Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 20(3); 2007 > Article
-
Original Article
- Risk Factors of New Compression Fractures in Adjacent Vertebrae after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty
- Myung-Ho Kim, Sang-Hyuk Min, Suk-Ha Jeon
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2007;20(3):260-265.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.3.260
Published online: June 14, 2016
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Sang-Hyuk Min, M.D. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Dankook University Medical Center, 16-5, Anseo-dong, Cheonan 330-715, Korea. Tel: 82-41-550-395, Fax: 82-41-550-3950, osmin71@naver.com
Copyright © The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved
- 697 Views
- 0 Download
- 6 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- To evaluate the risk factors related to the development of new fractures in adjacent vertebrae after vertebroplasty.
-
Materials and Methods
- The study was conducted on 46 patients in whom 296 patients were performed during last 9 years. We were especially concerned with the restoration rate of vertebral height and kyphotic angle and estimated them on simple X-ray films.
-
Results
- In patients experienced subsequent vertebral fractures and no subsequent vertebral fractures after vertebroplasty, the mean height restoration rate of treated vertebra were 16.7% and 7.07%, and the kyphotic angle difference were 2.53 degree and 4.2 degree. The greater degree of height restoration of the vertebral body, especially in middle vertebral height and the lesser degree of kyphotic angle difference increased the risk of adjacent vertebral fracture risk. This results were available statistically (all p<0.05, Logistic regression test, SPSS 13.0).
-
Conclusion
- It may be thought that the vertebral body height restoration rate will become risk factor of adjacent vertebral fractures.
- 1. Baroud G, Nemes J, Ferguson SJ, Steffen T. Material changes in osteoporotic human cancellous bone following infiltration with acrylic bone cement for a vertebral cement augmentation. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin, 2003;6:133-139.
- 2. Belkoff SM, Mathis JM, Erbe EM, Fenton DC. Biomechamical evaluation of a new bone cement for use in vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 2000;25:1061-1064.
- 3. Berlemann U, Ferguson SJ, Nolte LP, Heini PF. Adjacent vertebral failure after vertebroplasty. A biomechanical investigation. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2002;84:748-752.
- 4. Delmas PD, Ensrud KE, Adachi JD, et al. Efficacy of raloxifene on vertebral fracture risk reduction in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: four-year results from a randomized clinical trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2002;87:3609-3617.
- 5. Evans AJ, Jensen ME, Kip KE, et al. Vertebral compression fractures: pain reduction and improvement in functional mobility after percutaneous polymethylmechacrylate vertebroplasty retrospective report of 245 cases. Radiology, 2003;226:366-372.
- 6. Ferguson SJ, Berlemann U, Heini PF, Nolte LP. Evaluation of adjacent segment failure following vertebroplasty. Orthop Res Soc, 2001;280:362-637.
- 7. Hwang J, Kim C, Kim J. Vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic compression fracture more than 1 year follow up. J Korean Fract Soc, 2004;17:368-373.
- 8. Jensen ME, Dion JE. Percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic compression fractures. Neuroimaging Clin N Am, 2000;10:547-568.
- 9. Kim SH, Kang HS, Choi JA, Ahn JM. Risk factors of new compression fractures in adjacent vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty. Acta Radiol, 2004;45:440-445.
- 10. Kumpan W, Salomonowitz E, Seidl G, Wittich GR. The intravertebral vacuum phenomenon. Skeletal Radiol, 1986;15:444-447.
- 11. Liebschner MA, Rosenberg WS, Keaveny TM. Effects of bone cement volume and distribution on vertebral stiffness after vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 2001;26:1547-1554.
- 12. Lindsay R, Silverman SL, Cooper C, et al. Risk of new vertebral fracture in the year following a fracture. JAMA, 2001;285:320-323.
- 13. Min SH, Kim MH, Park HG, Paik HD. A clinical analysis of 260 percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic compression fracture. J Korean Fract Soc, 2006;19:357-362.
- 14. Polikeit A, Nolte AP, Ferguson SJ. The effect of cement augumentation on load transfer in an osteoporotic functional spine unit. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 2003;28:991-996.
- 15. Schlaich C, Minne HW, Bruckner T, et al. Reduced pulmonary function in patients with spinal osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int, 1998;8:261-267.
- 16. Silverman SL. The clinical consequences of vertebral compression fracture. Bone, 1992;13:Suppl 2. S27-S31.
- 17. Uppin AA, Hirsch JA, Centenera LV, Pfiefer BA, Pazianos AG, Choi IS. Occurrence of new vertebral body fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty in patients with osteoporosis. Radiology, 2003;226:119-124.
REFERENCES
Fig. 3

72 year-old female visited in our hospital because of back pain after vertebroplasty of T12 Without trauma history. (A) Simple radiograph and (B) Magnetic Resonance Image after 6 months since T12 vertebroplasty in local clinic. The large amount of cement augmented in midportion of vertebral body.

Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Outcome Comparison between Percutaneous Vertebroplasty and Conservative Treatment in Acute Painful Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture
Hwa-Yeop Na, Young-Sang Lee, Tae-Hoon Park, Tae-Hwan Kim, Kang-Won Seo
Journal of Korean Society of Spine Surgery.2014; 21(2): 70. CrossRef - Adjacent Vertebral Compression Fracture after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty
Chung-Hwan Kim, Jae-Kwang Hwang, Jun-Seok Park
Journal of Korean Society of Spine Surgery.2013; 20(4): 163. CrossRef - Cement Leakage into Disc after Kyphoplasty: Does It Increases the Risk of New Adjacent Vertebral Fractures?
Hoon-Sang Sohn, Seong-Kee Shin, Eun-Seok Seo, Kang-Seob Chang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(4): 361. CrossRef - Risk Factors of New Compression Fractures in Adjacent Vertebrae after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty
Myung-Ho Kim, Andrew S. Lee, Sang-Hyuk Min, Sung-Hyun Yoon
Asian Spine Journal.2011; 5(3): 180. CrossRef - The Effect of Adjacent Vertebral Body on Vertebroplasty for Compression Fracture
Yong-Chan Kim, Ho-Geun Chang, Kee-Byung Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(1): 97. CrossRef - The Factors that Affect the Deformity Correction of Vertebral Body during Kyphoplasty of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture
Young-Do Koh, Jong-Seok Yoon, Sung-Il Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2008; 21(1): 57. CrossRef
Risk Factors of New Compression Fractures in Adjacent Vertebrae after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty
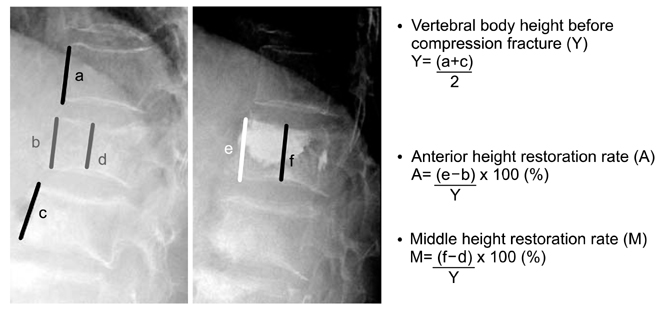
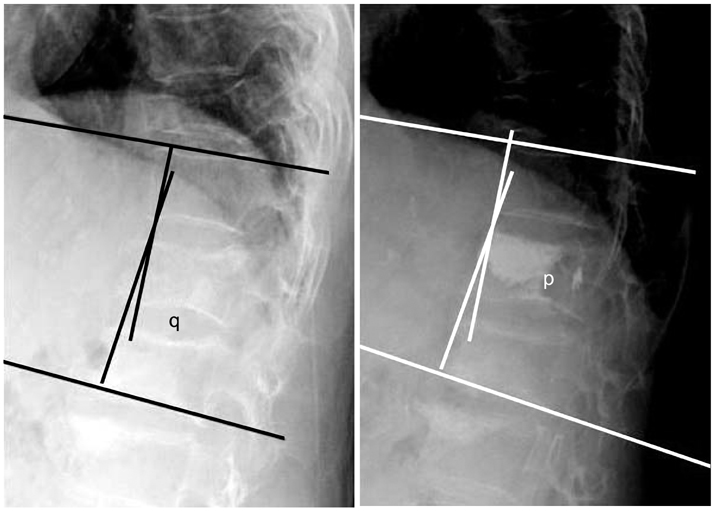
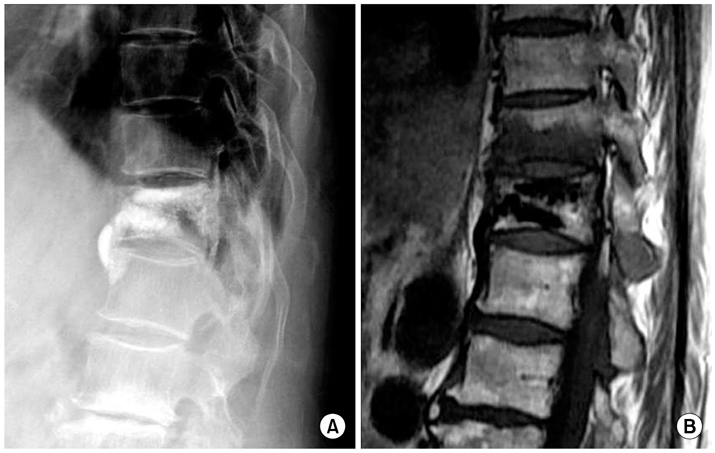
Fig. 1
The method of estimating in vertebral body height restoration rate.
Fig. 2
The method of estimating in Kyphotic angle differences. Kyphotic angle difference = p-q.
Fig. 3
72 year-old female visited in our hospital because of back pain after vertebroplasty of T12 Without trauma history. (A) Simple radiograph and (B) Magnetic Resonance Image after 6 months since T12 vertebroplasty in local clinic. The large amount of cement augmented in midportion of vertebral body.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Risk Factors of New Compression Fractures in Adjacent Vertebrae after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty
The comparison between subsequent fractures group & no subsequent fractures group
The distance from previous treated vertebra to adjacent new fracture
The statistic analysis using Logistic regression test (SPSS13.0)
The statistic analysis using Pearson correlation analysis (SPSS 13.0)
Table 1
The comparison between subsequent fractures group & no subsequent fractures group
Table 2
The distance from previous treated vertebra to adjacent new fracture
Table 3
The statistic analysis using Logistic regression test (SPSS13.0)
Table 4
The statistic analysis using Pearson correlation analysis (SPSS 13.0)

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS






 Cite
Cite

