-
Biomechanical finite element analysis of a femoral neck system fixation construct for femur neck fractures and clinical implications
-
Hoon-Sang Sohn, Se-Lin Jeong, Gu-Hee Jung
-
J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):133-142. Published online July 22, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00108
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Background
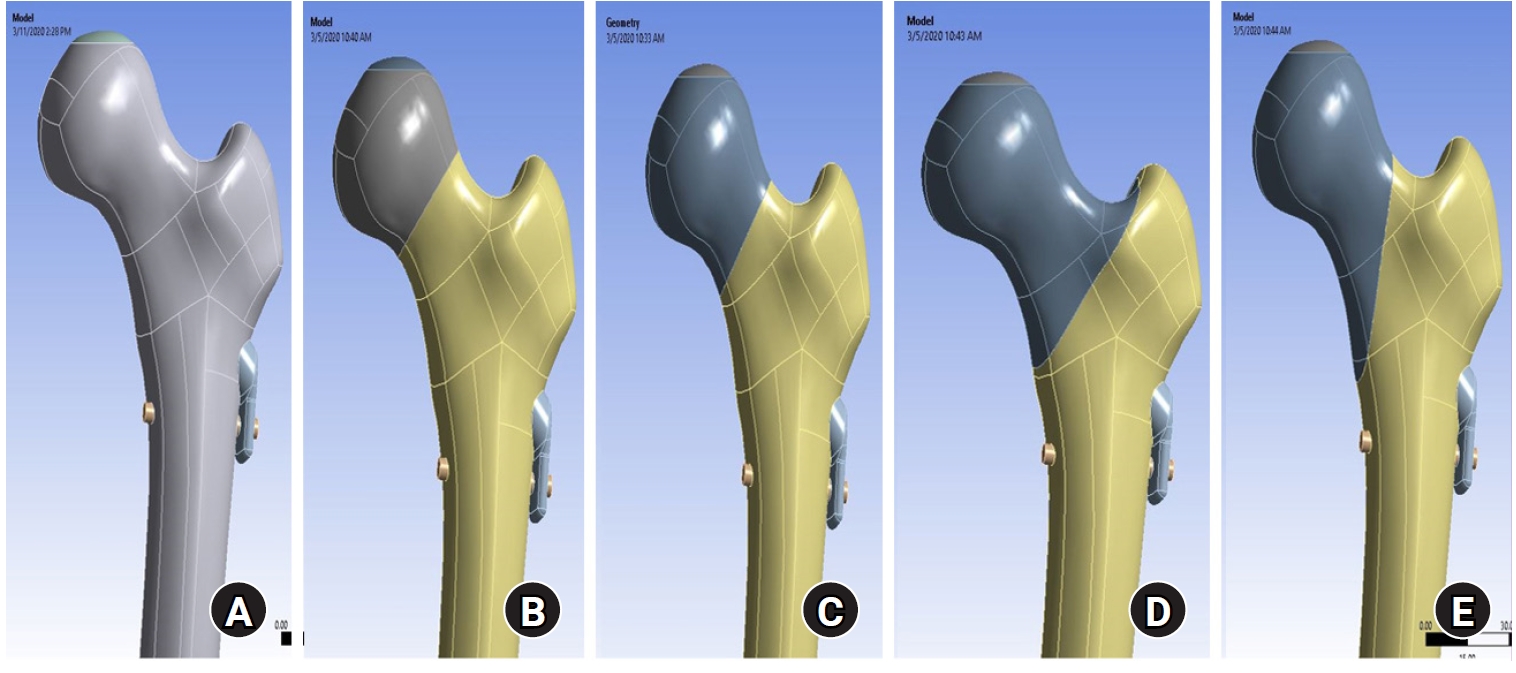
This study assessed the structural/mechanical stability of fixation constructs with a femoral neck system (FNS) via finite element analysis after simulating femoral neck fractures and explored the clinical implications.
Methods
We simulated subcapital, transcervical, basicervical, and vertical fracture models using a right femur (SAWBONES) and imported the implant model of FNS to Ansys (Ansys 19.0, Ansys Inc.) to place the implant in the optimal position. The distal end of the femur model was completely fixed and was abducted 7°. The force vector was set laterally at an angle of 3° and posteriorly at an angle of 15° in the vertical ground. The analysis was conducted using Ansys software with the von Mises stress (VMS) in megapascals (MPa).
Results
The maximum VMS of the fracture site was 67.01 MPa for a subcapital, 68.56 MPa for a transcervical, 344.54 MPa for a basicervical, and 130.59 MPa for a vertical model. The maximum VMS of FNS was 840.34 MPa for a subcapital, 637.37 MPa for a transcervical, 464.07 MPa for a basicervical, and 421.01 MPa for a vertical model. The stress distribution of basicervical and vertical fractures differed significantly, and the basicervical fracture had higher VMS at the bone, implant, and fracture sites.
Conclusions
FNS fixation should be performed with consideration the osseous anchorage in the femoral head, and this technique might be appropriate for vertical fractures. Regarding the VMS at the fracture site, FNS might be applied cautiously only to basicervical fractures with anatomical reduction without a gap or comminution. Level of evidence: IV.
-
Fracture-related infections: a comprehensive review of diagnosis and prevention
-
HoeJeong Chung, Hoon-Sang Sohn
-
J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):86-95. Published online April 25, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00164
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
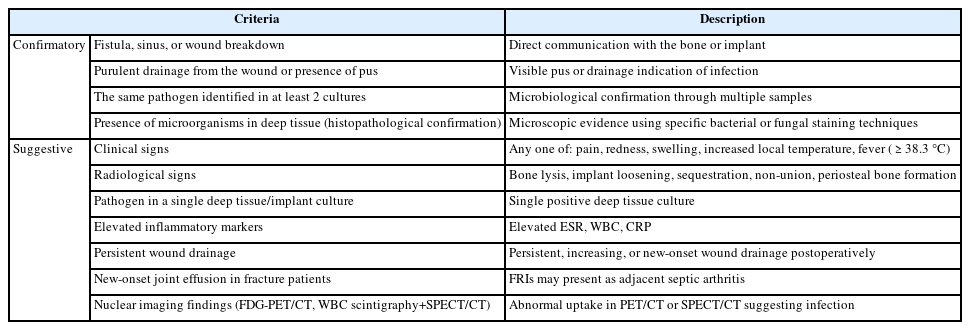
- Fracture-related infections are challenging complications in orthopedic trauma that often require prolonged treatment and impose a significant healthcare burden. Accurate diagnosis and effective prevention strategies are essential for minimizing their occurrence. A recent international consensus has established standardized diagnostic criteria based on clinical, microbiological, radiological, and histopathological findings. Prevention is the top priority and involves a thorough preoperative risk assessment, along with glycemic control, nutritional optimization, and management of comorbidities, as well as intraoperative and postoperative measures such as appropriate antibiotic prophylaxis, surgical site antisepsis, and meticulous wound care. A multidisciplinary approach involving orthopedic surgeons, infectious disease specialists, and microbiologists is crucial for successfully reducing the burden of fracture-related infections.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Personalized Approaches to Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies in Periprosthetic Fracture-Related Infections (PFRIs): Case Series and Literature Review
Marianna Faggiani, Marco Zugnoni, Matteo Olivero, Salvatore Risitano, Giuseppe Malizia, Silvia Scabini, Marcello Capella, Stefano Artiaco, Simone Sanfilippo, Alessandro Massè
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2025; 15(12): 576. CrossRef - Pathogen-Specific Risk for Iterative Surgical Debridement in Orthopedic Infections: A Prospective Multicohort Analysis
Flamur Zendeli, Anna Jędrusik, Raymond O. Schaefer, David Albrecht, Michael Betz, Felix W. A. Waibel, Tanja Gröber, Nathalie Kühne, Sören Könneker, İlker Uçkay
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(24): 8750. CrossRef
-
6,291
View
-
239
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
Short-term Treatment Comparison of Teriparatide and Percutaneous Vertebroplasty in Patients with Acute Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures
-
Joonoh Seo, Ki Youn Kwon, Bumseok Lee, Hoon-Sang Sohn
-
J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):15-21. Published online January 31, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.15
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
This study compared the 3-month treatment effects of teriparatide and percutaneous vertebroplasty for acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.
Materials and Methods
A retrospective study was conducted on 76 patients diagnosed with acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures from January 1, 2020 to December 31, 2022. The patients were divided into the teriparatide group and the percutaneous vertebroplasty+alendronate group. The visual analog scale (VAS), Oswestry disability index (ODI), and height of the vertebrae anterior wall were measured before treatment and at 1 and 3 months after treatment.
Results
Of the 76 patients, 42 were treated with teriparatide, and 34 were treated with percutaneous vertebroplasty. The symptoms improved in both groups, with a decrease in the VAS and ODI scores at 1 and 3 months after treatment, respectively. On the other hand, there was no significant difference in the VAS, ODI score, and anterior vertebral body height between the two groups before treatment and at 1 and 3 months after treatment.
Conclusion
In the treatment of acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures, conservative treatment using teriparatide showed similar short-term (3 months) treatment results to percutaneous vertebroplasty in terms of improvement in back pain and function and degree of reduction in anterior vertebral body height.
-
Fracture-Related Complications: What You Can Do to Prevent Infection
-
HoeJeong Chung, Jin Woo Lee, Sang-Ho Lee, Hoon-Sang Sohn
-
J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(4):139-147. Published online October 31, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.4.139
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Fracture-related infections (FRI) can occur when bacteria enter the wound during a traumatic injury. All efforts should be made to prevent FRI-associated complications due to the complexity of treatment at the time of onset and poor treatment outcomes. The risk factors for FRIs vary and several preoperative, perioperative, and postoperative measures can be implemented to prevent infections. Preoperative measures include blood sugar control, nutritional support, discontinuation of steroids and immunosuppressants, treatment of accompanying pre-existing infections, and decolonization of pathogens, specifically Staphylococcus aureus. The perioperative and postoperative measures include the use of prophylactic antibiotics, proper surgical site preparation (hair removal, preoperative washing, skin antisepsis), suitable surgical environment (operating room ventilation system, behavioral interventions in the operating room), correct surgical techniques (debridement, irrigation, wound closure, and negative pressure wound therapy). All medical staff should pay careful attention and ensure the implementation of the correct preventive measures.
-
Bisphosphonate: An Invaluable Medication or Abandoned Acid?
-
HoeJeong Chung, Jin Woo Lee, Jae Woong Um, Hoon-Sang Sohn
-
J Korean Fract Soc 2021;34(3):122-130. Published online July 31, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.3.122
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Over the last two decades, bisphosphonate has widely been applied in the treatment of osteoporosis.
We reviewed the various adverse effects, current trials involving diverse bone metabolic diseases, and the future direction of bisphosphonate. Acute phase reaction, hypocalcemia, ocular inflammation, and gastrointestinal disturbances are the well-known short-term side-effects of bisphosphonate. Long term side-effects include osteonecrosis of the jaws and atypical femur fracture. In the modern clinical setting, bisphosphonate is widely used in treatments for osteoporosis, osteopenia, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and metastatic bone cancer. Further studies are underway for expanding the application as a bone-targeting agent in bone-related diseases. Bisphosphonate remains useful and invaluable as the 1st line medication for osteoporosis. Considering the numerous clinical situations, including time to medication after fracture, duration of drug usage, and individual drug holiday, an optimal and proper use of bisphosphonate needs to be achieved. In the current scenario, bisphosphonate will retain a strong position due to good efficacy and effectiveness for osteoporosis treatment, and the precise ap- plication to various bone diseases. We anticipate a key role of bisphosphonate for future application in the treatment of metabolic bone diseases. Further studies and advancement are highly anticipated, considering the high potential of bisphosphonate for various uses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Ocular Inflammation with Use of Oral Bisphosphonates
Jee Hyun Jeong, Kyung Tae Kang, Yu Cheol Kim
Journal of the Korean Ophthalmological Society.2025; 66(2): 128. CrossRef
-
633
View
-
6
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Risk Factors Affecting the Early Complications of Femoral Head Fractures
-
HoeJeong Chung, Jin-Woo Lee, Dong Woo Lee, Hoon-Sang Sohn
-
J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(4):204-209. Published online October 31, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.4.204
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
This study analyzed the prognostic factors in patients with femoral head fractures by comparing two groups with and without complications.
Materials and Methods
A retrospective study was performed on femoral head fracture patients who visited two different level-1 trauma centers from January 1, 2014 to June 30, 2018. Thirty-three patients with a follow-up period of more than one year were included. Early complications were defined as fair or poor in the Thompson–Epstein clinical evaluation criteria and grades 3 or 4 in the Kellgren– Lawrence classification within one year after the fracture. The patients were divided into two groups, with and without early complications. Statistical analysis was performed for the nominal variables with a Fisher’s exact test and continuous variables using a Mann–Whitney U test.
Results
Nine patients (27.3%) had early complications, and there were no significant differences according to age, sex, treatment method, combined fractures, Pipkin classification, and AO/OTA classification between the two groups.
Conclusion
The prognosis in femoral head fractures is difficult to predict. Therefore, the validation of existing classifications or a new classification is necessary.
|