Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 23(2); 2010 > Article
-
Original Article
- Related Factors of Ligamentotaxis with Posterior Instrumentation for the Surgical Treatment of Thoracolumbar Bursting Fracture
- Sang-Bum Kim, M.D., Taek-Soo Jeon, M.D., Seung-Hwan Kim, M.D., Han Chang, M.D., Cheol-Mog Hwang, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2010;23(2):213-219.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.2.213
Published online: April 30, 2010
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inje University College of Medicine, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea.
*Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
†Department of Radiology, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Taek-Soo Jeon, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Spine Center, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, 1435, Jwa-dong, Haeundae-gu, Busan 612-030, Korea. Tel: 82-51-797-0240, Fax: 82-51-797-0249, sirjeon@paik.ac.kr
Copyright © 2010 The Korean Fracture Society
- 404 Views
- 2 Download
Abstract
-
Purpose
- To investigate factors influencing the amount of indirect reduction by ligamentotaxis according to timing of surgery, extent of surgery, and characteristics of fractures.
-
Materials and Methods
- We reviewed 22 cases of thoracolumbar fracture which had been performed posterior instrumentation and fusion using pedicle screw system. We divided patients into each group according to timing of surgery, number of fusion segment, insertion of screw on fractured vertebra, and rupture of posterior ligament complex, and Denis type. We measured changes of kyphotic angle, anterior vertebral height and wedge angle on plain radiographs, and we compared spinal canal area before and after operation using computed tomographic scans.
-
Results
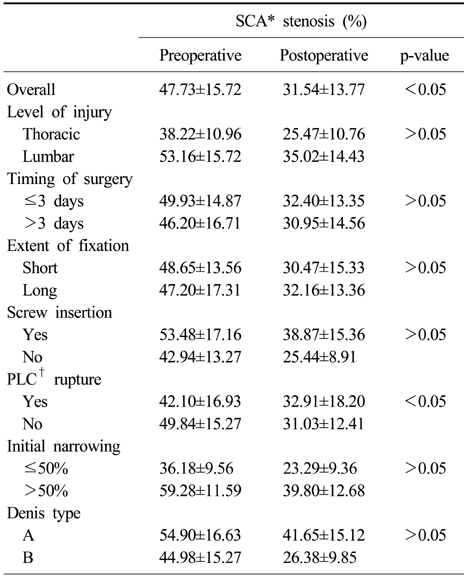
- Kyphotic angle, anterior vertebral height, wedge angle, and area of spinal canal showed significant improvement postoperatively. The wedge angle improved significantly operated within 3 days after injury, however, kyphotic angle and anterior vertebral height had no correlation with variable factors except the rupture of posterior ligament complex. The amount of restoration of spinal canal also affected only by rupture of posterior ligament complex.
-
Conclusion
- There is little relationship between timing of surgery and canal restoration, so we cannot conclude that prompt operation helps reduction of narrowed spinal canal. Otherwise narrowed spinal canal had much less restored by ligamentotaxis when there were rupture of posterior ligament complexes.
- 1. Aebi M, Etter C, Kehl T, Thalgott J. Stabilization of the lower thoracic and lumbar spine with the internal spinal skeletal fixation system. Indications, techniques, and first results of treatment. . Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 1987;12:544-551.Article
- 2. Dick W. The "fixateur interne" as a versatile implant for spine surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 1987;12:882-900.Article
- 3. Dick W, Kluger P, Magerl F, Woersdörfer O, Zäch G. A new device for internal fixation of thoracolumbar and lumbar spine fractures: the 'fixateur interne'. Paraplegia, 1985;23:225-232.Article
- 4. Garfin SR, Mowery CA, Guerra J Jr, Marshall LF. Confirmation of the posterolateral technique to decompress and fuse thoracolumbar spine burst fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 1985;10:218-223.Article
- 5. Gertzbein SD, Crowe PJ, Fazl M, Schwartz M, Rowed D. Canal clearance in burst fractures using the AO internal fixator. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 1992;17:558-560.Article
- 6. Guerra J Jr, Garfin SR, Resnick D. Vertebral burst fractures: CT analysis of the retropulsed fragment. Radiology, 1984;153:769-772.Article
- 7. Handel SF, Twiford TW Jr, Reigel DH, Kaufman HH. Posterior lumbar apophyseal fractures. Radiology, 1979;130:629-633.Article
- 8. Hashimoto T, Kaneda K, Abumi K. Relationship between traumatic spinal canal stenosis and neurologic deficits in thoracolumbar burst fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 1988;13:1268-1272.Article
- 9. Kim YT, Kim YJ, Jung JK. Treatment of the unstable thoracolumbar spine fractures using posterior approacxh. J Korean Orthop Assoc, 1995;30:1670-1679.ArticlePDF
- 10. Kostuik JP. Anterior fixation for burst fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine with or without neurological involvement. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 1988;13:286-293.Article
- 11. Kuner EH, Kuner A, Schlickewei W, Mullaji AB. Ligamentotaxis with an internal spinal fixator for thoracolumbar fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1994;76:107-112.ArticlePDF
- 12. Kuner EH, Schlickewei W, Kuner A, Hauser U. Restoration of the spinal canal by the internal fixator and remodeling. Eur Spine J, 1997;6:417-422.ArticlePDF
- 13. Lee JH, Jun DS, Shin WJ, Ahn SJ. The effect of pedicle screw instrumentation on fractured vertebrae in unstable thoracolumbar burst fractures with canal encroachment and clinical result. J Korean Soc Spine Surg, 2006;13:10-15.Article
- 14. Lindahl S, Willen J, Irstam L. Computed tomography of bone fragments in the spinal canal. An experimental study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 1983;8:181-186.Article
- 15. Mueller LA, Mueller LP, Schmidt R, Forst R, Rudig L. The phenomenon and efficiency of ligamentotaxis after dorsal stabilization of thoracolumbar burst fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 2006;126:364-368.ArticlePDF
- 16. Mumford J, Weinstein JN, Spratt KF, Goel VK. Thoracolumbar burst fractures. The clinical efficacy and outcome of nonoperative management. Spine, 1993;18:955-970.Article
- 17. Willén J, Lindahl S, Irstam L, Nordwall A. Unstable thoracolumbar fractures. A study by CT and conventional roentgenology of the reduction effect of Harrington instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 1984;9:214-219.Article
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

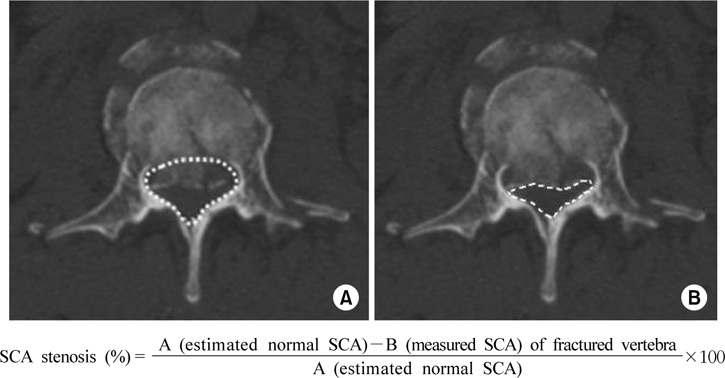
Figure 1
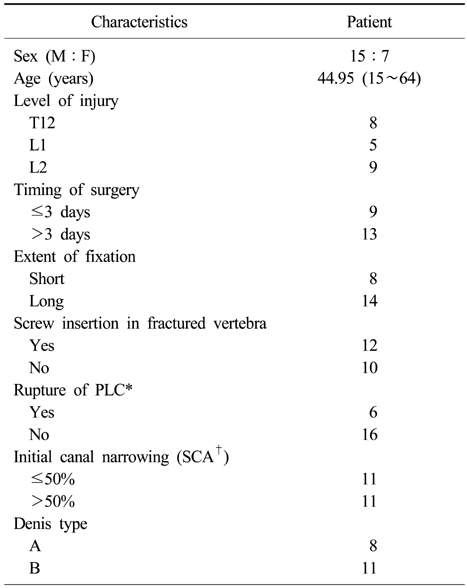
Characteristics of the 22 patients who underwent operation for thoracolumbar fracture using ligamentotaxis
*Posterior ligament complex, †Spinal canal area.
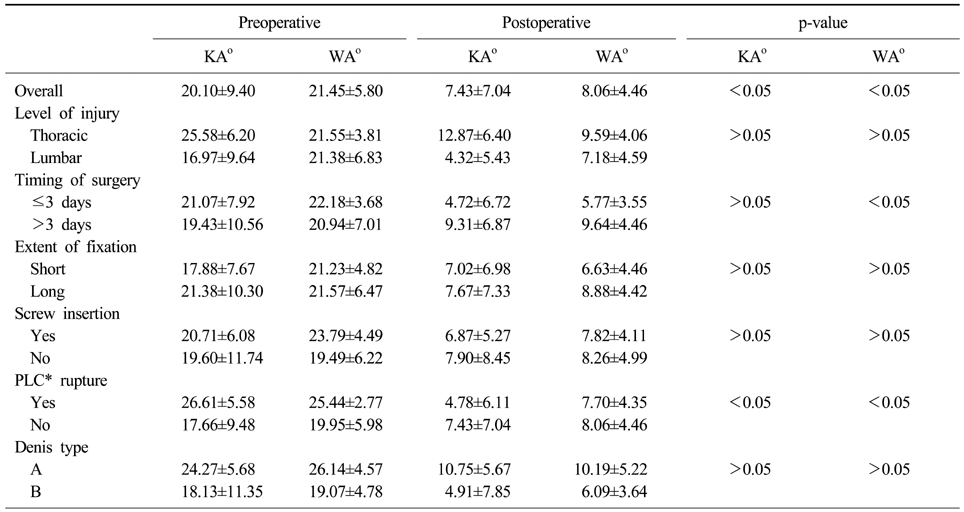
Change of kyphotic angle (KA) and wedge angle (WA)
*Posterior ligament complex.
Change of anterior height (AH)
*Posterior ligament complex.
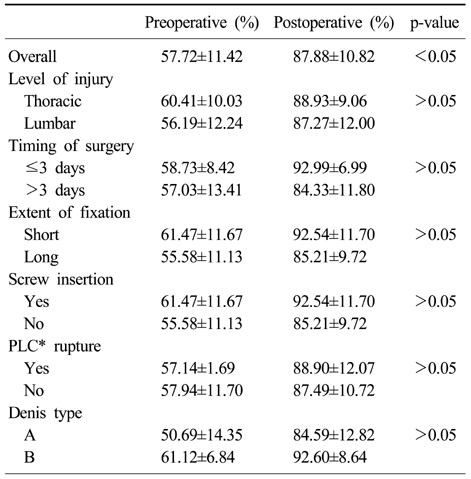
Change of canal encroachment
*Spinal canal area, †Posterior ligament complex.
*Posterior ligament complex, †Spinal canal area.
*Posterior ligament complex.
*Posterior ligament complex.
*Spinal canal area, †Posterior ligament complex.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 Cite
Cite

