Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 26(4); 2013 > Article
-
Original Article
- The Treatment of Subtrochanteric Fractures with Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation
- Chi Hyoung Pak, M.D., Sang Hong Lee, M.D., Sang Ho Ha, M.D., Gwang Chul Lee, M.D., Kyoung Chul Song, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2013;26(4):284-291.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.4.284
Published online: October 18, 2013
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Sang Hong Lee, M.D. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chosun University Hospital, 365 Pilmun-daero, Dong-gu, Gwangju 501-717, Korea. Tel: 82-62-220-3147, Fax: 82-62-226-3379, shalee@chosun.ac.kr
Copyright © 2013 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 325 Views
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study was to analyze the results of treating subtrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA).
-
Materials and Methods
- Twenty five consecutive patients diagnosed with subtrochanteric femoral fractures underwent intramedullary fixation using PFNA and followed-up for over 12 months. According to the Seinsheimer's classification, there were 2 type IIA, 9 type IIB, 2 type IIIA, 3 type IV and 9 type V. According to the AO classification, there were 10 type A, 9 type B and 6 type C. There were 16 cases of closed reduction group and 9 cases of limited open reduction group. Retrospectively, radiological outcomes were assessed at the union period, change of neck shaft angle, tip-apex distance, Cleveland index, sliding of lag screw and complication.
-
Results
- Union was achieved in 23 of 25 cases, over an average of 17 weeks. Limb length shortening below 2 cm occurred in 7 patients. The Cleveland index was shown in 80% of 5, 6, 8 and 9 zone; the tip apex distance was 19.6 mm; the mean sliding distance was 4.4 mm; and the mean change of femur neck and shaft angle was varus 3 degree at the final follow-up. Complications included 3 cases of delayed union and 2 cases of nonunion.
-
Conclusion
- With its early bony union, ambulation, rehabilitation and low complication, PFNA is a useful and reliable choice for the treatment of subtrochanteric fractures of the femur. Limited open reduction and additional fixation such as cable grip are recommended if it is difficult to obtain anatomical reduction by closed reduction.
The present study was supported by grants from the Clinical Medicine Research Institute at Chosun University Hospital.
- 1. Afsari A, Liporace F, Lindvall E, Infante A Jr, Sagi HC, Haidukewych GJ. Clamp-assisted reduction of high subtrochanteric fractures of the femur: surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2010;92:Suppl 1 Pt 2. 217-225.PubMed
- 2. Boopalan PR, Jepegnanam TS, Nithyananth M, Venkatesh K, Cherian VM. Functional outcome of biological condylar blade plating of subtrochanteric fractures. J Orthop Sci, 2012;17:567-573.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Borens O, Wettstein M, Kombot C, Chevalley F, Mouhsine E, Garofalo R. Long gamma nail in the treatment of subtrochanteric fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 2004;124:443-447.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 4. Byun YS. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis, MIPO. J Korean Fract Soc, 2007;20:99-114.Article
- 5. Choi JS, Moon DH, Noh YT. The treatment of subtrochanteric fracture with cephallomedually nail: minimal incision and lowman clamp assisted reduction. J Korean Fract Soc, 2011;24:301-306.Article
- 6. Chung PH, Kang S, Kim JP, Kim YS, Lee HM, Huh DJ. Treatment of unstable pertrochanteric fractures with a long intramedullary nail. Hip Pelvis, 2013;25:51-56.Article
- 7. Fielding JW, Cochran GV, Zickel RE. Biomechanical characteristics and surgical management of subtrochanteric fractures. Orthop Clin North Am, 1974;5:629-650.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Forte ML, Virnig BA, Kane RL, et al. Geographic variation in device use for intertrochanteric hip fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2008;90:691-699.ArticlePubMed
- 9. French BG, Tornetta P 3rd. Use of an interlocked cephalomedullary nail for subtrochanteric fracture stabilization. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1998;(348):95-100.Article
- 10. Froimson AI. Treatment of comminuted subtrochanteric fractures of the femur. Surg Gynecol Obstet, 1970;131:465-472.PubMed
- 11. Garg B, Marimuthu K, Kumar V, Malhotra R, Kotwal PP. Outcome of short proximal femoral nail antirotation and dynamic hip screw for fixation of unstable trochanteric fractures. A randomised prospective comparative trial. Hip Int, 2011;21:531-536.PubMed
- 12. Haidukewych GJ, Berry DJ. Nonunion of fractures of the subtrochanteric region of the femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 2004;(419):185-188.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Herrera A, Domingo J, Martinez A. Results of osteosynthesis with the ITST nail in fractures of the trochanteric region of the femur. Int Orthop, 2008;32:767-772.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 14. Jiang LS, Shen L, Dai LY. Intramedullary fixation of subtrochanteric fractures with long proximal femoral nail or long gamma nail: technical notes and preliminary results. Ann Acad Med Singapore, 2007;36:821-826.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Katz S, Ford AB, Moskowitz RW, Jackson BA, Jaffe MW. Studies of illness in the aged. The index of adl: a standardized measure of biological and psychosocial function. JAMA, 1963;185:914-919.ArticlePubMed
- 16. Kennedy MT, Mitra A, Hierlihy TG, Harty JA, Reidy D, Dolan M. Subtrochanteric hip fractures treated with cerclage cables and long cephalomedullary nails: a review of 17 consecutive cases over 2 years. Injury, 2011;42:1317-1321.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Kim JH, Lee SH, Lee KC, Cho SW. The PFNA nail for pertrochanteric fracture of the femur without fracture table. J Korean Fract Soc, 2011;24:217-222.Article
- 18. Kinast C, Bolhofner BR, Mast JW, Ganz R. Subtrochanteric fractures of the femur. Results of treatment with the 95 degrees condylar blade-plate. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1989;(238):122-130.
- 19. Koch JC. The laws of bone architecture. Am J Anat, 1917;21:117-298.Article
- 20. Koval KJ, Skovron ML, Aharonoff GB, Meadows SE, Zuckerman JD. Ambulatory ability after hip fracture. A prospective study in geriatric patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1995;(310):150-159.
- 21. Kulkarni SS, Moran CG. Results of dynamic condylar screw for subtrochanteric fractures. Injury, 2003;34:117-122.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Macheras GA, Koutsostathis SD, Galanakos S, Kateros K, Papadakis SA. Does PFNA II avoid lateral cortex impingement for unstable peritrochanteric fractures? Clin Orthop Relat Res, 2012;470:3067-3076.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 23. Micic ID, Mitkovic MB, Park IH, et al. Treatment of subtrochanteric femoral fractures using Selfdynamisable internal fixator. Clin Orthop Surg, 2010;2:227-231.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 24. Park J, Yang KH. Correction of malalignment in proximal femoral nailing--Reduction technique of displaced proximal fragment. Injury, 2010;41:634-638.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Pelet S, Arlettaz Y, Chevalley F. Osteosynthesis of perand subtrochanteric fractures by blade plate versus gamma nail. A randomized prospective study. Swiss Surg, 2001;7:126-133.PubMed
- 26. Saini P, Kumar R, Shekhawat V, Joshi N, Bansal M, Kumar S. Biological fixation of comminuted subtrochanteric fractures with proximal femur locking compression plate. Injury, 2013;44:226-231.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Shukla S, Johnston P, Ahmad MA, Wynn-Jones H, Patel AD, Walton NP. Outcome of traumatic subtrochanteric femoral fractures fixed using cephalo-medullary nails. Injury, 2007;38:1286-1293.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Simmermacher RK, Ljungqvist J, Bail H, et al. The new proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) in daily practice: results of a multicentre clinical study. Injury, 2008;39:932-939.ArticlePubMed
- 29. Strauss E, Frank J, Lee J, Kummer FJ, Tejwani N. Helical blade versus sliding hip screw for treatment of unstable intertrochanteric hip fractures: a biomechanical evaluation. Injury, 2006;37:984-989.PubMed
- 30. Windolf J, Hollander DA, Hakimi M, Linhart W. Pitfalls and complications in the use of the proximal femoral nail. Langenbecks Arch Surg, 2005;390:59-65.ArticlePubMedPDF
REFERENCES
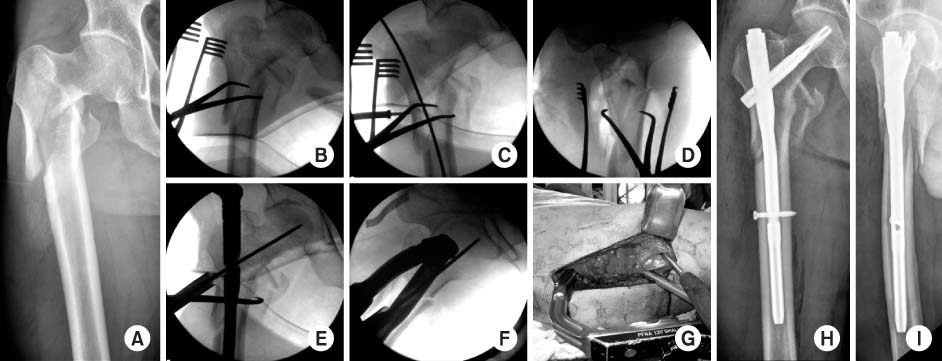
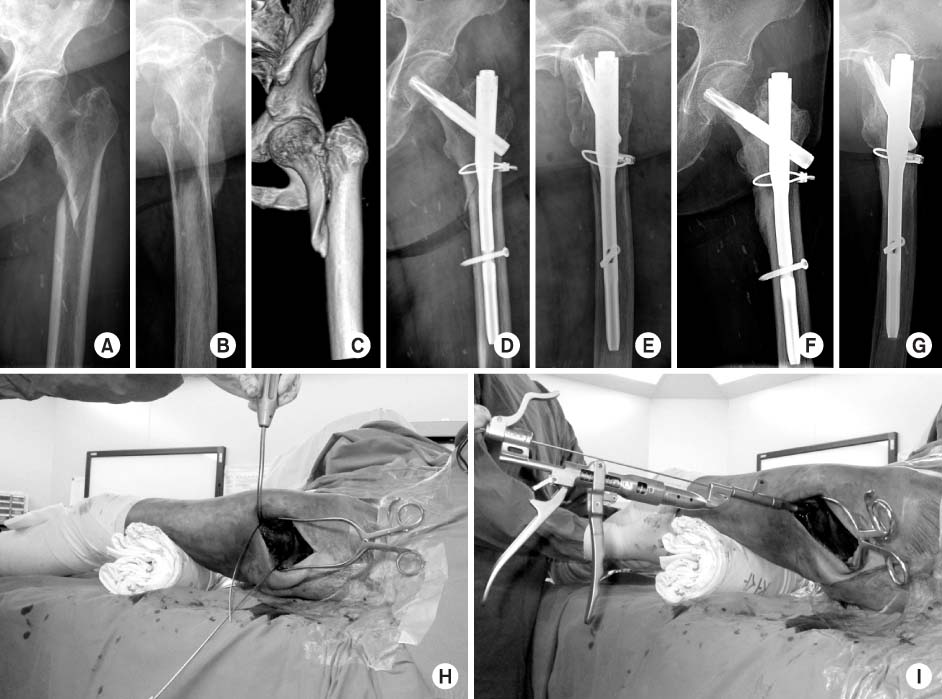
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Subtrochanteric Fracture Reduction during Intramedullary Nailing: Technical Note
Gyu Min Kong
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2019; 32(2): 107. CrossRef
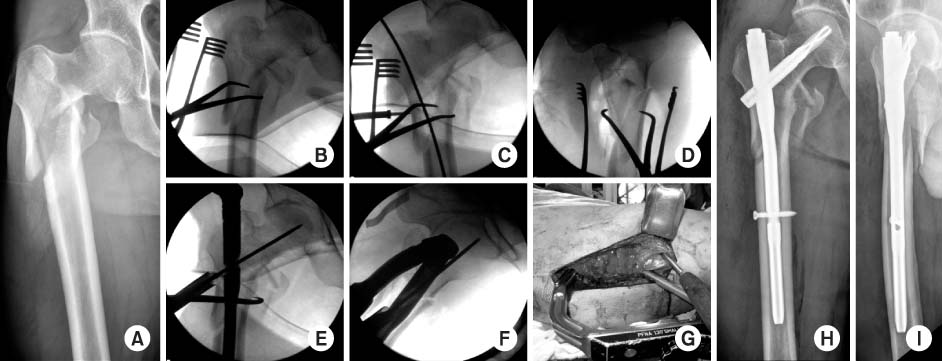
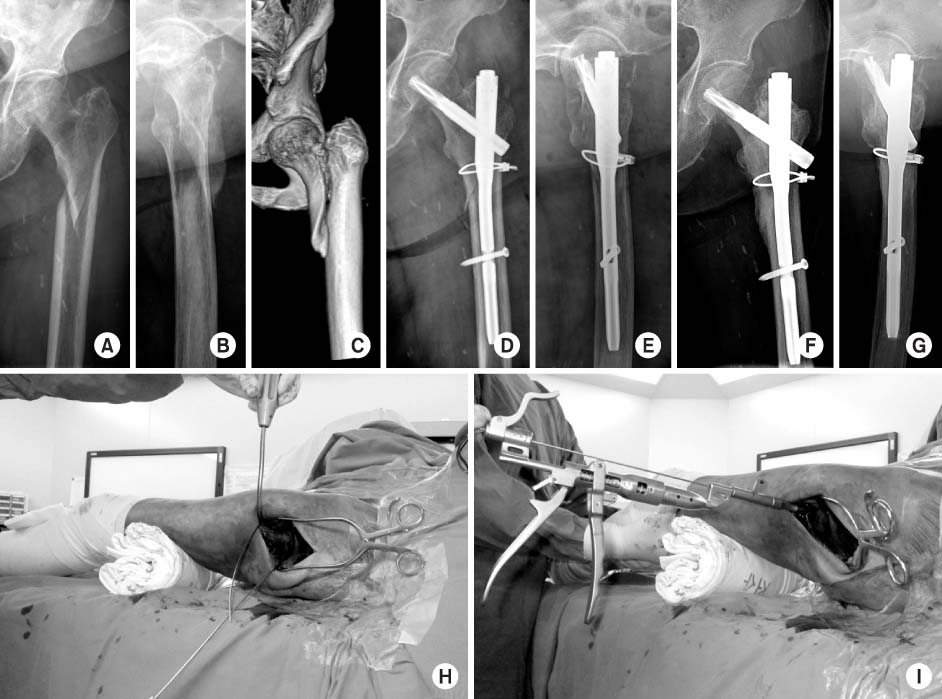
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Katz Activities of Daily Living Index
Independence: 1, Dependence: 0.
Koval Score
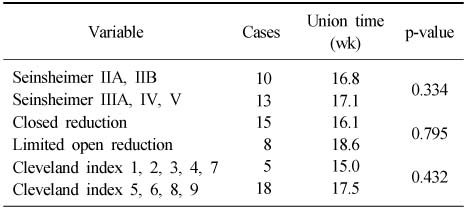
Comparison of Results for Comminution, Reduction Method, Cleveland Index
Nonunion: 2 cases.
Independence: 1, Dependence: 0.
Nonunion: 2 cases.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA


 Cite
Cite

