Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 28(1); 2015 > Article
-
Original Article
- Treatment of Fractures of the Distal Radius Using Variable-Angle Volar Locking Plate
- Jae-Cheon Sim, M.D., Sung-Sik Ha, M.D., Ki-Do Hong, M.D., Tae-Ho Kim, M.D., Min-Chul Sung, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2015;28(1):46-52.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.1.46
Published online: January 20, 2015
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Sahmyook Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Sung-Sik Ha, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Sahmyook Medical Center, 82 Mangu-ro, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul 130-711, Korea. Tel: 82-2-2210-3324, Fax: 82-2-2212-2673, crash1401@naver.com
• Received: October 6, 2014 • Revised: November 26, 2014 • Accepted: December 5, 2014
Copyright © 2015 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 472 Views
- 3 Download
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study is to evaluate outcome of variable-angle volar locking plate for treatment of distal radius fractures.
-
Materials and Methods
- We retrospectively analyzed the results in 45 cases treated by variable-angle volar locking plate. We evaluated the clinical results according to the Mayo wrist performance scoring system and radiographic results.
-
Results
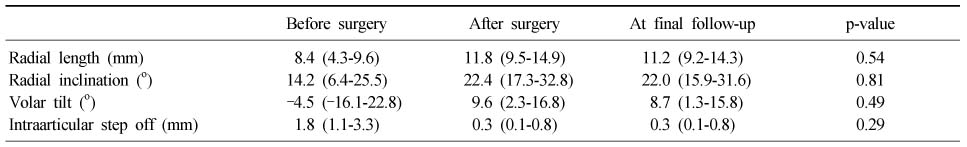
- All cases had bony union. The mean Mayo wrist performance scoring system was 84.8. Between preoperative and immediate postoperative radiographic measurement, the mean radial length improved from 8.4 to 11.8 mm, radial inclination from 14.2° to 22.4°, volar tilt from -4.5° to 9.6°, and intraarticular step-off from 1.8 to 0.3 mm (p<0.05). Between immediate postoperative and latest follow-up radiographic measurements, the mean loss of radial length measured 0.8 mm, radial inclination 0.4°, and volar tilt 0.9° (p>0.05). All cases showed bone union with no evidence of malunion, nonunion, or metal failure.
-
Conclusion
- Treatment of distal radius fractures using variable angle volar locking plate showed satisfactory outcomes. It is a good option to obtain stable fixation without significant loss of reduction.
- 1. Moon ES, Kim MS, Kong IK. The amount and related factors of reduction loss in distal radius fracture after treatment by Kapandji technique. J Korean Fract Soc, 2007;20:252-259.Article
- 2. Cha SD, Park JH, Kim HS, et al. Comparative analysis of the results of fixed-angle versus variable-angle volar locking plate for distal radius fracture fixation. J Korean Fract Soc, 2012;25:197-202.Article
- 3. MacDermid JC, Roth JH, Richards RS. Pain and disability reported in the year following a distal radius fracture: a cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord, 2003;4:24. ArticlePDF
- 4. Papadonikolakis A, Shen J, Garrett JP, Davis SM, Ruch DS. The effect of increasing distraction on digital motion after external fixation of the wrist. J Hand Surg Am, 2005;30:773-779.Article
- 5. Leung F, Zhu L, Ho H, Lu WW, Chow SP. Palmar plate fixation of AO type C2 fracture of distal radius using a locking compression plate: a biomechanical study in a cadaveric model. J Hand Surg Br, 2003;28:263-266.ArticlePDF
- 6. Trumble TE, Culp RW, Hanel DP, Geissler WB, Berger RA. Intra-articular fractures of the distal aspect of the radius. Instr Course Lect, 1999;48:465-480.Article
- 7. Kamano M, Honda Y, Kazuki K, Yasuda M. Palmar plating for dorsally displaced fractures of the distal radius. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 2002;(397):403-408.Article
- 8. Lipton HA, Wollstein R. Operative treatment of intraarticular distal radial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1996;(327):110-124.Article
- 9. Cho CH, Bae KC, Kwon DH. Volar T-locking compression plate for treatment of unstable distal radius fractures. J Korean Fract Soc, 2008;21:220-224.Article
- 10. Koval KJ, Hoehl JJ, Kummer FJ, Simon JA. Distal femoral fixation: a biomechanical comparison of the standard condylar buttress plate, a locked buttress plate, and the 95-degree blade plate. J Orthop Trauma, 1997;11:521-524.Article
- 11. Cooney WP, Bussey R, Dobyns JH, Linscheid RL. Difficult wrist fractures. Perilunate fracture-dislocations of the wrist. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1987;(214):136-147.Article
- 12. Lim JY, Lee HY, Song JH, Kang JW, Lee JY. Evaluation of the reliability, construct validity, and responsiveness of the Korean version of the DASH. J Korean Soc Surg Hand, 2005;10:192-198.Article
- 13. Choi JY, Kim KC, Kim KH. Analysis of result of operative treatment for distal radius fracture. J Korean Soc Fract, 2000;13:338-342.Article
- 14. Jupiter JB, Lipton H. The operative treatment of intraarticular fractures of the distal radius. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1993;(292):48-61.Article
- 15. Lee LW, Putnam MD. Unstable fractures of the distal radius: an algorithmic method of treatment. Orthop Trans, 1988;12:357-541.Article
- 16. Choi WS, Kim WY, Choi DW, Shin YH, Kim JY. Anterior approach and volar T-plate fixation of distal radius fracture. J Korean Soc Fract, 2003;16:244-252.Article
- 17. Ha SS, Kim TH, Hong KD, Sim JC, Kim JH. Comparison of operative management in distal radius fractures using 3.5 mm versus 2.4 mm volar locking compression plates. J Korean Fract Soc, 2011;24:156-162.Article
- 18. Palmer AK, Werner FW. Biomechanics of the distal radioulnar joint. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1984;(187):26-35.Article
- 19. Herron M, Faraj A, Craigen MA. Dorsal plating for displaced intra-articular fractures of the distal radius. Injury, 2003;34:497-502.Article
- 20. Lowry KJ, Gainor BJ, Hoskins JS. Extensor tendon rupture secondary to the AO/ASIF titanium distal radius plate without associated plate failure: a case report. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ), 2000;29:789-791.Article
- 21. Harrison MR, Hamilton S, Johnstone AJ. Pseudo-rupture of Extensor Pollicis Longus following Kischner wire fixation of distal radius fractures. Acta Orthop Belg, 2004;70:492-494.Article
- 22. Martineau PA, Berry GK, Harvey EJ. Plating for distal radius fractures. Orthop Clin North Am, 2007;38:193-201.Article
- 23. Rein S, Schikore H, Schneiders W, Amlang M, Zwipp H. Results of dorsal or volar plate fixation of AO type C3 distal radius fractures: a retrospective study. J Hand Surg Am, 2007;32:954-961.Article
- 24. Haidukewych GJ. Innovations in locking plate technology. J Am Acad Orthop Surg, 2004;12:205-212.Article
- 25. Perren SM. Evolution and rationale of locked internal fixator technology. Introductory remarks. Injury, 2001;32:Suppl 2. B3-B9.Article
- 26. Park KC, Lee CH. Short term results of operative management with 2.4 mm volar locking compression plates in distal radius fractures. J Korean Fract Soc, 2009;22:264-269.Article
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
(A) A 40-year-old female patient presented with a distal radius fracture as AO classification C2. (B) Postoperative radiographs show acceptable reduction with variable angle volar locking compression plate. (C) Postoperative 12-month radiographs show complete bone union.
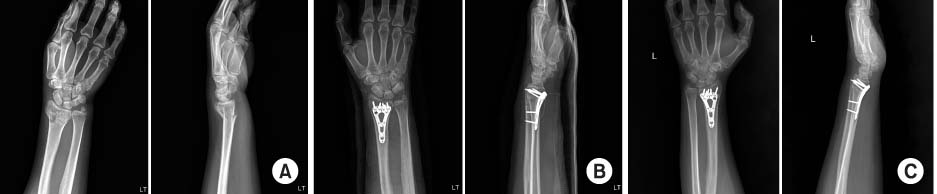

Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

Treatment of Fractures of the Distal Radius Using Variable-Angle Volar Locking Plate
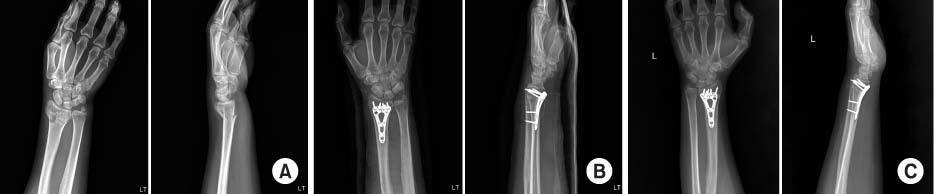
Fig. 1
(A) A 40-year-old female patient presented with a distal radius fracture as AO classification C2. (B) Postoperative radiographs show acceptable reduction with variable angle volar locking compression plate. (C) Postoperative 12-month radiographs show complete bone union.
Fig. 1
Treatment of Fractures of the Distal Radius Using Variable-Angle Volar Locking Plate
Radiographic Data for Distal Radius Fractures Treated with Variable Angle Volar Locking Compression Plates
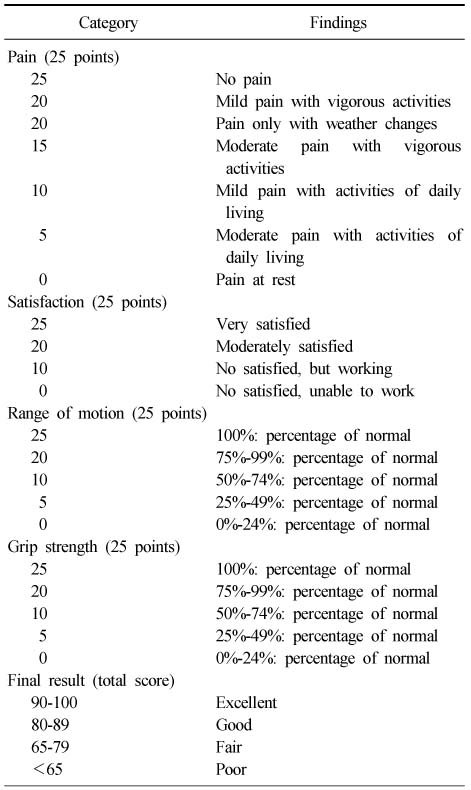
Clinical Evaluation by Mayo Wrist Score System
Table 1
Radiographic Data for Distal Radius Fractures Treated with Variable Angle Volar Locking Compression Plates
Table 2
Clinical Evaluation by Mayo Wrist Score System

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

