Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 22(4); 2009 > Article
-
Review Article
- Distal Tibial Nailing
- Kyu Hyun Yang, M.D., Ph.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2009;22(4):300-305.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.4.300
Published online: October 30, 2009
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Kyu Hyun Yang, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, 146-92, Dokok-dong, Gangnam-gu, Seoul 135-720, Korea. Tel: 82-2-2019-3410, Fax: 82-2-573-5393, kyang@yuhs.ac
Copyright © 2009 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 552 Views
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref
- 1. Hahn D, Bradbury N, Hartley R, Radford PJ. Intramedullary nail breakage in distal fractures of the tibia. Injury, 1996;27:323-327.
- 2. Konrath G, Moed BR, Watson JT, Kasneshiro S, Karges DE, Cramer KE. Intramedullary nailing of unstable disphyseal fractures of the tibia with distal intraarticular involvement. J Orthop Trauma, 1997;11:200-205.
- 3. Krettek C, Miclau T, Schandelmaier P, Stephan C, Möhlmann U, Tscherne H. The mechanical effect of blocking screws ("Poller screws") in stabilizing tibia fractures with short proximal or distal fragments after insertion of small-diameter intramedullary nail. J Orthop Trauma, 1999;13:550-553.
- 4. Nork SE, Schwartz AK, Agel J, Holt SK, Schrick JL, Winquist RA. Intramedullary nailing of distal metaphyseal tibial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2005;87:1213-1221.
- 5. Oh CW, Kyung HS, Park IH, Kim PT, Ihn JC. Distal tibial metaphyseal fractures treated with percutaneous plate osteosynthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 2003;408:286-291.
- 6. Robinson CM, McLauchlan GJ, Mclean IP, Court-Brown CM. Distal metaphyseal fracture of tibia with minimal involvement of the ankle. Classification and treatment by locked intramedullary nailing. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1995;77:781-787.
- 7. Vallier HA, Le TT, Bedi A. Radiographic and clinical comparisons of distal tibia shaft fractures (4 to 11 cm proximal to the plafond): plating versus intramedullary nailing. J Orthop Trauma, 2008;22:307-311.
- 8. Wysocki RW, Kapatas JS, Virkus WW. Intramedullary nailing of proximal and distal one-third tibial shaft fractures with intraoperative two-pin external fixation. J Trauma, 2009;66:1135-1139.
- 9. Yang KH, Han DY, Park SJ. Intramedullary nailing in distal tibial metaphyseal fracture. J Korean Orthop Assoc, 2000;35:325-332.PDF
REFERENCES
Fig. 3Distal interlocking screws must be inserted from postero-medial cortex to antero-lateral one in order to spare the distal tibio-fibular syndesmosis.
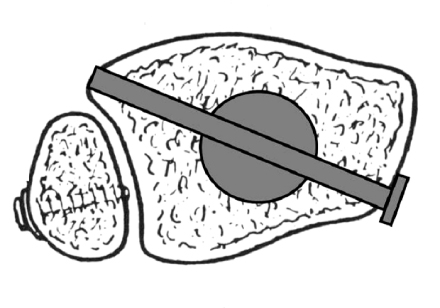

Fig. 4Undisplaced articular fragments are fixed by three cannulated screws before distal tibial nailing. These screws should not obliterate the nail passage.
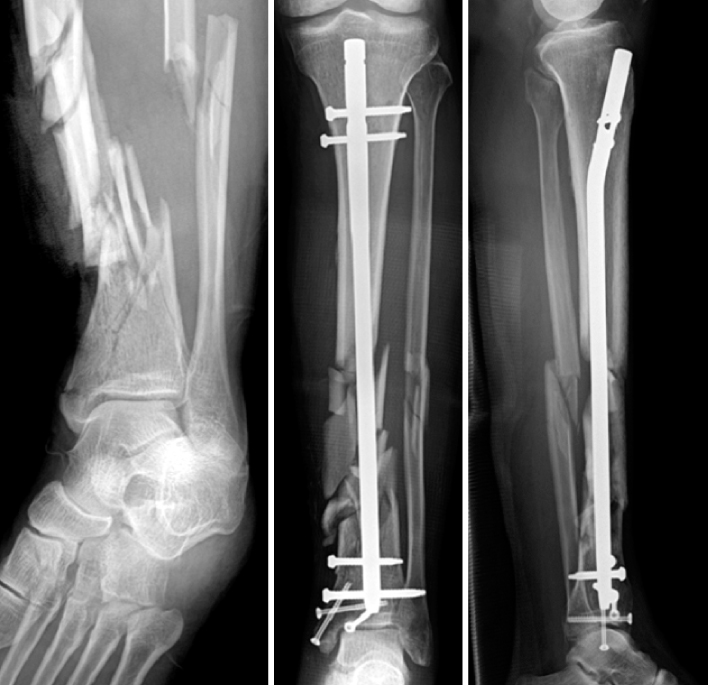

Fig. 5Unstable distal fibular fracture and displaced medial malleolar fracture are fixed before distal tibial nailing.
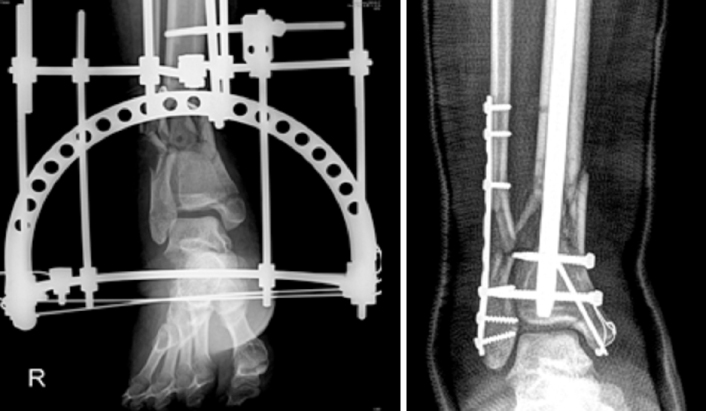

Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Clinical Outcome after Treatment of Tibia Segmental Fracture with Intramedullary Nailing and Minimal Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis
Jun Young Lee, Hyung Seok Park, Dong Hyuk Cha
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2020; 33(3): 142. CrossRef - Management of Open Fracture
Gu-Hee Jung
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(2): 236. CrossRef
Distal Tibial Nailing
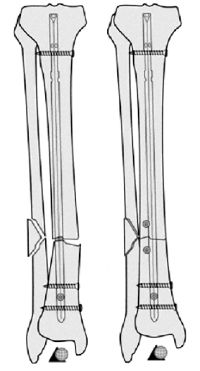
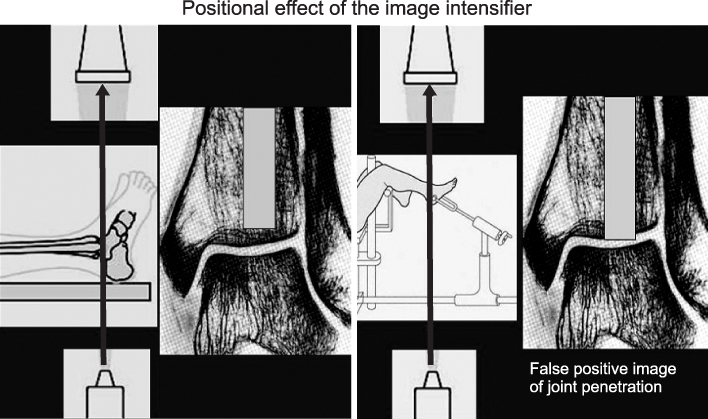
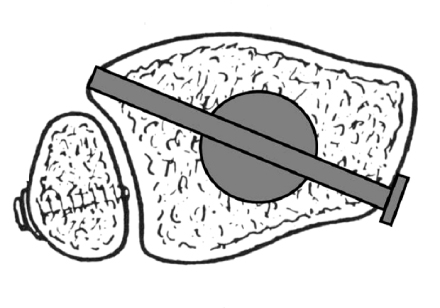
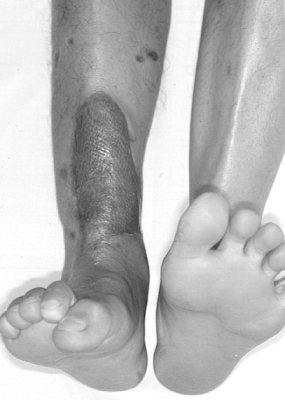
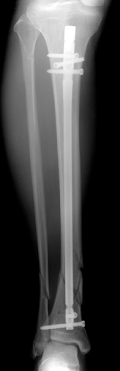
Fig. 1
Correction of angular malalignment using Poller screws.
Fig. 2
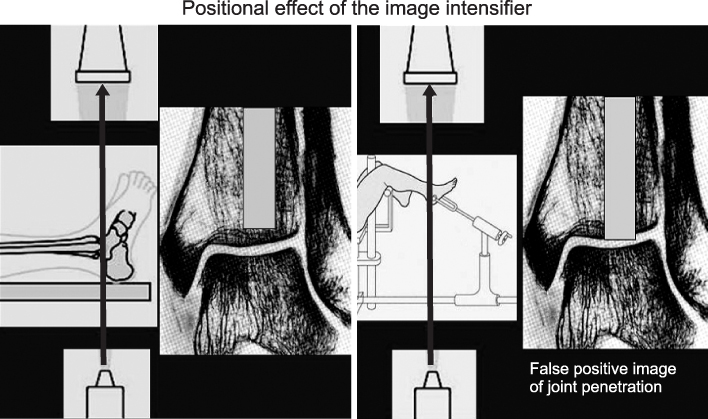
Image intensifier must be placed perpendicular to the ankle joint.
Fig. 3
Distal interlocking screws must be inserted from postero-medial cortex to antero-lateral one in order to spare the distal tibio-fibular syndesmosis.
Fig. 4
Undisplaced articular fragments are fixed by three cannulated screws before distal tibial nailing. These screws should not obliterate the nail passage.
Fig. 5
Unstable distal fibular fracture and displaced medial malleolar fracture are fixed before distal tibial nailing.
Fig. 6
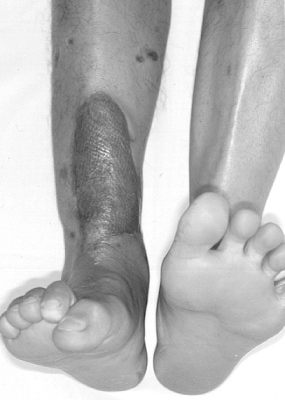
Claw toe deformity (clawing of great toe and lesser toes during dorsiflexion of ankle joint) is caused by compartment syndrome of posterior leg or adhesion of long flexor tendon to healing callus.
Fig. 7
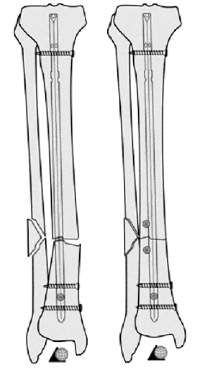
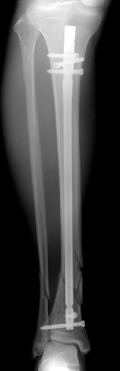
Parallelism between distal interlocking screws and tibial distal articular surface is an important tip to avoid axial malalignment in distal tibial nailing.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Fig. 6
Fig. 7
Distal Tibial Nailing

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

