-
Epidemiological changes and surgical trends of distal radius fractures in adults over 50 years during the COVID-19 pandemic in Korea: a nationwide repeated cross-sectional study
-
Han-Kook Yoon, So Ra Yoon, Kee-Bum Hong, Youngsu Jung, SeongJu Choi, Jun-Ku Lee
-
J Musculoskelet Trauma 2026;39(1):12-19. Published online January 25, 2026
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00297
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material
- Background
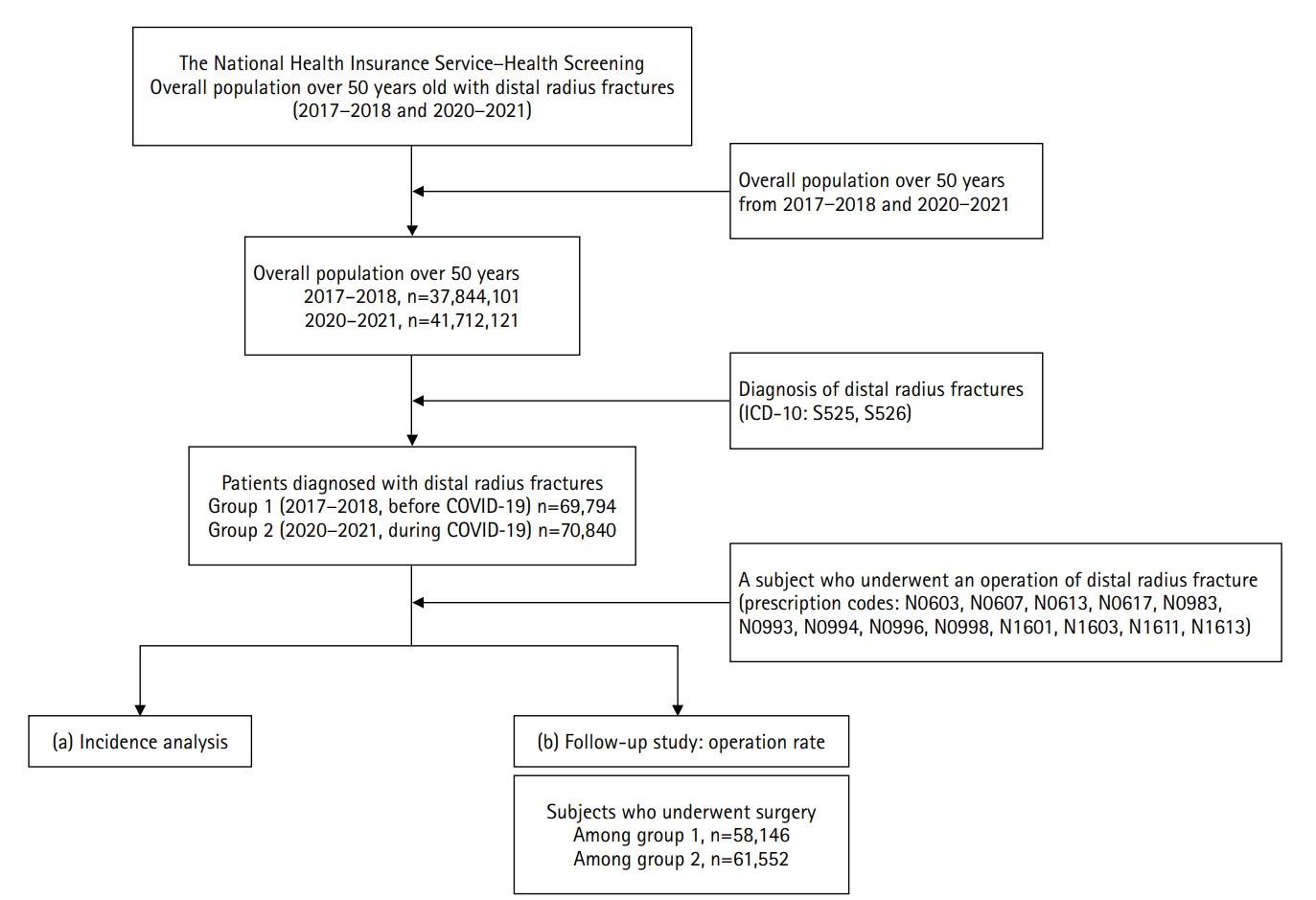
The COVID-19 pandemic is likely to have affected bone health in older adults in Korea. This study aimed to analyze changes in the epidemiology and management of distal radius fractures (DRFs) in older adults before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods
Patients with DRF aged over 50 years in 2017, 2018, 2020, and 2021 were included in this study. Patients were classified into a group with DRF occurring between 2017 and 2018 (before COVID-19) and a group with DRF occurring between 2020 and 2021 (during COVID-19). We calculated the incidence rates of DRF and compared them between the two groups. We also analyzed and compared demographic data (age, sex, income, residence) and the operation rate for DRF between the two groups. Patient selection and treatment were based on International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision codes.
Results
A total of 140,634 patients with DRF (before COVID-19, 69,794; during COVID-19, 70,840) were included. The incidence of DRF before COVID-19 (184.4/100,000 person-years) was higher than during COVID-19 (169.8/100,000 person-years). The operation rate was higher during COVID-19 (86.9%) than before COVID-19 (83.3%).
Conclusion
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the incidence of DRF decreased in South Korea. However, the rate of surgical treatment increased and exceeded the global surgical rate.
Level of evidence: III.
-
Clinical Outcomes of Triple Tension Band Wirings in Comminuted Patellar Fracture: A Comparison with Conventional Tension Band Wiring
-
Hyun-Cheol Oh, Han-Kook Yoon, Joong-Won Ha, Sang Hoon Park, Sungwoo Lee
-
J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(2):82-86. Published online April 30, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.2.82
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
This study devised triple tension band wirings (TTBW) fixation in patients with comminuted patella fractures to compare the clinical result of TTBW with that of tension band wiring (TBW).
Materials and Methods
This study was conducted on 91 patients who had undergone surgery diagnosed with acute patella fracture from January 2011 to December 2016. The study included 51 double TBW patients (Group 1) and 40 patients with TTBW (Group 2).
Results
Five out of 51 cases had a loss of reduction and fixation failure in Group 1, and no failure of fracture formation healing occurred in Group 2. Nonunion was noted in one case in Group 1 and no case in Group 2. Eight K-wire migration cases were observed in Group 1, which was not observed in Group 2. Six patients in Group 1 underwent revisional surgery. No patients in Group 2 had a reoperation. As a result of a one-year follow-up after the operation, the mean range of motion of the knee joint in groups 1 and 2 was 128.3°±11.3° and 127.9°±10.8°, respectively. The Lysholm’s scores for groups 1 and 2 were 90.8±4.2 and 90.3±3.8 points, respectively, which was not statistically significant.
Conclusion
TTBW is a helpful technique for the surgical treatment of comminuted patella fractures. The TTBW method has less reoperation due to nonunion and fixation failure. After a one-year followup, the clinical results were similar to the conventional TBW method.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Lateral marginal fractures of the patella and patellofemoral pain
Jae-Ang Sim, Chul-Ho Kim, Ji Wan Kim
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(3): 152. CrossRef
-
799
View
-
6
Download
-
1
Crossref
|