-
Three-dimensional computed tomography-based differentiation of engaged versus displaced intertrochanteric fractures using the anterior fracture line: a cross-sectional study from Korea
-
Jae-Suk Chang, Jin Yeob Park, Sang-Ok Chun, Chul-Ho Kim
-
J Musculoskelet Trauma 2026;39(1):30-37. Published online January 25, 2026
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00318
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Background
With the advent of an aging society, osteoporotic fractures—particularly hip fractures—are increasing, with a 1-year mortality rate of 17%. Achieving stable fixation that enables early ambulation is essential but remains challenging because complex intertrochanteric (IT) fracture patterns are often underestimated on plain radiographs. Using three-dimensional computed tomography (3D-CT), this study analyzed whether the anterior fracture line lies medial or lateral to the IT line and examined its relationship with displacement or distal medullary canal engagement, highlighting the potential influence of the joint capsule and capsular ligaments on fracture morphology and fixation stability.
Methods
A retrospective review was conducted on 96 osteoporotic IT fractures in patients aged ≥60 years treated between April 2013 and December 2022 at National Police Hospital and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. Fractures were classified as engaged, completely displaced, and partially displaced based on 3D-CT findings. The anterior fracture-line position (medial or lateral to the IT line) and the status of the lesser trochanter (LT) were evaluated. The chi-square or Fisher exact test was used for statistical comparisons.
Results
In total, 96 patients were analyzed. Of these, 49 cases (51.0%) were classified as engaged type, 27 cases (28.1%) as completely displaced type, and 20 cases (20.8%) as partially displaced type. When comparing fracture pattern with anterior fracture-line position, the completely displaced type showed a significantly higher proportion of lateral anterior fracture lines than the other two types (P<0.001). However, no significant association was identified between fracture pattern and LT displacement. When the anterior fracture-line position and LT displacement were evaluated together, only the engaged type demonstrated a possible association between a lateral anterior fracture line and LT displacement, though the statistical significance was weak (P=0.047).
Conclusions
Fracture lines lateral to the IT line were strongly associated with displacement in IT fractures; however, their relationship with LT involvement, reflecting iliopsoas tendon traction, was not clearly demonstrated. Although the factors contributing to the engaged-type fracture remain uncertain, the statistical association between fracture pattern and anterior fracture-line position suggests that capsular structures may play a stabilizing role in select fracture configurations. Further studies are needed to clarify these anatomical interactions.
Level of evidence:
-
Innovative applications of artificial intelligence in orthopedics focusing on fracture and trauma treatment: a narrative review
-
Chul-Ho Kim, Ji Wan Kim
-
J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):178-185. Published online October 24, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00283
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
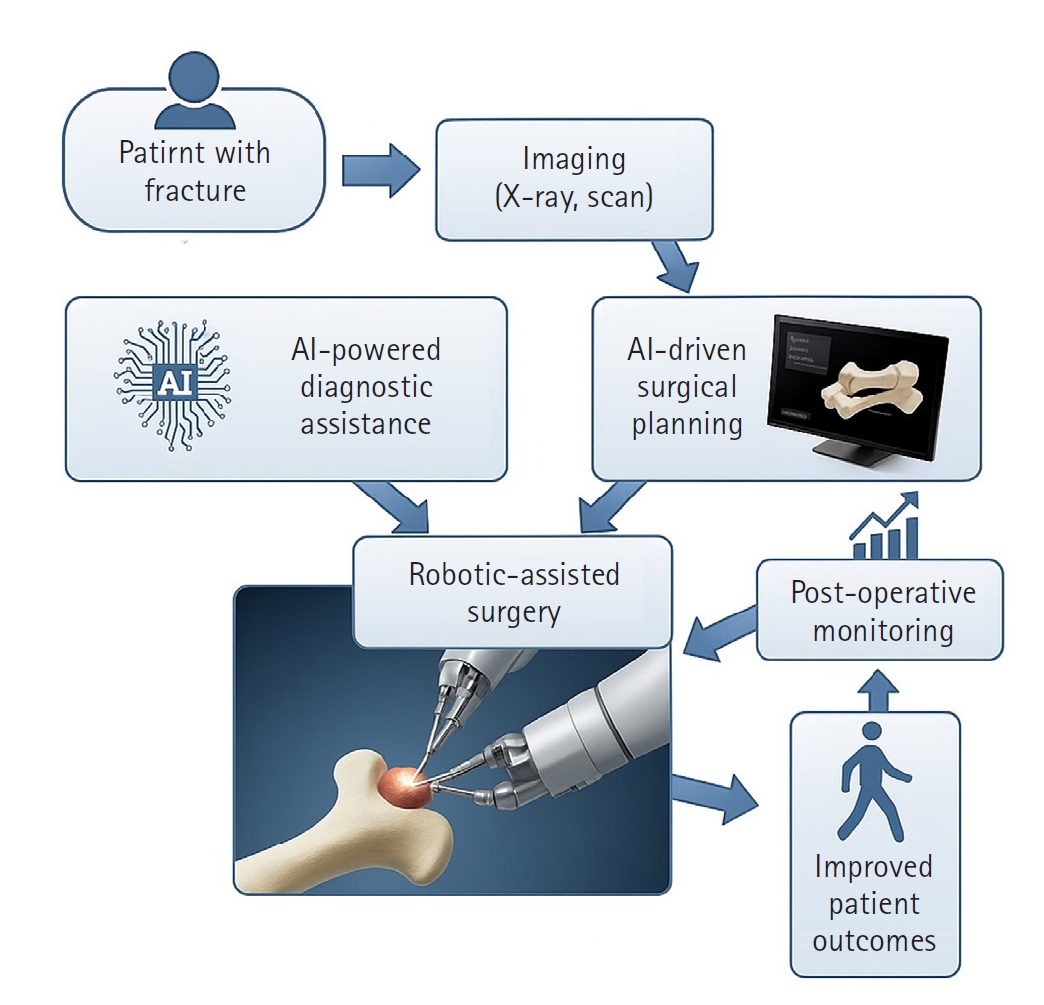
- Artificial intelligence (AI) is bringing about transformative changes in orthopedic surgery, with its potential being particularly prominent in the field of fracture and trauma treatment. This review explores the current applications and future prospects of AI-driven surgical planning and simulation, robot and image-based navigation surgery, and image-assisted diagnostic technologies. Robotic assistance in orthopedic surgery, which was initially applied to improve accuracy in component implantation for knee and hip arthroplasty and to achieve high precision in spinal screw placement, has recently expanded its use to include accurate, minimally invasive reduction of pelvic fractures. In diagnostics, AI aids in the early prediction and classification of ambiguous fractures in various anatomical regions—for example, detecting shoulder or hip fractures, identifying incomplete atypical femur fractures, and classifying femoral neck fractures—through X-ray image analysis. This improves diagnostic accuracy and reduces medical costs. However, significant challenges remain, including high initial costs, steep learning curves, a lack of long-term studies, data bias, and ethical concerns. Continued research, interdisciplinary collaboration, and policy support are crucial for the widespread adoption of these technologies.
-
917
View
-
2,147,483,661
Download
-
Lateral marginal fractures of the patella and patellofemoral pain
-
Jae-Ang Sim, Chul-Ho Kim, Ji Wan Kim
-
J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):152-159. Published online July 22, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00171
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Background
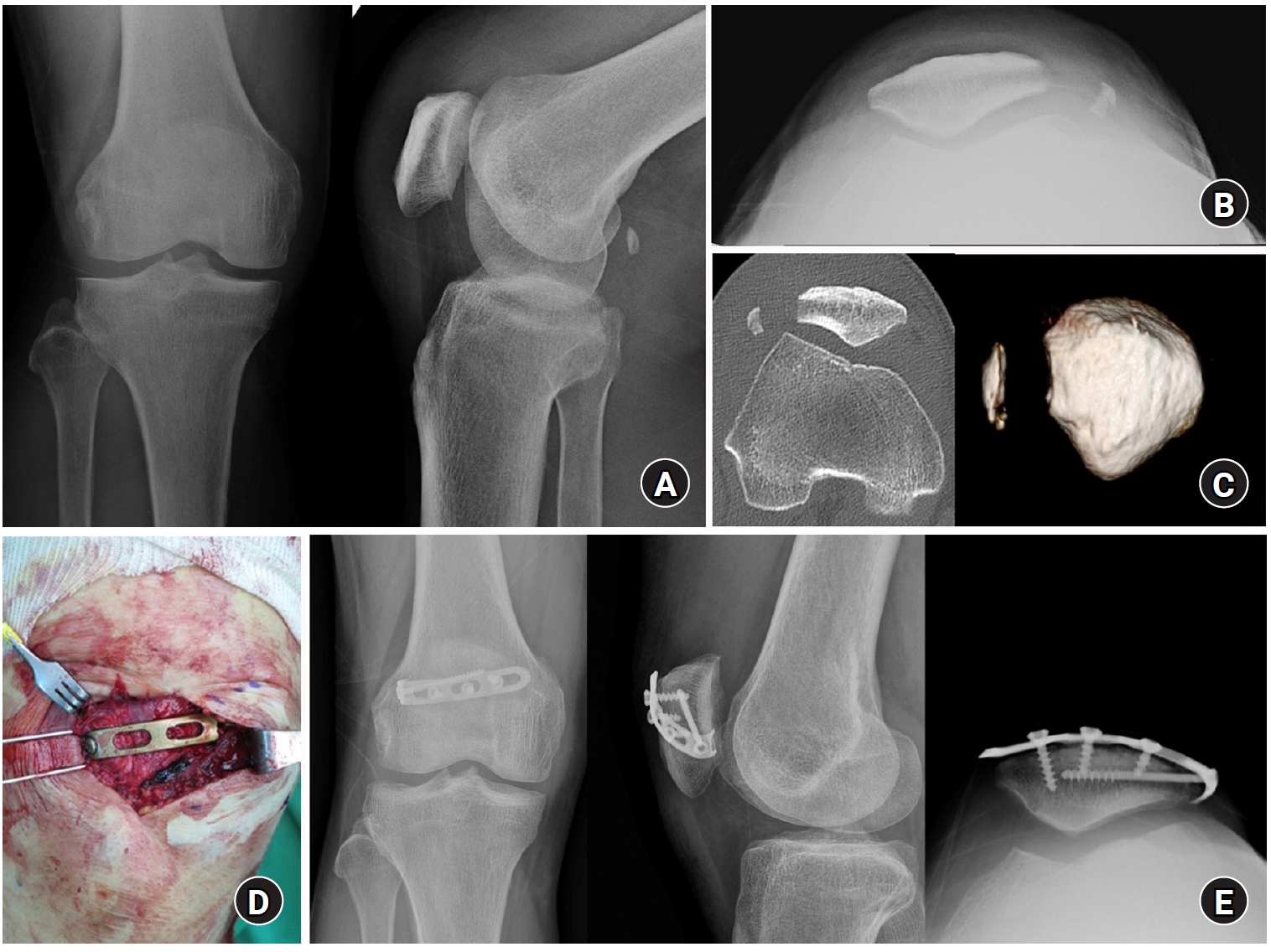
This study investigated the characteristics of lateral marginal fractures of the patella and evaluated the clinical outcomes.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed all patients with lateral marginal fractures of the patella, defined as a vertical fracture line within 15 mm of the lateral patellar border, from 2008 to 2020. In total, 41 patients were included. Patient characteristics, radiologic findings, and clinical outcomes, including the Lysholm score at 1 year postoperation, were evaluated.
Results
The injury mechanisms were direct in 34 cases and indirect in seven. Furthermore, 85% of patients had a skyline view of the patella at the initial visit, and one medial subluxation of the patella was found. Forty of the 41 patients underwent surgery. Anatomical and nonanatomical (>1-mm displacement or excision) reductions were carried out in 36 cases (88%) and five cases (12%), respectively. The average Lysholm score was 89.1 (range, 67–99). The nonanatomical reduction group had a poorer functional score (79.8 vs. 90.4; P=0.010). Lateral patellar compression syndrome occurred in two patients with nonanatomical reduction.
Conclusions
Lateral marginal fractures of the patella affected patellofemoral stability. Anatomical reduction showed good functional outcomes, while nonanatomical reduction was associated with patellofemoral stability and pain. Therefore, surgeons should perform anatomical reduction with any appropriate fixation method.
Level of Evidence: IV
-
Risk factors of surgical complications after use of the femoral neck system: a random forest analysis
-
Chul-Ho Kim, Hyun-Chul Shon, Han Soul Kim, Ji Wan Kim, Eic Ju Lim
-
J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):160-167. Published online July 23, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00157
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Background
The femoral neck system (FNS), a novel fixation device for managing femoral neck fractures (FNFs), has gained popularity in recent years. However, analyses of the surgical complications and reoperation risks associated with the use of FNS remain limited.
Methods
This retrospective observational study analyzed 57 patients who had undergone FNS fixation for FNF at two university hospitals between July 2019 and February 2024. Demographic, perioperative, and outcome variables, including age, sex, fracture classification (Garden, Pauwels, and AO), implant characteristics, tip-apex distance (TAD), neck shortening, and neck-shaft alignment, were analyzed. In addition to univariate analysis, a machine learning analysis was conducted using a random forest classifier with stratified sampling (80% training, 20% testing). The accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and area under the receiver’s operating curve were calculated to assess model performance.
Results
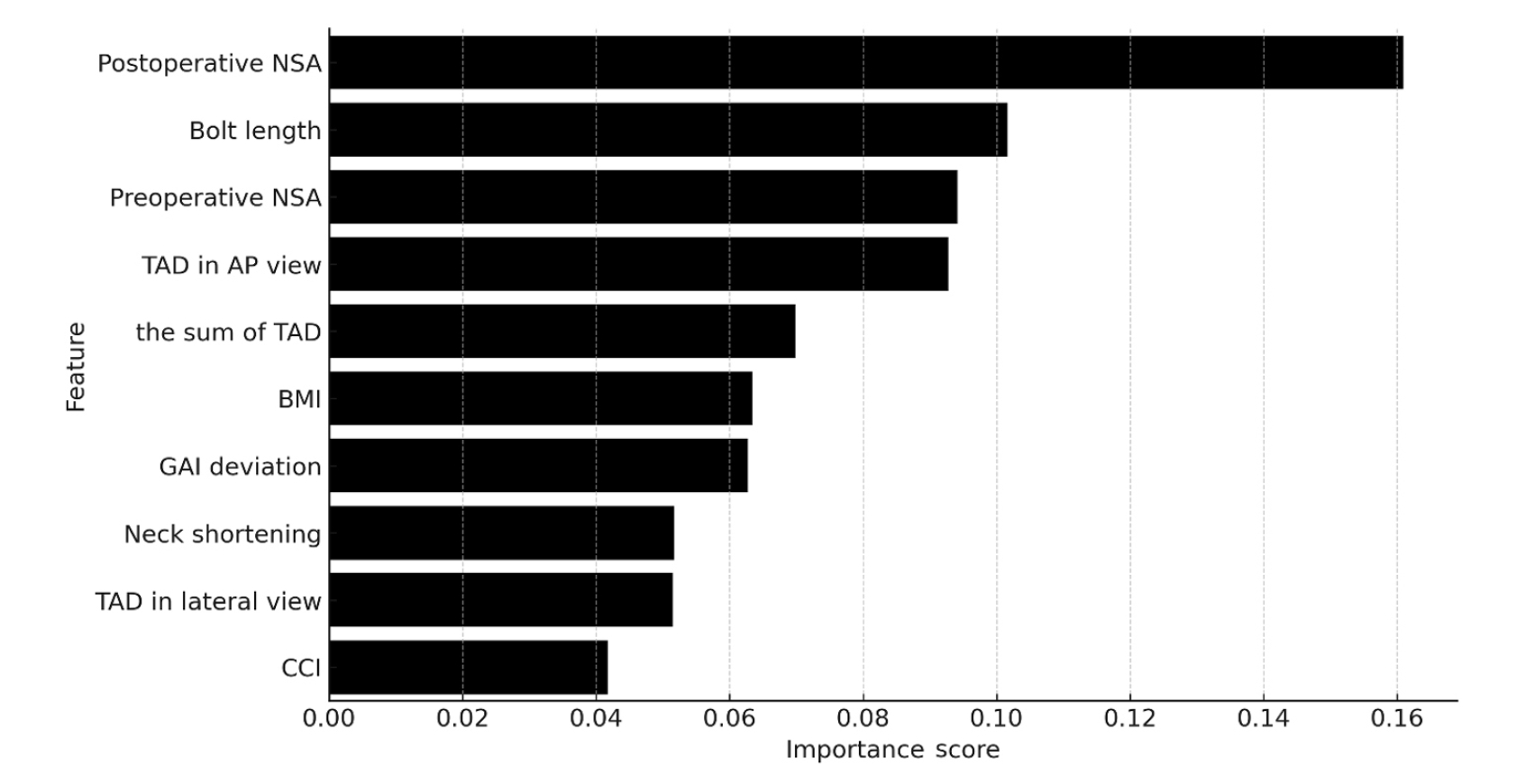
Ten patients experienced osteonecrosis of the femoral head (n=6), implant cut-out or penetration (n=3), and peri-implant fracture (n=1). Univariate analysis revealed that the TAD in the complication group was significantly shorter than that in the control group (12.1 vs. 16.7 mm; P=0.012). Additionally, neck shortening in the complication group was greater than that in the control group (4.9 vs. 2.3 mm; P=0.011). The random forest model achieved an accuracy of 83.3% and identified postoperative neck-shaft angle (NSA) as the most important predictor of complications (feature importance, 0.161), followed by bolt length (0.102) and preoperative NSA (0.094).
Conclusions
Risk factor analysis conducted using a random forest model identified postoperative NSA as the most important feature associated with postoperative complications following FNS. Therefore, care should be taken to normalize the postoperative NSA during FNF surgery.
Level of Evidence: III.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Length-stable fixation reduces femoral neck shortening in unstable femoral neck fractures: A retrospective comparative study of length-stable dynamic hip screw versus femoral neck system fixation
Seonghyun Kang, Wonseok Choi, Jeong Seok Choi, Eic Ju Lim, SungJin Ahn, Jong-Keon Oh, William T. Kent, Whee Sung Son, Jae-Woo Cho
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
-
1,127
View
-
43
Download
-
1
Crossref
|