Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 26(2); 2013 > Article
-
Original Article
- The Result Treated by Open Reduction and Internal Fixation with Minimally Invasive Technique in Joint Depressive Calcaneal Fracture
- Sueng-Hwan Jo, M.D., Jun-Young Lee, M.D., Sang-Ho Ha, M.D., Sung-Won Cho, M.D., Sang-Ha Park, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2013;26(2):126-132.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.2.126
Published online: April 22, 2013
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Jun-Young Lee, M.D. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chosun University Hospital, 365 Pilmun-daero, Dong-gu, Gwangju 501-717, Korea. Tel: 82-62-220-3147, Fax: 82-62-226-3379, leejy88@chosun.ac.kr
• Received: July 19, 2012 • Revised: September 17, 2012 • Accepted: January 14, 2013
Copyright © 2013 The Korean Fracture Society
- 624 Views
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- To evaluate the short term follow-up results of minimally invasive technique in the management of Sanders type II, III, and IV joint depressive calcaneal fracture.
-
Materials and Methods
- Between May 2008 and May 2011, we studied 17 cases undergoing treatment with minimally invasive technique with modified sinus tarsi approach for Sanders II, III, and IV joint depressive intra-articular calcaneal fracture and were followed up for more than 1 year. We evaluated the treatment result by assessing the radiologic parameters (Böhler angle, Gissane angle, and calcaneal height/width/length) and clinical outcomes (American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society [AOFAS] score and visual analog scale [VAS]) and investigating the complication.
-
Results
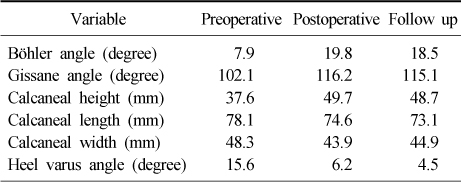
- Radiological results improved from 7.9° to 19.8° in the Böhler angle after the operation. Satisfactory results were obtained in clinical assessment with average AOFAS score of 82.45 and the average VAS score of 3.94. We experienced 3 cases of complications, 1 case of superficial wound infection and radiologic findings of subtalar arthritis in 2 cases.
-
Conclusion
- Minimally invasive technique may be a useful alternative surgical method in the management of Sanders type II, III, and IV joint depressive calcaneal fracture that cannot adopt extensile approach, which enable to obtain good radiological and clinical results.
- 1. Abidi NA, Dhawan S, Gruen GS, Vogt MT, Conti SF. Wound-healing risk factors after open reduction and internal fixation of calcaneal fractures. Foot Ankle Int, 1998;19:856-861.PDF
- 2. Allon SM, Mears DC. Three dimensional analysis of calcaneal fractures. Foot Ankle, 1991;11:254-263.PDF
- 3. Barei DP, Bellabarba C, Sangeorzan BJ, Benirschke SK. Fractures of the calcaneus. Orthop Clin North Am, 2002;33:263-285.
- 4. Carr JB. Surgical treatment of intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a review of small incision approaches. J Orthop Trauma, 2005;19:109-117.
- 5. Chae SU, Yang JH. Minimally-invasive percutaneous screw fixation of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc, 2010;14:73-78.
- 6. Chung HJ, Ahn JK, Bae SY, Jung H. Operative treatment of intraarticular calcaneal fractures using extensile lateral approach. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc, 2009;13:60-67.
- 7. Ebraheim NA, Elgafy H, Sabry FF, Freih M, Abou-Chakra IS. Sinus tarsi approach with trans-articular fixation for displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. Foot Ankle Int, 2000;21:105-113.PDF
- 8. Essex-lopresti P. The mechanism, reduction technique, and results in fractures of the os calcis. Br J Surg, 1952;39:395-419.PDF
- 9. Fernandez DL, Koella C. Combined percutaneous and "minimal" internal fixation for displaced articular fractures of the calcaneus. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1993;(290):108-116.
- 10. Folk JW, Starr AJ, Early JS. Early wound complications of operative treatment of calcaneus fractures: analysis of 190 fractures. J Orthop Trauma, 1999;13:369-372.
- 11. Freund M, Thomsen M, Hohendorf B, Zenker W, Heller M. Optimized preoperative planning of calcaneal fractures using spiral computed tomography. Eur Radiol, 1999;9:901-906.PDF
- 12. Guyer BH, Levinsohn EM, Fredrickson BE, Bailey GL, Formikell M. Computed tomography of calcaneal fractures: anatomy, pathology, dosimetry, and clinical relevance. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 1985;145:911-919.
- 13. Harvey EJ, Grujic L, Early JS, Benirschke SK, Sangeorzan BJ. Morbidity associated with ORIF of intra-articular calcaneus fractures using a lateral approach. Foot Ankle Int, 2001;22:868-873.PDF
- 14. Kocis J, Stoklas J, Kalandra S, Cizmár I, Pilnỳ J. Intra-articular calcaneal fractures. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech, 2006;73:164-168.
- 15. Kundel K, Funk E, Brutscher M, Bickel R. Calcaneal fractures: operative versus nonoperative treatment. J Trauma, 1996;41:839-845.
- 16. Leung KS, Yuen KM, Chan WS. Operative treatment of displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneum. Medium-term results. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1993;75:196-201.PDF
- 17. Meraj A, Zahid M, Ahmad S. Management of intra-articular calcaneal fractures by minimally invasive sinus tarsi approach-early results. Malay Orthop J, 2012;6:13-17.
- 18. O'Farrell DA, O'Byrne JM, McCabe JP, Stephens MM. Fractures of the os calcis: improved results with internal fixation. Injury, 1993;24:263-265.
- 19. Paley D, Hall H. Intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. A critical analysis of results and prognostic factors. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1993;75:342-354.
- 20. Palmer I. The mechanism and treatment of fractures of the calcaneus; open reduction with the use of cancellous grafts. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1948;30A:2-8.
- 21. Rammelt S, Amlang M, Barthel S, Zwipp H. Minimally-invasive treatment of calcaneal fractures. Injury, 2004;35:Suppl 2. SB55-SB63.
- 22. Randle JA, Kreder HJ, Stephen D, Williams J, Jaglal S, Hu R. Should calcaneal fractures be treated surgically? A meta-analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 2000;(377):217-227.
- 23. Sanders R. Displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2000;82:225-250.
- 24. Sanders R, Gregory P. Operative treatment of intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. Orthop Clin North Am, 1995;26:203-214.
- 25. Sangeorzan BJ, Benirschke SK, Carr JB. Surgical management of fractures of the os calcis. Instr Course Lect, 1995;44:359-370.
- 26. Shigemasa C, Abe K, Taniguchi S, et al. The influence of diabetes mellitus on thyrotropin response to thyrotropin-releasing hormone in untreated acromegalic patients. J Endocrinol Invest, 1988;11:231-237.PDF
- 27. Thordarson DB, Krieger LE. Operative vs: nonoperative treatment of intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus: a prospective randomized trial. Foot Ankle Int, 1996;17:2-9.PDF
- 28. Zwipp H, Rammelt S, Barthel S. Calcaneal fractures--the most frequent tarsal fractures. Ther Umsch, 2004;61:435-450.
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
(A) Exposure of posterior facet using the sinus tarsi approach with 3-5 cm size skin incision.
(B) Intra-operative lateral fluoroscope image shows posterior facet reduction using schantz-pin.
(C) Lateral fluoroscope image shows stabilized posterior facet fragment with a 4.5 cannulated screw.
(D) Other fragment fixation with a 6.5 cannulated screw.
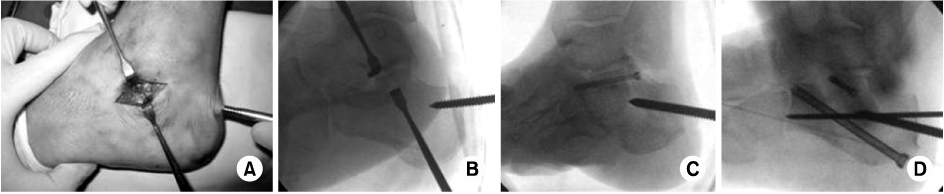

Fig. 2Methods of measurement of Gissane angle, calcaneal length (A), Böhler angle, calcaneal height (B) and calcaneal width and heel varus angle (C).
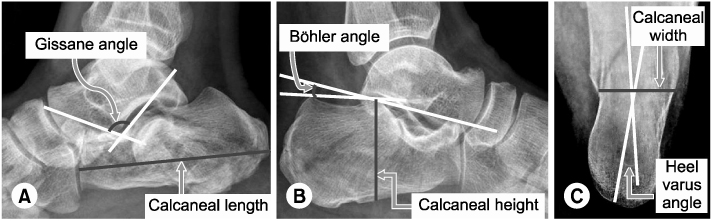

Fig. 3
(A, B) Preoperative lateral radiograph and computed tomography (CT) image of a 40 year old male patient shows Sanders IIIab type joint depression calcaneal fracture. Preoperative Böhler angle is 2.2 degrees and Gissane angle is 108.8 degrees.
(C) Postoperative radiograph shows increased Böhler angle to 15.8 degrees and Gissane angle to 116.1 degrees.
(D, E) After twelve months, a follow-up lateral radiograph shows Böhler angle 14.6 degrees and CT image shows complete bone union and good alignment of subtalar joint.
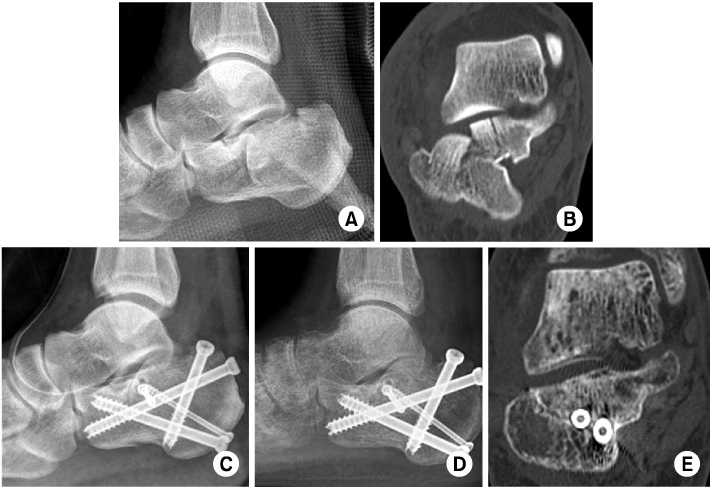

Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Outcomes of Minimally Invasive Surgery in Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures: Sanders Type III, Joint Depressive Type Calcaneal Fracture
Je Hong Ryu, Jun Young Lee, Kang Yeol Ko, Sung Min Jo, Hyoung Tae Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2023; 36(3): 85. CrossRef - Towards uniformity in communication and a tailor-made treatment for displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures
Tim Schepers
International Orthopaedics.2014; 38(3): 663. CrossRef
The Result Treated by Open Reduction and Internal Fixation with Minimally Invasive Technique in Joint Depressive Calcaneal Fracture

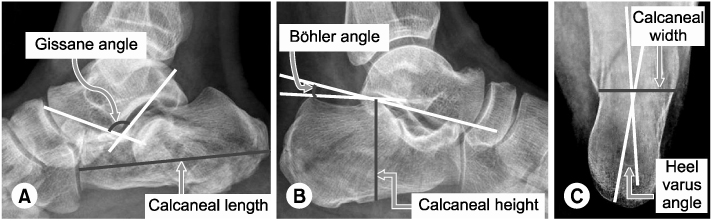
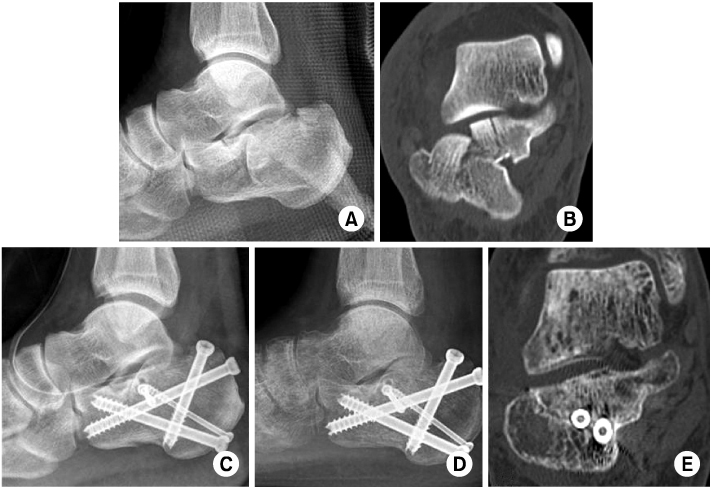
Fig. 1
(A) Exposure of posterior facet using the sinus tarsi approach with 3-5 cm size skin incision.
(B) Intra-operative lateral fluoroscope image shows posterior facet reduction using schantz-pin.
(C) Lateral fluoroscope image shows stabilized posterior facet fragment with a 4.5 cannulated screw.
(D) Other fragment fixation with a 6.5 cannulated screw.
Fig. 2
Methods of measurement of Gissane angle, calcaneal length (A), Böhler angle, calcaneal height (B) and calcaneal width and heel varus angle (C).
Fig. 3
(A, B) Preoperative lateral radiograph and computed tomography (CT) image of a 40 year old male patient shows Sanders IIIab type joint depression calcaneal fracture. Preoperative Böhler angle is 2.2 degrees and Gissane angle is 108.8 degrees.
(C) Postoperative radiograph shows increased Böhler angle to 15.8 degrees and Gissane angle to 116.1 degrees.
(D, E) After twelve months, a follow-up lateral radiograph shows Böhler angle 14.6 degrees and CT image shows complete bone union and good alignment of subtalar joint.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
The Result Treated by Open Reduction and Internal Fixation with Minimally Invasive Technique in Joint Depressive Calcaneal Fracture
Dermographic Data of the Patients
F/U: Follow up.
Dermographic Data of the Patients Classified by Cause and Accompanied Injury
The Result of Radiologic Assessment
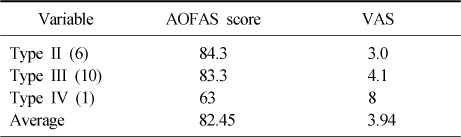
The Result of Clinical Assessment of AOFAS Score and VAS
AOFAS: American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society, VAS: Visual Analog Scale.
Table 1
Dermographic Data of the Patients
F/U: Follow up.
Table 2
Dermographic Data of the Patients Classified by Cause and Accompanied Injury
Table 3
The Result of Radiologic Assessment
Table 4
The Result of Clinical Assessment of AOFAS Score and VAS
AOFAS: American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society, VAS: Visual Analog Scale.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

