53-58. Published online January 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.1.53
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
We compared visible blood loss and calculated blood loss after intramedullary fixation in intertrochanteric fracture, and evaluated correlation between blood loss and its risk factors.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 256 patients who underwent closed reduction and intramedullary fixation in femoral intertrochanteric fracture between 2004 and 2013 were enrolled in this study. The total blood loss was calculated using the formula reported by Mercuiali and Brecher. We analyzed several factors, including fracture pattern (according to Evans classification), gender, age, body mass index (BMI), anesthesia method, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease, preoperative anemia, American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) score and use of antithrombotic agents.
RESULTS
Total calculated blood loss (2,100+/-1,632 ml) differed significantly from visible blood loss (564+/-319 ml). In addition, the blood loss of unstable fracture patient was 2,496+/-1,395 ml and multivariate analysis showed a significant relationship between blood loss and fracture pattern (p<0.01). However, other factors showed no statistically significant difference.
CONCLUSION
Total calculated blood loss was much greater than visible blood loss. Patients with unstable intertrochanteric fracture should be treated with care in order to reduce blood loss.
- 449 View
- 0 Download

- Neurologic Injury within Pelvic Ring Injuries
- Ji Wan Kim, Dong Hoon Baek, Jae Hyun Kim, Young Chang Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(1):17-22. Published online January 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.1.17
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the incidence of neurologic injury in pelvic ring injuries and to assess the risk factors for neurologic injury related to pelvic fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sixty-two patients with the pelvic ring injury were enrolled in the study from March 2010 to May 2013. When the neurologic injury was suspected clinically, the electro-diagnostic tests were performed. Combined injuries, fracture types, and longitudinal displacements were examined for correlations with the neurologic injury.
RESULTS
There were 7 cases of AO/OTA type A, 37 cases of type B, and 18 cases of type C. Among them, 25 patients (40%) had combined spine fractures, and the average of longitudinal displacement was 7 mm (1-50 mm). Of the 62 patients, 13 (21%) had neurologic injury related with pelvic fractures; 5 with lumbosacral plexus injury, 5 with L5 or S1 nerve injury, 2 with obturator nerve injury, and 1 case of lateral femoral cutaneous nerve injury. There were no relationships between the neurologic injuries and fracture types (p=0.192), but the longitudinal displacements of posterior ring and combined spine fractures were related to the neurologic injury within pelvic ring injury (p=0.006, p=0.048).
CONCLUSION
The incidence of neurologic injury in pelvis fracture was 21%. In this study, the longitudinal displacements of posterior ring and combined spine fractures were risk factors for neurological injury in pelvic ring injury. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surgical Outcome of Posterior Pelvic Fixation Using S1, S2 Screws in Vertically Unstable Pelvic Ring Injury
Kwang Hee Yeo, Nam Hoon Moon, Jae Min Ahn, Jae Yoon Jeong, Jae Hoon Jang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2018; 31(1): 9. CrossRef
- Surgical Outcome of Posterior Pelvic Fixation Using S1, S2 Screws in Vertically Unstable Pelvic Ring Injury
- 599 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Delirium after Intertrochanteric Fractures of Femur in Elderly Patients
- Kyu Bok Kang, Dong Hun Suh, Seong Rok Oh
- J Korean Fract Soc 2011;24(2):131-137. Published online April 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.2.131
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the incidence, risk factors and prognosis of delirium in elderly patients with intertrochanteric fractures of femur.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
162 patients who underwent operation for intertrochanteric fracture of femur from July 2005 to January 2007 were reviewed retrospectively. Delirium was diagnosed by using Confusion Assessment Method (CAM). Medical records were reviewed for the information of the patients, Gross motor function classification of Palisano et al. was used for the evaluation of ambulatory status. Univariate analysis and multivariate analysis were done to find out the risk factors.
RESULTS
2 cases out of 162 (1.2%) met the criteria of delirium at admission, and 39 cases (24.1%) after surgery. Univariate analysis and multivariate analysis identified age, hematocrit, dementia, the duration of opiate use, and pulmonary complication as risk factors. Hospital stay was longer and postoperative ambulatory status was worse in the patients with delirium.
CONCLUSION
Delirium is a frequent complication of intertrochanteric fractures of old age and associated with worse results. Cognitive function as well as physical status should be evaluated before and after surgery. Delirium needs more active prevention and treatment for better results. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Incidence and Associated Factors of Delirium after Orthopedic Surgery
Si-Wook Lee, Chul-Hyun Cho, Ki-Cheor Bae, Kyung-Jae Lee, Eun-Seok Son, Sang-Hyun Um
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2019; 54(2): 157. CrossRef - Laozi. De la figure du maître mythique à la divinité taoïque
Kyong-Kon Kim
Archimède. Archéologie et histoire ancienne.2019; 6: 16. CrossRef - Outcomes of Patients With Delirium in Long-Term Care Facilities: A Prospective Cohort Study
Kyoung Ja Moon, Heeok Park
Journal of Gerontological Nursing.2018; 44(9): 41. CrossRef - Relationship between Delirium and Clinical Prognosis among Older Patients underwent Femur Fracture Surgery
Jae-Lan Shim, Seon-Young Hwang
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(2): 649. CrossRef - The effects of a tailored intensive care unit delirium prevention protocol: A randomized controlled trial
Kyoung-Ja Moon, Sun-Mi Lee
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2015; 52(9): 1423. CrossRef - Automatic Delirium Prediction System and Nursing-Sensitive Outcomes in the Medical Intensive Care Unit
Ha-young Cho, Xianghua Song, Jinshi Piao, Yinji Jin, Sun-Mi Lee
Clinical Nursing Research.2015; 24(1): 29. CrossRef - Postoperative Delirium in Elderly Patients with Osteoarthritis Surgery: Incidence and Risk Factors
Eun A Park, Min Young Kim
Journal of muscle and joint health.2015; 22(2): 57. CrossRef - Is Delirium an Unrecognized Threat to Patient Safety in Korean Intensive Care Units?
Kyoung-Ja Moon, Jinshi Piao, Yinji Jin, Sun-Mi Lee
Journal of Nursing Care Quality.2014; 29(1): 91. CrossRef
- Incidence and Associated Factors of Delirium after Orthopedic Surgery
- 889 View
- 9 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Risk Factors of Postoperative Delirium in Elderly Patients with Hip Fractures
- Ki Hwan Kim, Duk Hwan Kho, Ju Yong Shin, Jin Yong Choi, Eung Sik Kim, Dong Heon Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2008;21(3):189-194. Published online July 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.3.189
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To find out the relationship between various risk factors and post-operative delirium in elderly patients with hip fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Out of 135 patients older than 65 years old who underwent the surgery for hip fracture in our department, between the periods of March 2003 to March 2005, 14 patients (10.4%) developed post-operative delirium and 121 patients (89.6%) did not. We studied risk factors of post-operative delirium in two groups.
RESULTS
In chi-square test between delirium group and non-delirium group, the patients were more likely to develop post-operative delirium if they had previous episodes of delirium, abnormal cognitive function, low walking ability before admission, high dependency on ADL (Activities of Daily Living), other medical accompanying diseases, history of dementia, post-operative hypoxia, post-operative electrolyte imbalance, low post-operative hemoglobin and hematocrit, low post-operative albumin and were older than 75 years old (p<0.05). Sex, type of fracture, anesthesia and the time between admission and operation did not show much difference between the two groups.
CONCLUSION
The risk factors of postoperative delirium in elderly patients with hip fracture have a tendency to be multifactorial. Therefore, we conclude that being prepared by thorough understanding of the risk factors and their relationships will help prevent post-operative delirium and result in good postoperative prognosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Increased Serum Neuropeptide Galanin Level Is a Predictor of Cognitive Dysfunction in Patients with Hip Fracture
Zichao Xue, Ke Zhang, Biao Luo, Long Fan, Ruizhe Zhao, Guangliang Hu, Yuzhen Xu
Disease Markers.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Sleep Disturbance Strongly Related to the Development of Postoperative Delirium in Proximal Femoral Fracture Patients Aged 60 or Older
Myung-Rae Cho, Suk-Kyoon Song, Cheol-Hwan Ryu
Hip & Pelvis.2020; 32(2): 93. CrossRef - Incidence and Associated Factors of Delirium after Orthopedic Surgery
Si-Wook Lee, Chul-Hyun Cho, Ki-Cheor Bae, Kyung-Jae Lee, Eun-Seok Son, Sang-Hyun Um
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2019; 54(2): 157. CrossRef - Relationship between Delirium and Clinical Prognosis among Older Patients underwent Femur Fracture Surgery
Jae-Lan Shim, Seon-Young Hwang
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(2): 649. CrossRef - Relationship between Knowledge, Stress, and Nursing Performance about Care for Delirium in Geriatric Hospital Nurses
Eun-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Clinical Health Science.2016; 4(2): 593. CrossRef - The effects of a tailored intensive care unit delirium prevention protocol: A randomized controlled trial
Kyoung-Ja Moon, Sun-Mi Lee
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2015; 52(9): 1423. CrossRef - Is Delirium an Unrecognized Threat to Patient Safety in Korean Intensive Care Units?
Kyoung-Ja Moon, Jinshi Piao, Yinji Jin, Sun-Mi Lee
Journal of Nursing Care Quality.2014; 29(1): 91. CrossRef - The Effects of Delirium Care Training Program for Nurses in Hospital Nursing Units
Moonja Kim, Haejung Lee
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2014; 26(5): 489. CrossRef - Knowledge, Performance and Stress about Care for Delirium in Orthopedic Hospital Nurses
Mi Young Kim, Young Eun
Journal of muscle and joint health.2013; 20(1): 72. CrossRef - The Experience of Delirium Care and Clinical Feasibility of the CAM-ICU in a Korean ICU
Joo-Hee Jung, Jung-Hye Lim, Eun-Jung Kim, Hyo-Chan An, Min-Kyung Kang, Jin Lee, Yu-Kyung Min, Eun-Zoo Park, Xiang-Hwa Song, Hye-Ryoung Kim, Sun-Mi Lee
Clinical Nursing Research.2013; 22(1): 95. CrossRef - Development and validation of the Korean Nursing Delirium Scale
Kyoung-Nam Kim, Cheol-Ho Kim, Kwang-Il Kim, Hyun-Jung Yoo, Si-Young Park, Yeon-Hwan Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(3): 414. CrossRef - Influencing Factors of the Incidence of Delirium in Elderly Patients with Arthroplasty
Young-Whee Lee, Hye-Bin Im, Eun-Jeong Jeong, Hee-Sun Ma
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(4): 348. CrossRef - Delirium After Spinal Surgery in Korean Population
Jin Kyu Lee, Ye-Soo Park
Spine.2010; 35(18): 1729. CrossRef - The Incidence and Related Factors of Delirium in Elderly Patients with Hip Fracture after Surgery
Bo-Kyung Sohn, Yerl-Bo Sung, Eun-Jin Park, Dong-Woo Lee
Journal of the Korean Geriatrics Society.2010; 14(3): 162. CrossRef
- Increased Serum Neuropeptide Galanin Level Is a Predictor of Cognitive Dysfunction in Patients with Hip Fracture
- 1,978 View
- 5 Download
- 14 Crossref

- The Evaluation of Clinical and Radiographic Prognostic Factors for the Surgically Treated Unstable Ankle Fractures
- Hong Geun Jung, Hee Kon Park, Moon Jib Yoo, Tai Won Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(2):216-225. Published online April 30, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.2.216
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to analyze the clinical and radiographic prognostic factors which may affect the postoperative clinical results of the unstable ankle fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study is based on 75 unstable ankle fractures treated by open reduction and internal fixation from May 1994 to August 2000, with a minimum follow-up period of 12 months(range : 13 months-7 years 3 months). The 75 patients were average 40.5 years old with male: female ratio of 52:23. Based on Lauge-Hansen classification, the supination-external rotation type was the most common with 42 (56.0%) cases. The clinical results was assessed by American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society(AOFAS) functional scale. The sex, age, side of injury, body weight, trauma-operation interval, operation time, cause of injury as the possible postoperative clinical prognostic factors and fracture type, anatomical reduction of fracture, preoperative medial clear space, postoperative medial clear space, talo-crural angle, talar tilt, tibio-fibular clear space, tibio-fibular overlap space as the possible radiographic prognostic factor were statistically analyzed RESULT: Postoperative AOFAS functional scale was average 81.0 points with 23(30.7%) cases excellent, 17(22.7%) good, 18(24.0%) fair and 17(22.7%) cases poor results. The age, the operation time(p<0.001) and the anatomical reduction of fracture(p<0.005) were found to be statistically significant factors affecting the prognosis. The other clinical and radiographic factors did not significantly affect the clinical results.
CONCLUSION
The surgically treated unstable ankle fractures in patients whose age was above 41 years old or operation time exceeding 90 minutes or unsatisfied anatomical reduction of fractures showed significantly poor clinical results. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Bone Mineral Density of Ankle Fracture Patients
Tae Hyung Kim, Jae Hyung Lee, Seung-Hwan Park
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2021; 56(4): 334. CrossRef
- Analysis of Bone Mineral Density of Ankle Fracture Patients
- 604 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Complications and Affecting Factors for Intracapsular Femoral Neck Fractures Treated by Multiple Pinning
- Sung Jung Kim, Shin Yoon Kim, Gi Bong Cha, Chang Wug Oh, Il Hyung Park, Joo Chul Ihn
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(2):201-208. Published online April 30, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.2.201
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To investigate the relationship between the complications of intracapsular femoral neck fractures treated by multiple pinning and several affecting factors.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sixty-eight patients with intracapsular femoral neck fractures were treated by multiple pinning from March 1993 to January 2000 and followed at more than one year. Relationship between the complications such as failure of union, collapse of femoral head due to osteonecrosis of femoral head and several affecting factors including displacement of fracture according to Garden stage, state of reduction, position of screws, time interval from injury to operation, and fracture level were analyzed. The Fisher exact test, chi-square test, and multivariate logistic regression analysis were used to find the relevant factors influencing incidence of complications. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
RESULTS
Position of screw was the most important single factor affecting the results of treatment of intracapsular femoral neck fracture (p=0.046). Moreover, the Garden stage and position of screw were revealed affecting the incidence of complications together with other factors (each p value was 0.028 and 0.027).
CONCLUSION
We considered that satisfactory position of screw was important to reduce complications after multiple pinning for intracapsular femoral neck fracture. And the results of operation also seemed to closely relate with multiple factors including Garden stage and status of reduction. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Predicting Complications after Internal Fixation of Femoral Neck Fractures
Tae-Ho Kim, Jong-Oh Kim, Sung-Sik Kang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(2): 79. CrossRef
- Factors Predicting Complications after Internal Fixation of Femoral Neck Fractures
- 514 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Factors influencing the results of treatment in Lisfranc injury of the foot
- Hyoun Oh Cho, Kyoung Duck Kwak, Soo Min Sohn, Woo Kun Jung, Pill Hwan Oh, Dai Hwan Lim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1999;12(4):961-967. Published online October 31, 1999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1999.12.4.961
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
: The purpose of this study is to detect the factors influencing the results of treatment for Lisfranc injuries of the foot.
MATERIALS and METHODS
: We assessed the correlation between the AOFAS Scale and each of the variables which might influence the results of treatment in 25 cases of Lisfranc injuries, using the SPSS version 7.5.
RESULTS
The mean AOFAS Scale rated 81.48 points. The degrees of initial soft tissue injury had close correlation with the AOFAS Scale; while time from injury to operation, accuracy of reduction such as the alignment of the tarsometatarsal joints, gap between the first and the second metatarsal bases, and the foot arch angles had moderate correlation with AOFAS Scale(p<0.05). The age at operation, types of fractures, joint space of the tarsometatarsal joints had little or fair degrees of correlation with the AOFAS Scale(p>0.05).
CONCLUSION
: The factorf influencing the results of treatment for Lisfranc injuries included initial deree of soft tissue injury, time form injury to operation, and variables related to the accuracy of reduction such as the alignment of tarsometatarsal joints, gap between the first and the second metatarsal bases, and the maintenance of the foot arch.
- 336 View
- 0 Download

- Traumatic Fracture - Dislocation of the Hip
- Chung Nam Kang, Jong Oh Kim, Dong Wook Kim, Young Do Koh, Sang Hoon Ko, Jae Doo Yoo, Joo Seok Eom, Dong Wook Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 1997;10(4):772-777. Published online October 31, 1997
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1997.10.4.772
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Traumatic dislocation or fracture-dislocation of the hip is relatively uncommon, but high velocity accidents have increased its incidence in recent years. The purpose of this study was to review the result of the treatment and to evaluate the prognostic factor. We retroprospectively reviewed 28 patients with traumatic fracture-dislocation of the hip between October, 1993 and March, 1996. 21 were males and 7 females. The mean age was 33.5 years(range, 11 to 67 years). Average follow-up was 18 months(range, 13 to 28 months). Exellent or good results were obtained in 19 patients(68%) by the criteria of Epstein. The complications were followings 2 cases of avascular necrosis and 1 case of osteoarthritis. Factors associated with a good prognosis included an early reduction, low level of initial trauma, abscence of associated injury.
- 333 View
- 0 Download

- Clinical Study of Prognostic Factors in Patellar Fractures
- Duck Yun Cho, Hee Chun Kim, Chung Hwan Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1996;9(4):977-983. Published online October 31, 1996
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1996.9.4.977
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Most authors report 70% to 80% good to excellent results following open reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the patella. As with most intraarticular fractures, the prognosis for healing and restoration of function in fractures of the patella is dependent on the amount of articular cartilage damage and exact reduction of fracture. In order to document clinical results and describe any prognostic factors, we evaluated the results of 69 patellar fractures treated in 66 patients who had been treated with open reduction and internal fixation at the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Nationanl Medical Center, from January 1990 to December 1994. The average age at the time of surgery was 41.2 years(16 years-75 years) and the average follow-up time was 38.7 months(14 months-74 months). The results were as fellows: 1. The mechanism of injury(traffic accident), concomittant inury of ipsilateral lower extremity, fracture morphology, immgbilization period less than two weeks and accuracy of reduction were significant prognostic factors. 2. Age and method of fixation were not significant prognostic factors. 3. The brisement of knee under general anesthesia was helpful, that had been performed following bony union.
- 351 View
- 0 Download

- The statistical analysis of factors influencing union of claviclefractures
- Shin Kun Kim, Koing Woo Kwon, Sang Wook Lee, Yung Seok Chung
- J Korean Soc Fract 1992;5(1):37-42. Published online May 31, 1992
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1992.5.1.37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - No abstract available.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative analysis of functional outcome of anatomical precontoured locking plate versus reconstruction plate in the management of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures
P Kingsly, M Sathish, N Deen Muhammad Ismail
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Operative Treatment of Clavicle Midshaft Fractures: Comparison between Reconstruction Plate and Reconstruction Locking Compression Plate
Chul-Hyun Cho, Kwang-Soon Song, Byung-Woo Min, Ki-Cheor Bae, Kyung-Jae Lee
Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery.2010; 2(3): 154. CrossRef
- Comparative analysis of functional outcome of anatomical precontoured locking plate versus reconstruction plate in the management of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures
- 574 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


