Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 34(3); 2021 > Article
- Review Article Bisphosphonate: An Invaluable Medication or Abandoned Acid?
- HoeJeong Chung, Jin Woo Lee, Jae Woong Um, Hoon-Sang Sohn
-
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma 2021;34(3):122-130.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.3.122
Published online: July 31, 2021
- 669 Views
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
Abstract
Over the last two decades, bisphosphonate has widely been applied in the treatment of osteoporosis. We reviewed the various adverse effects, current trials involving diverse bone metabolic diseases, and the future direction of bisphosphonate. Acute phase reaction, hypocalcemia, ocular inflammation, and gastrointestinal disturbances are the well-known short-term side-effects of bisphosphonate. Long term side-effects include osteonecrosis of the jaws and atypical femur fracture. In the modern clinical setting, bisphosphonate is widely used in treatments for osteoporosis, osteopenia, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and metastatic bone cancer. Further studies are underway for expanding the application as a bone-targeting agent in bone-related diseases. Bisphosphonate remains useful and invaluable as the 1st line medication for osteoporosis. Considering the numerous clinical situations, including time to medication after fracture, duration of drug usage, and individual drug holiday, an optimal and proper use of bisphosphonate needs to be achieved. In the current scenario, bisphosphonate will retain a strong position due to good efficacy and effectiveness for osteoporosis treatment, and the precise ap- plication to various bone diseases. We anticipate a key role of bisphosphonate for future application in the treatment of metabolic bone diseases. Further studies and advancement are highly anticipated, considering the high potential of bisphosphonate for various uses.
Published online Jul 23, 2021.
https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.3.122
Bisphosphonate: An Invaluable Medication or Abandoned Acid?
Abstract
Over the last two decades, bisphosphonate has widely been applied in the treatment of osteoporosis. We reviewed the various adverse effects, current trials involving diverse bone metabolic diseases, and the future direction of bisphosphonate. Acute phase reaction, hypocalcemia, ocular inflammation, and gastrointestinal disturbances are the well-known short-term side-effects of bisphosphonate. Long term side-effects include osteonecrosis of the jaws and atypical femur fracture. In the modern clinical setting, bisphosphonate is widely used in treatments for osteoporosis, osteopenia, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and metastatic bone cancer. Further studies are underway for expanding the application as a bone-targeting agent in bone-related diseases. Bisphosphonate remains useful and invaluable as the 1st line medication for osteoporosis. Considering the numerous clinical situations, including time to medication after fracture, duration of drug usage, and individual drug holiday, an optimal and proper use of bisphosphonate needs to be achieved. In the current scenario, bisphosphonate will retain a strong position due to good efficacy and effectiveness for osteoporosis treatment, and the precise application to various bone diseases. We anticipate a key role of bisphosphonate for future application in the treatment of metabolic bone diseases. Further studies and advancement are highly anticipated, considering the high potential of bisphosphonate for various uses.
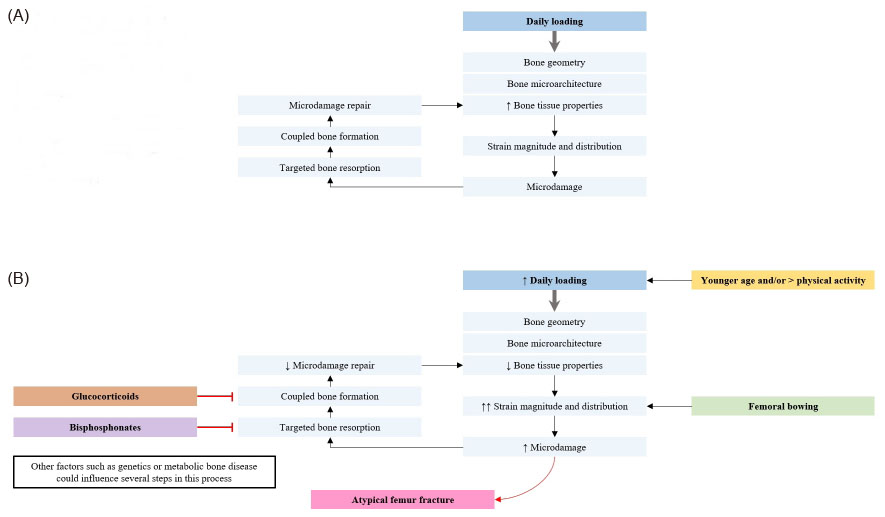
Fig. 1
Possible pathogenesis of atypical fracture. (A) Normal process for repair of microdamage via targeted remodeling. (B) Factors influencing the accumulation and repair of microdamage that may be related to the pathogenesis of atypical femoral fracture.
Financial support:None.
Conflict of interests:None.
References
-
U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Safety Alerts for Human Medical Products - Aredia (pamidronate disodium), Zometa (zoledronicacid) [Internet]. Silver Spring (MD): U.S. Food and Drug Administration; 2005 May 05; [cited 2021 Jun 26].Available from: https://wayback.archive-
it.org/7993/20170112170752/http://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch/SafetyInformation/SafetyAlertsforHumanMedicalProducts/ucm150676.htm.
-
-
U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Bisphosphonates (marketed as Actonel, Actonel+Ca, Aredia, Boniva, Didronel, Fosamax, Fosamax+D, Reclast, Skelid, and Zometa) information [Internet].. Silver Spring (MD): U.S. Food and Drug Administration; 2015 Jul 08; [updated 2016 Mar 25]. [cited 2016 Mar 19].Available from: http://wayback.archive-
it.org/7993/20170111075833/http:/www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/PostmarketDrugSafetyInformationforPatientsandProviders/ucm101551.htm.
-
-
Murad MH, Drake MT, Mullan RJ, et al. Clinical review. Comparative effectiveness of drug treatments to prevent fragility fractures: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Incidence rate of atypical femoral fracture after bisphosphonates treatment in Korea 2012;97:1871–1880.
-
-
Hong S, Youk T, Lee SJ, Kim KM, You HM, Jeon EK. In: Use of bisphosphonate and bone health in cancer patients with bone metastasis. Goyang: NHIS Ilsan Hospital Institute of Health Insurance & Clinical Research; 2016 Nov. pp. 71.Report No.: 2016-20-020.
-
-
Rudnick-Glick S, Corem-Salkmon E, Grinberg I, Gluz E, Margel S. Biodegradable bisphosphonate nanoparticles for imaging and therapeutic applications in osteosarcoma; Paper presented at: SPIE Nanoscience + Engineering; 2015 Aug 9–12; San Diego, USA. 2015.
-

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS


 Cite
Cite

