Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 23(2); 2010 > Article
-
Original Article
- The Comparison of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis and Intramedullary Nailing in the Treatment of the Proximal and Distal Tibia Fracture
- Joon Soon Kang, M.D., Seung Rim Park, M.D., Sang Rim Kim, M.D., Yong Geun Park, M.D., Jae Ho Jung, M.D., Sung Wook Choi, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2010;23(2):172-179.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.2.172
Published online: April 30, 2010
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
*Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Jeju National University College of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Sung Wook Choi, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Jeju National University Hospital, 1753-3, Ara-1-dong, Jeju 690-716, Korea. Tel: 82-64-717-1690, Fax: 82-64-757-8276, csw11@inha.com
Copyright © 2010 The Korean Fracture Society
- 979 Views
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- To compare the efficacy of the surgical treatment through the comparison of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPO) and Intramedullary (IM) nailing in the treatment of the tibial shaft fractures expended to metaphysis retrospectively.
-
Materials and Methods
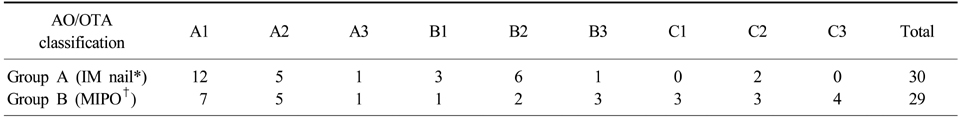
- Patients with proximal or distal third fracture of tibial shaft from May 2003 to Aug. 2006 were divided into two groups depending on the surgical method. Group A consisted of 30 patients treated with IM nailing, Group B was 29 patients treated with MIPO. The clinical outcomes were evaluated retrospectively from the time for bone union and callus formation confirmed by X-ray, functional score of knee or ankle joint, and complications including nonunion, malalignment and infection.
-
Results
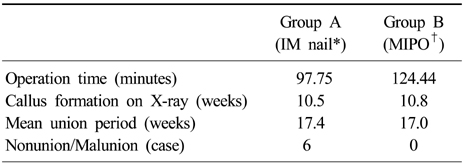
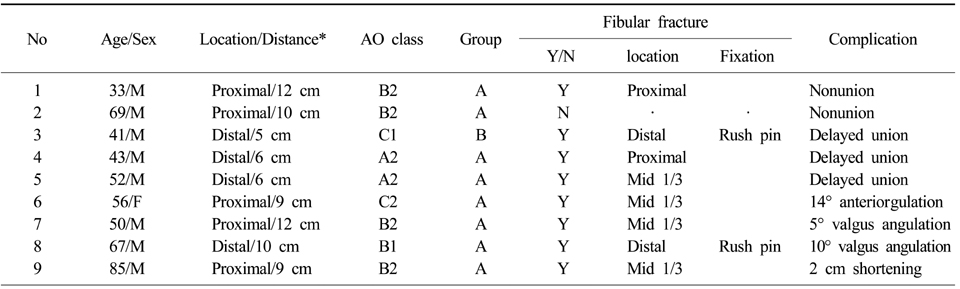
- Bone union was seen radiologically at a mean of 17.4 weeks in group A, and 17.0 weeks in group B. In postoperative complications, group A showed two nonunion, two delayed-union, six malalignment, and two wound infection while group B showed only one delayed-union and one wound infection.
-
Conclusion
- There were no significant differences in the time for bony union and functional score between IM nailing and MIPO. Conventional IM nailing with only interlocking technique showed higher incidence of malalignment and deformity than MIPO for the treatment of the proximal or distal third fracture of the tibial shaft.
- 1. Asche G. Results of the treatment of femoral and tibial fractures following interlocking nailing and plate osteosynthesis. A comparative retrospective study. Zentralbl Chir, 1989;114:1146-1154.
- 2. Bone LB, Johnson KD. Treatment of tibial fractures by reaming and intramedullary nailing. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1986;68:877-887.Article
- 3. Böstman O, Hänninen A. The fibular reciprocal fracture in tibial shaft fractures caused by indirect violence. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 1982;100:115-121.ArticlePDF
- 4. Burwell HN. Plate fixation of tibial shaft fractures. A survey of 181 injuries. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1971;53:258-271.
- 5. Claes L, Heitemeyer U, Krischak G, Braun H, Hierholzer G. Fixation technique influences osteogenesis of comminuted fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1999;(365):221-229.Article
- 6. D'Aubigne RM, Maurer P, Zucman J, Masse Y. Blind intramedullary nailing for tibial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1974;105:267-275.
- 7. Freedman EL, Johnson EE. Radiographic analysis of tibial fracture malalignment following intramedullary nailing. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1995;315:25-33.Article
- 8. Gorczyca JT, McKale J, Pugh K, Pienkowski D. Modified tibial nails for treating distal tibia fractures. J Orthop Trauma, 2002;16:18-22.Article
- 9. Gustilo RB, Anderson JT. Prevention of infection in the treatment of one thousand and twenty-five open fractures of long bones: retrospective and prospective analyses. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1976;58:453-458.
- 10. Hajek PD, Bicknell HR Jr, Bronson WE, Albright JA, Saha S. The use of one compared with two distal screws in the treatment of femoral shaft fractures with interlocking intramedullary nailing. A clinical and biomechanical analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1993;75:519-525.Article
- 11. Hasenboehler E, Rikli D, Babst R. Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fracture: a retrospective study of 32 patients. Injury, 2007;38:365-370.Article
- 12. Helfet DL, Suk M. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis of fractures of the distal tibia. Instr Course Lect, 2004;53:471-475.
- 13. Henley MB, Meier M, Tencer AF. Influences of some design parameters on the biomechanics of the unreamed tibial intramedullary nail. J Orthop Trauma, 1993;7:311-319.Article
- 14. Janssen KW, Biert J, van Kampen A. Treatment of distal tibial fractures: plate versus nail: a retrospective outcome analysis of matched pairs of patients. Int Orthop, 2007;31:709-714.
- 15. Johner R, Wruhs O. Classification of tibial shaft fractures and correlation with results after rigid internal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1983;178:7-25.Article
- 16. Konrath G, Moed BR, Watson JT, Kaneshiro S, Karges DE, Cramer KE. Intramedullary nailing of unstable diaphyseal fractures of the tibia with distal intraarticular involvement. J Orthop Trauma, 1997;11:200-205.Article
- 17. Krackhardt T, Dilger J, Flesch I, Höntzsch D, Eingartner C, Weise K. Fractures of the distal tibia treated with closed reduction and minimally invasive plating. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 2005;125:87-94.ArticlePDF
- 18. Lang GJ, Cohen BE, Bosse MJ, Kellam JF. Proximal third tibial shaft fractures. Should they be nailed? Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1995;315:64-74.
- 19. McFerran MA, Smith SW, Boulas HJ, Schwartz HS. Complications encountered in the treatment of pilon fractures. J Orthop Trauma, 1992;6:195-200.Article
- 20. McKibbin B. The biology of fracture healing in long bones. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1978;60:150-162.ArticlePDF
- 21. Melis GC, Sotgiu F, Lepori M, Guido P. Intramedullary nailing in segmental tibial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1981;63:1310-1318.Article
- 22. Oh CW, Oh JK, Jeon IH, et al. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate stabilization of proximal tibial fractures. J Korean Fract Soc, 2004;17:224-229.Article
- 23. Olerud C, Molander H. Bi- and trimalleolar ankle fractures operated with nonrigid internal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1986;206:253-260.Article
- 24. Ovadia DN, Beals RK. Fractures of the tibial plafond. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1986;68:543-551.Article
- 25. Perren SM. Evolution of the internal fixation of long bone fractures. The scientific basis of biological internal fixation: choosing a new balance between stability and biology. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2002;84:1093-1110.
- 26. Rasmussen PS. Tibial condylar fractures. Impairment of knee joint stability as an indication for surgical treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1973;55:1331-1350.
- 27. Ricci WM, O'Boyle M, Borrelli J, Bellabarba C, Sanders R. Fractures of the proximal third of the tibial shaft treated with intramedullary nails and blocking screws. J Orthop Trauma, 2001;15:264-270.Article
- 28. Richter D, Hahn MP, Laun RA, Ekkernkamp A, Muhr G, Ostermann PA. Ankle para-articular tibial fracture. Is osteosynthesis with the unreamed intramedullary nail adequate? Chirurg, 1998;69:563-570.
- 29. Robinson CM, McLauchlan GJ, McLean IP, Court-Brown CM. Distal metaphyseal fractures of the tibia with minimal involvement of the ankle. Classification and treatment by locked intramedullary nailing. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1995;77:781-787.ArticlePDF
- 30. Sohn HM, Lee JY, Ha SH, You JW, Lee SH, Lee KC. Treatment of high-energy distal tibia intraarticular fractures with two-staged delayed minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis. J Korean Fract Soc, 2007;20:19-25.Article
REFERENCES
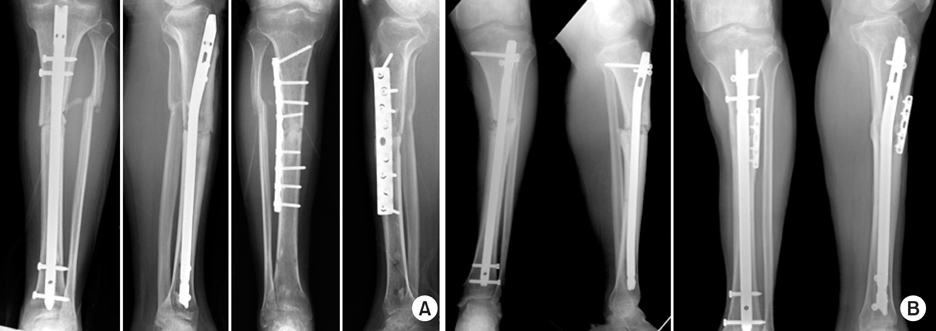
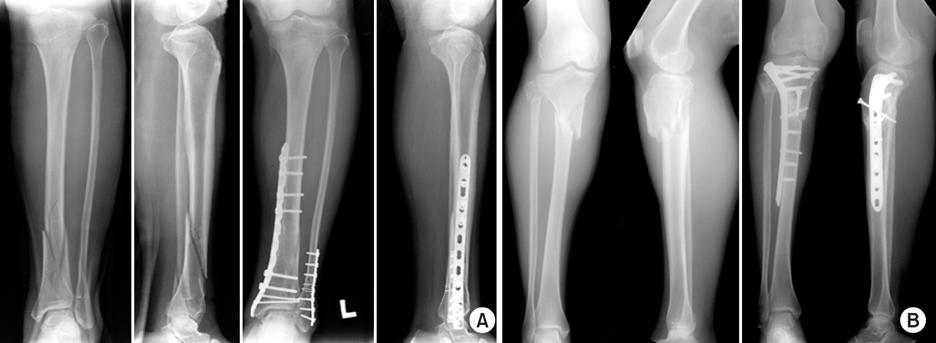
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

- Effect of Korean Medicine Treatments in Patients with Proximal Tibia Fracture: A Retrospective Observational Study
Jung Min Lee, Eun-Jung Lee
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2020; 30(3): 141. CrossRef
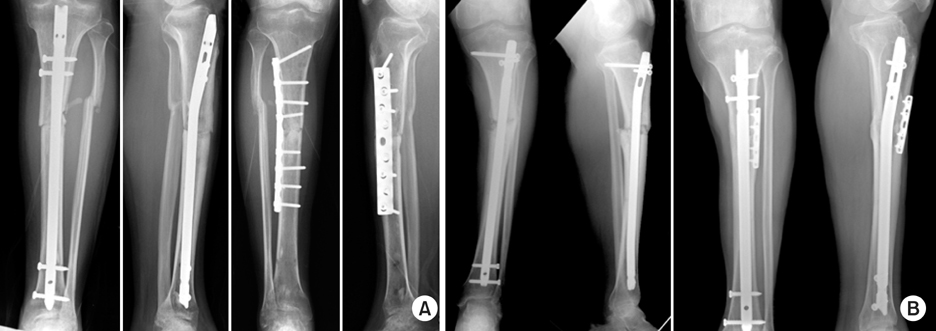
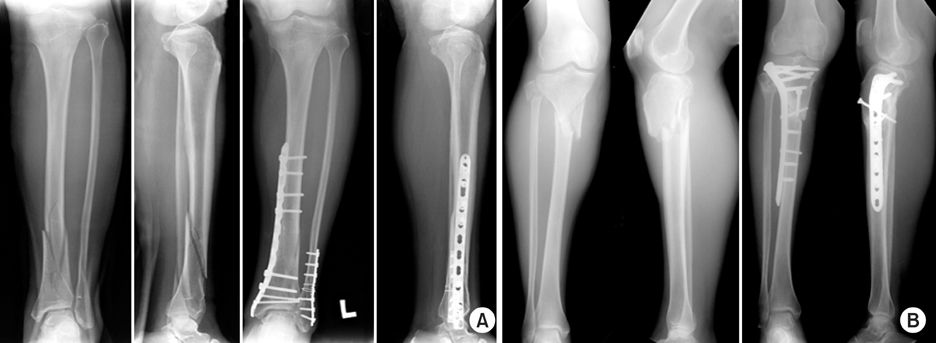
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Distribution of cases on the AO/OTA classification
*IM nail: Intramedullary nail, †MIPO: Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis.
Comparison of IM nail and MIPO on the clinical outcome
*IM nail: Intramedullary nail, †MIPO: Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis.
The data of complication cases
*Distance: Distance between the adjacent joint (a knee joint or a ankle joint) line and the main fracture line (cm).
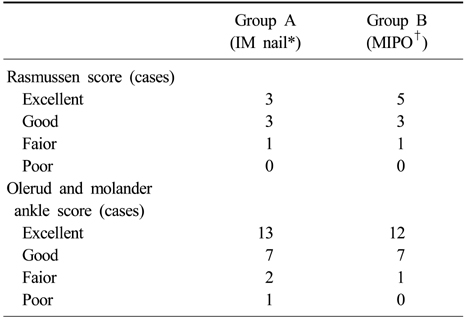
Comparison of IM nail and MIPO on the functional score
IM nail: Intramedullary nail, †MIPO: Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis.
*IM nail: Intramedullary nail, †MIPO: Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis.
*IM nail: Intramedullary nail, †MIPO: Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis.
*Distance: Distance between the adjacent joint (a knee joint or a ankle joint) line and the main fracture line (cm).
IM nail: Intramedullary nail, †MIPO: Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

