Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 27(1); 2014 > Article
-
Original Article
- The Clinical Results of Opening Wedge Osteotomy in the Volarly Malunited Distal Radius
- Seoung Joon Lee, M.D., Ph.D., Jin Ho Choi, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2014;27(1):29-35.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.1.29
Published online: January 17, 2014
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Seoung Joon Lee, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Konkuk University Medical Center, 120-1 Neungdong-ro, Gwangjin-gu, Seoul 143-729, Korea. Tel: 82-2-2030-7360, Fax: 82-2-2030-7369, lsjmd@naver.com
• Received: February 20, 2013 • Revised: July 6, 2013 • Accepted: October 12, 2013
Copyright © 2014 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 442 Views
- 3 Download
Abstract
-
Purpose
- To report the clinical results of opening wedge osteotomy graft in the volarly malunited distal radius.
-
Materials and Methods
- Ten patients with volarly malunited distal radius fractures treated by opening wedge osteotomy were included in this study. Grip power, range of motion of the wrist, radiographic parameter and Mayo wrist scores were retrospectively evaluated.
-
Results
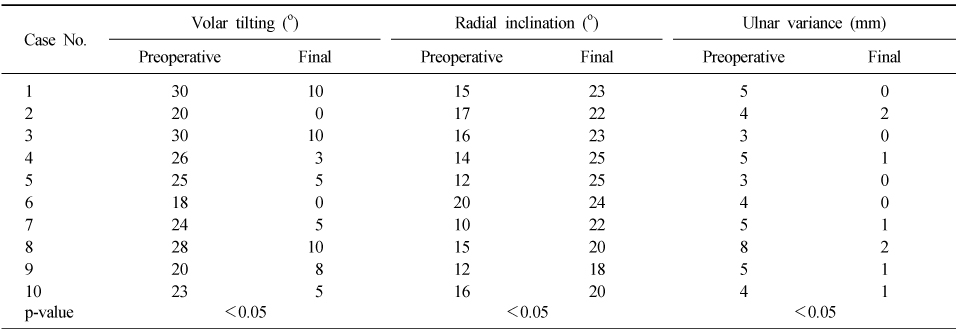
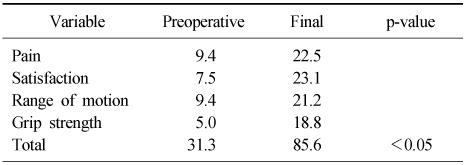
- At the final follow-up, the rotation of the forearm, the range of motion of wrist, and the grip power were improved. The average radial inclination improved to 22.2°, the average volar tilting improved to 5.6°, and the average ulnar variance improved to 0.8 mm. The average Mayo wrist score was improved to 85.6.
-
Conclusion
- Opening wedge osteotomy for volarly malunited distal radius was considered as one of the good treatments to restore anatomy of the distal radius and distal radioulnar joint and also to improve the function of the wrist joint.
- 1. Adams BD. Effects of radial deformity on distal radioulnar joint mechanics. J Hand Surg Am, 1993;18:492-498.Article
- 2. Ambrose L, Posner MA. Biplanar osteotomy for the treatment of malunited colles' fractures, In: Presented at the 43rd Annual Meeting of the American Society for Surgery of the Hand; Sep. 14-17, 1998; Baltimore. Baltimore, American Society for Surgery of the Hand; 1998.Article
- 3. Bronstein AJ, Trumble TE, Tencer AF. The effects of distal radius fracture malalignment on forearm rotation: a cadaveric study. J Hand Surg Am, 1997;22:258-262.Article
- 4. Brown JN, Bell MJ. Distal radial osteotomy for malunion of wrist fractures in young patients. J Hand Surg Br, 1994;19:589-593.ArticlePDF
- 5. Cooney WP 3rd, Dobyns JH, Linscheid RL. Complications of Colles' fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1980;62:613-619.Article
- 6. Fernandez DL. Radial osteotomy and Bowers arthroplasty for malunited fractures of the distal end of the radius. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1988;70:1538-1551.Article
- 7. Jupiter JB, Ruder J, Roth DA. Computer-generated bone models in the planning of osteotomy of multidirectional distal radius malunions. J Hand Surg Am, 1992;17:406-415.Article
- 8. Kanterewicz E, Yañez A, Pérez-Pons A, Codony I, Del Rio L, Díez-Pérez A. Association between Colles' fracture and low bone mass: age-based differences in postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int, 2002;13:824-888.ArticlePDF
- 9. Kazuki K, Kusunoki M, Shimazu A. Pressure distribution in the radiocarpal joint measured with a densitometer designed for pressure-sensitive film. J Hand Surg Am, 1991;16:401-408.Article
- 10. Ladd AL, Huene DS. Reconstructive osteotomy for malunion of the distal radius. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1996;(327):158-171.Article
- 11. Linder L, Stattin J. Malunited fractures of the distal radius with volar angulation: corrective osteotomy in 6 cases using the volar approach. Acta Orthop Scand, 1996;67:179-181.Article
- 12. McQueen M, Caspers J. Colles fracture: does the anatomical result affect the final function? J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1988;70:649-651.ArticlePDF
- 13. Pogue DJ, Viegas SF, Patterson RM, et al. Effects of distal radius fracture malunion on wrist joint mechanics. J Hand Surg Am, 1990;15:721-727.Article
- 14. Prommersberger KJ, Froehner SC, Schmitt RR, Lanz UB. Rotational deformity in malunited fractures of the distal radius. J Hand Surg Am, 2004;29:110-115.Article
- 15. Prommersberger KJ, Van Schoonhoven J, Lanz UB. Outcome after corrective osteotomy for malunited fractures of the distal end of the radius. J Hand Surg Br, 2002;27:55-60.ArticlePDF
- 16. Sato K, Nakamura T, Iwamoto T, Toyama Y, Ikegami H, Takayama S. Corrective osteotomy for volarly malunited distal radius fracture. J Hand Surg Am, 2009;34:27-33.Article
- 17. Shea K, Fernandez DL, Jupiter JB, Martin C Jr. Corrective osteotomy for malunited, volarly displaced fractures of the distal end of the radius. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1997;79:1816-1826.Article
- 18. Taleisnik J, Watson HK. Midcarpal instability caused by malunited fractures of the distal radius. J Hand Surg Am, 1984;9:350-357.Article
- 19. Thivaios GC, McKee MD. Sliding osteotomy for deformity correction following malunion of volarly displaced distal radial fractures. J Orthop Trauma, 2003;17:326-333.Article
- 20. Wada T, Isogai S, Kanaya K, Tsukahara T, Yamashita T. Simultaneous radial closing wedge and ulnar shortening osteotomies for distal radius malunion. J Hand Surg Am, 2004;29:264-272.Article
REFERENCES
Fig. 1Intraoperative photographs show surgical approach (A), wedge osteotomy and wedge shaped iliac bone (B, C, D), and plate fixation (E).
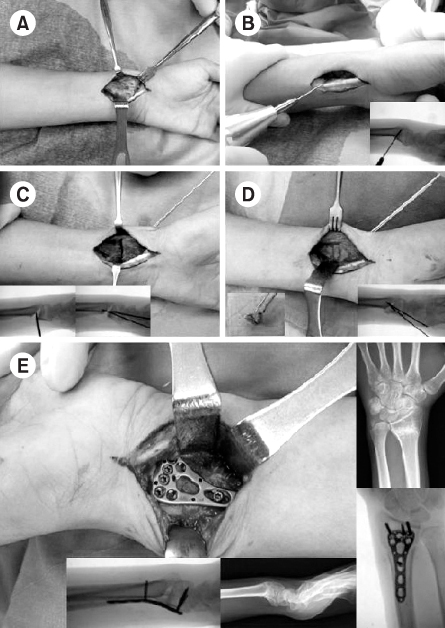

Fig. 2
(A, B) Initial simple radiographs show unstable distal radius fracture. (C, D) Simple radiographs after external fixation and K-wire fixation show radial inclination of 20°, volar tilt 5°, and neutral ulnar variance. (E, F) Simple radiographs after removal of external fixation and K-wire show the volarly malunited distal radius with volar tilt of 25°, 12° radial inclination, 3 mm ulnar positive variance. (G, H) Simple radiographs after open wedge osteotomy show a good alignment of distal radius with volar tilt of 5°, 25° radial inclination, 0 mm ulnar variance.
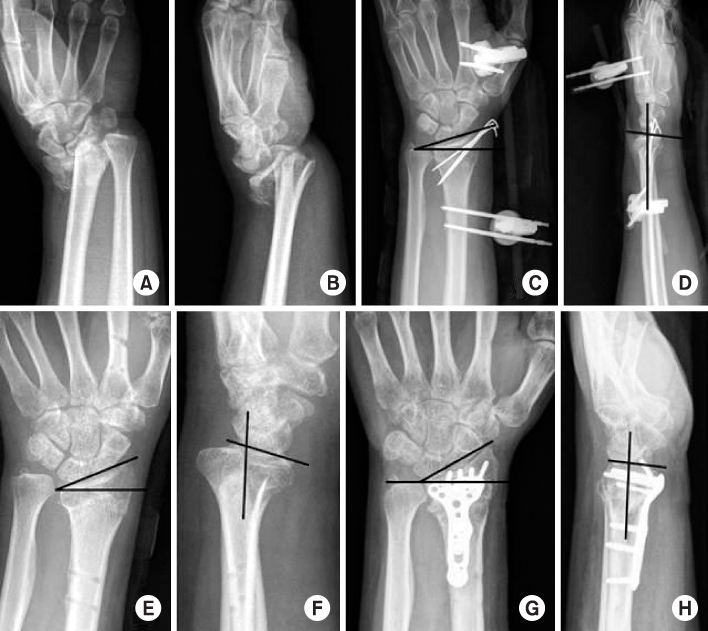

Fig. 3
(A, B) Initial simple radiographs show Colles' fracture with ulnar styloid fracture. (C, D) Simple radiographs after closed reduction and splinting show a good alignment of distal radius. (E, F) At 2 months after trauma, simple radiographs show volarly displaced distal radius fracture with volar tilt of 30°, 15° radial inclination, 5 mm ulnar positive variance. (G, H) Simple radiographs after open wedge osteotomy show a good alignment of distal radius with volar tilt of 10°, 23° radial inclination, 0 mm ulnar variance.
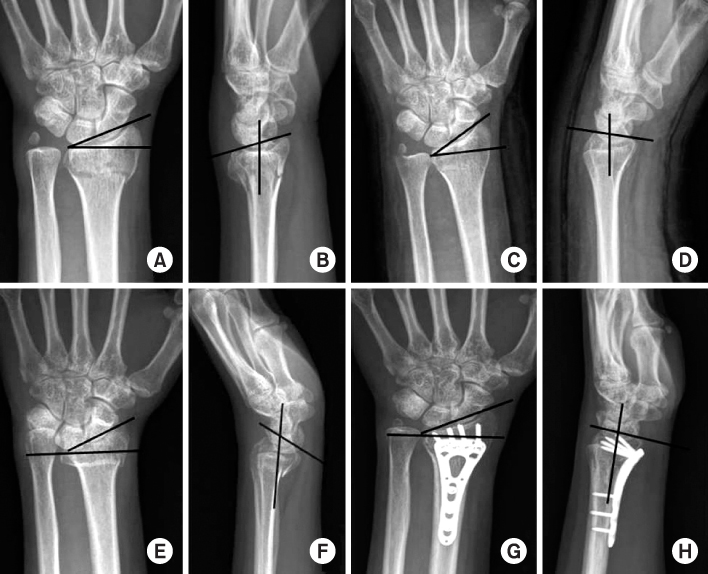

Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

The Clinical Results of Opening Wedge Osteotomy in the Volarly Malunited Distal Radius
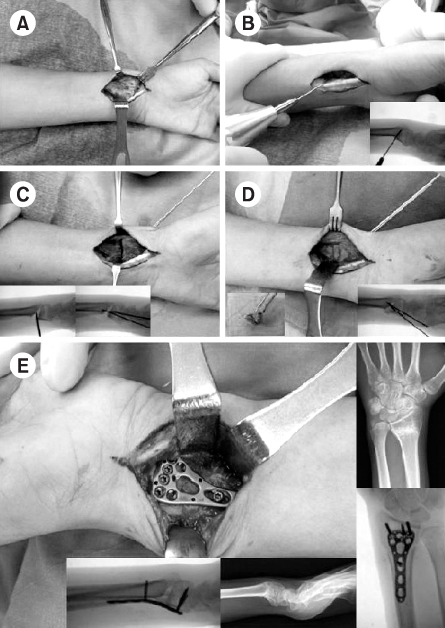
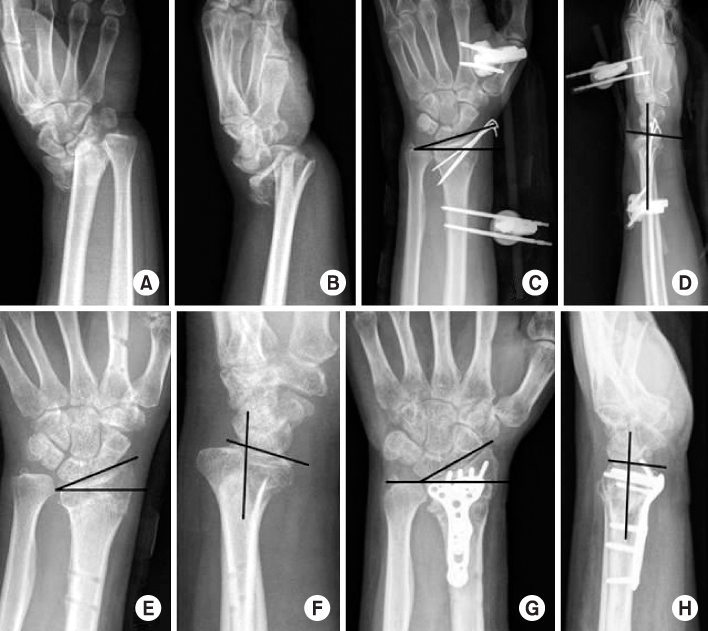
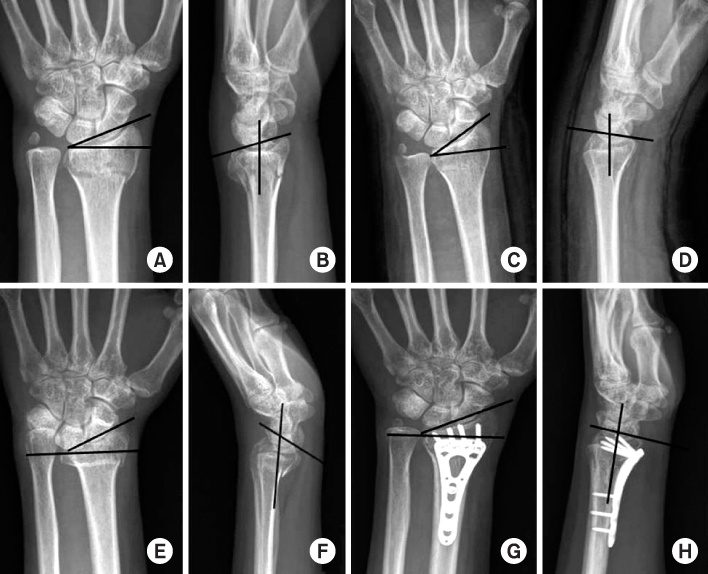
Fig. 1
Intraoperative photographs show surgical approach (A), wedge osteotomy and wedge shaped iliac bone (B, C, D), and plate fixation (E).
Fig. 2
(A, B) Initial simple radiographs show unstable distal radius fracture. (C, D) Simple radiographs after external fixation and K-wire fixation show radial inclination of 20°, volar tilt 5°, and neutral ulnar variance. (E, F) Simple radiographs after removal of external fixation and K-wire show the volarly malunited distal radius with volar tilt of 25°, 12° radial inclination, 3 mm ulnar positive variance. (G, H) Simple radiographs after open wedge osteotomy show a good alignment of distal radius with volar tilt of 5°, 25° radial inclination, 0 mm ulnar variance.
Fig. 3
(A, B) Initial simple radiographs show Colles' fracture with ulnar styloid fracture. (C, D) Simple radiographs after closed reduction and splinting show a good alignment of distal radius. (E, F) At 2 months after trauma, simple radiographs show volarly displaced distal radius fracture with volar tilt of 30°, 15° radial inclination, 5 mm ulnar positive variance. (G, H) Simple radiographs after open wedge osteotomy show a good alignment of distal radius with volar tilt of 10°, 23° radial inclination, 0 mm ulnar variance.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
The Clinical Results of Opening Wedge Osteotomy in the Volarly Malunited Distal Radius
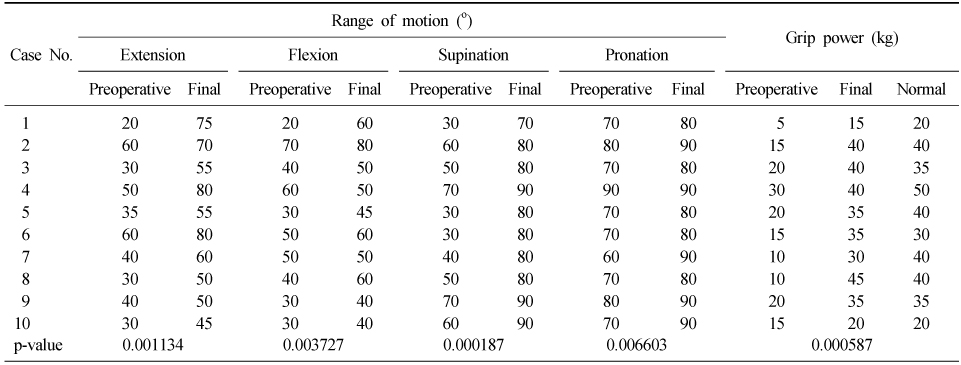
The Preoperative and Postoperative Range of Motion and Grip Power
Preoperative and Postoperative Radiological Values
Mayo Wrist Score
Table 1
The Preoperative and Postoperative Range of Motion and Grip Power
Table 2
Preoperative and Postoperative Radiological Values
Table 3
Mayo Wrist Score

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

