Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 23(1); 2010 > Article
-
Original Article
- Treatment for Unstable Distal Radius Fracture with Osteoporosis: Internal Fixation versus External Fixation
- Jin Rok Oh, M.D., Tae Yean Cho, M.D., Sung Min Kwan, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2010;23(1):76-82.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.1.76
Published online: July 15, 2010
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Wonju College of Medicine, Yonsei University, Wonju, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Jin Rok Oh, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Wonju College of Medicine, Yonsei University, Ilsan-dong, Wonju 220-701, Korea. Tel: 82-33-741-1355, Fax: 82-33-746-7326, jroh@yonsei.ac.kr
• Received: September 30, 2009 • Accepted: November 23, 2009
Copyright © 2010 The Korean Fracture Society
- 479 Views
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- To compare the functional and radiological outcomes of volar plating to that of external fixation for treating unstable osteoporotic distal radius fracture.
-
Materials and Methods
- From March 2006 to March 2008, 36 patients with osteoporosis over 60-year old were selected for this study. They were divided into two groups; group I (open reduction and internal fixation with volar fixed angle plate) and group II (closed reduction and external fixation). Clinical outcomes and radiologic outcomes were evaluated.
-
Results
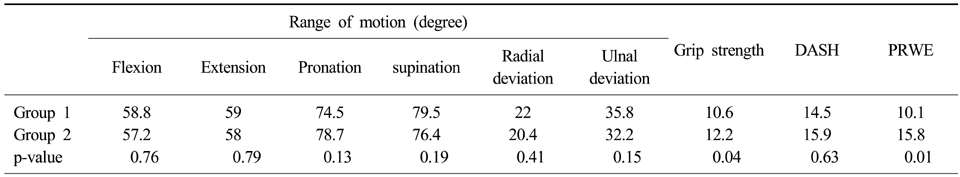
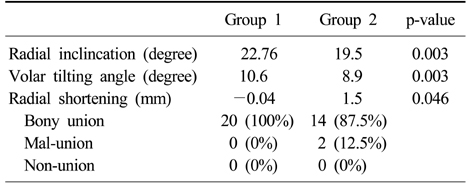
- There was no statistical difference between group I and group II in range of motion and DASH score, BMD score. However, the grip strength and PRWE score were found to be higher in group II (p<0.05). In radiologic evaluation, group I showed higher radial inclination, volar tilting angle (p<0.05).
-
Conclusion
- Internal fixation using Volar-fixed Angle Plate seems to give more stable fixation for distal articular fragments compared to external fixation. it could allow early postoperative exercise and could result in low incidence of postoperative complication such as pin track infections and joint stiffness. Therefore, the internal fixation could be more desirable treatment method to manage unstable distal radius fracture.
- 1. Cho CH, Jung SW, Sohn SW, Kang CH, Bae KC, Lee KJ. Comparison of outcomes for unstable distal radius intraarticular fractures: T-locking compression plate versus external fixator. J Korean Fract Soc, 2008;21:51-56.Article
- 2. Cho DY, Kim SJ, Im SJ, Kim YW, Kim BC. Treatment of the distal radius intraarticular fractures with percutaneous pinning and external fixator. J Korean Orthop Assoc, 2001;36:519-523.ArticlePDF
- 3. DePALMA AF. Comminuted fractures of the distal end of the radius treated by ulnar pinning. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1952;24:651-662.Article
- 4. Fracture and dislocation compendium. Orthopaedic trauma association committee for coding and classification. J Orthop Trauma, 1996;10:Suppl 1. v-ix. 1-154.
- 5. Haidukewych GJ. Innovations in locking plate technology. J Am Acad Orthop Surg, 2004;12:205-212.Article
- 6. Horesh Z, Volpin G, Hoerer D, Stein H. The surgical treatment of severe comminuted intraarticular fractures of the distal radius with the small AO external fixation device A prospective three-and-one-half-year follow-up study. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1991;263:147-153.
- 7. Jakob RP. The small external fixator. Z Unfallchir Versicherungsmed Berufskr, 1985;78:53-55.
- 8. Kapoor H, Agarwal A, Dhaon BK. Displaced intra-articular fractures of distal radius: a comparative evaluation of results following closed reduction, external fixation and open reduction with internal fixation. Injury, 2000;31:75-79.
- 9. Lee KH. Volar plating of distal radius fractures. J Korean Fract Soc, 2008;21:325-333.Article
- 10. Lim JY, Song JH, Lee JY, Lee HY, Kang JW. Evaluation of the reliability, construct validity, and responsiveness of the korean version of the DASH. J Korean Soc Surg Hand, 2005;10:192-198.
- 11. MacDermid JC. The Patient-Rated Wrist Evaluation (PRWE)© User Manual, 2007.
- 12. McKay SD, MacDermid JC, Roth JH, Richards RS. Assessment of complications of distal radius fractures and development of a complication checklist. J Hand Surg Am, 2001;26:916-922.Article
- 13. Muller SD MJ, Roth JH, Richards RS. Manual of internal fixation: techniques recommended by the AO-ASIF Group, 1991;3rd ed. New York, Springer. 1-3.
- 14. Park JY, Jung HG, Yoo MJ, Kim JW. Comparison of results according to the type and procedure in unstable fracture of the distal radius. J Korean Soc Fract, 1998;11:435-441.
- 15. Rizzo M, Katt BA, Carothers JT. Comparison of locked volar plating versus pinning and external fixation in the treatment of unstable intraarticular distal radius fractures. Hand (N Y), 2008;3:111-117.ArticlePDF
- 16. Schmelzer-Schmied N, Wieloch P, Martini AK, Daecke W. Comparison of external fixation, locking and non-locking palmar plating for unstable distal radius fractures in the elderly. Int Orthop, 2009;33:773-778.ArticlePDF
- 17. Song SW. Osteoporotic distal radius fracture-conservative treatment. J Korean Fract Soc, 2008;21:81-86.Article
- 18. Vaughan PA, Lui SM, Harrington IJ, Maistrelli GL. Treatment of unstable fractures of the distal radius by external fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1985;67:385-389.
- 19. Wright TW, Horodyski M, Smith DW. Functional outcome of unstable distal radius fractures: ORIF with a volar fixed-angle tine plate versus external fixation. J Hand Surg Am, 2005;30:289-299.Article
- 20. Zagorski JB. Comminuted fractures of the distal radius. Instr Course Lect, 1990;39:255-258.
REFERENCES
Fig. 2
67-year-old woman with unstable distal radius fracture was treated by OR & IF with Acu-loc® volar fixed angle plate (BMD: -3.5).
(A) Preoperative radiographs show AO classification C2.
(B) Immediate postoperative radiographs show reduction and fixation.
(C) Radiographs at 13 months postoperatively show no significant change.
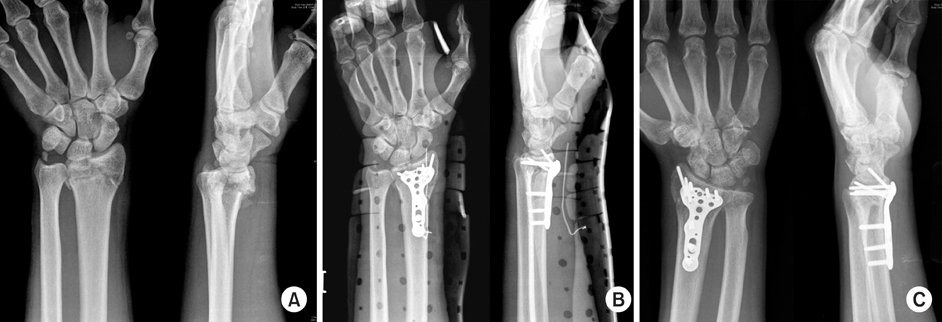

Fig. 4
65-years-old woman with unstable distal radius fracture was treated by CR pinning & EF with Penning Orthofix® external fixation and MIIG® injection (BMD: -5.2).
(A) Preoperative radiographs and CT shows AO classification C3. In CT, there was severe comminution and joint depression, the fracture lines in tidal mark of distal radius. Therefore, it was not available internal fixation.
(B) Immediate postoperative radiographs shows closed reduction and percutaneous pinning with K-wires with external fixator and MIIG® injection.
(C) Postoperative radiographs at 6 months shows bony union and restroring joint congruity.
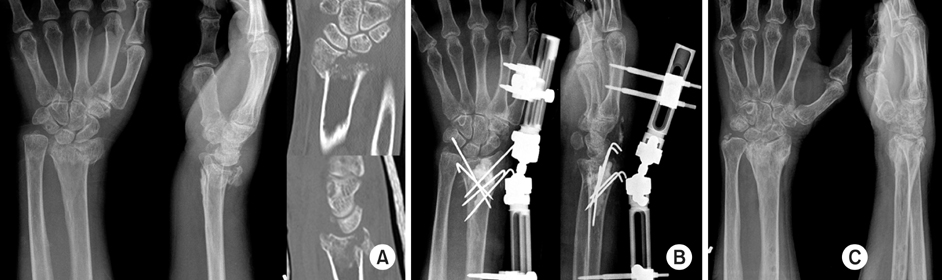

Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Functional Outcomes of Percutaneous K-Wire Fixation for Distal Radius Fractures with or without Osteoporosis
Ki-Chan An, Gyu-Min Kong, Jang-Seok Choi, Hi-Chul Gwak, Joo-Yong Kim, Sung-Yub Jin
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2013; 26(4): 248. CrossRef
Treatment for Unstable Distal Radius Fracture with Osteoporosis: Internal Fixation versus External Fixation
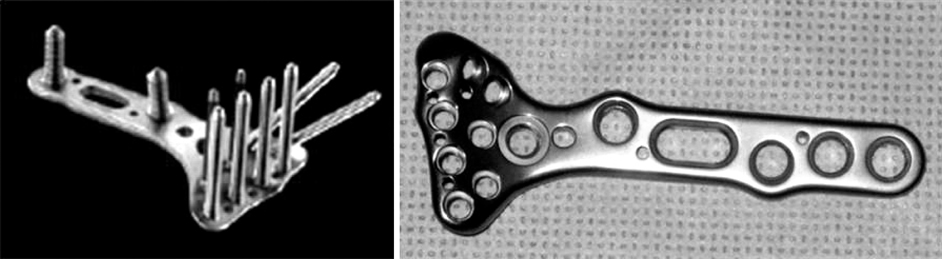
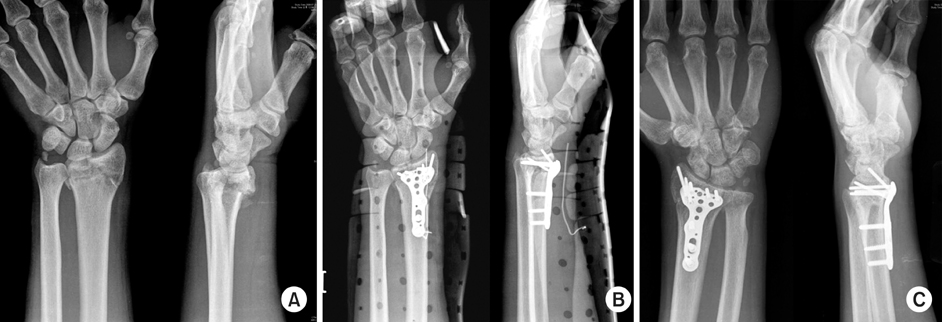
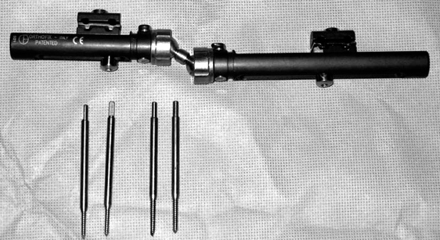
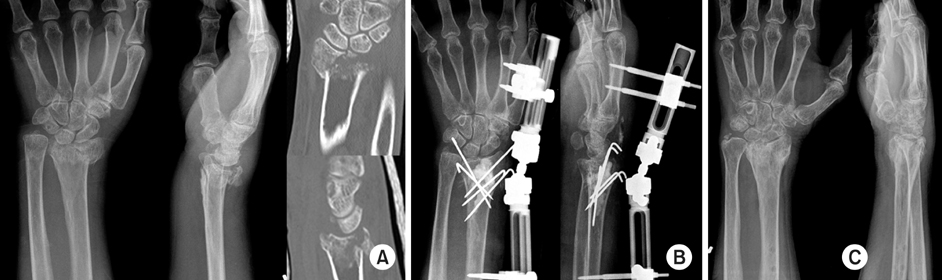
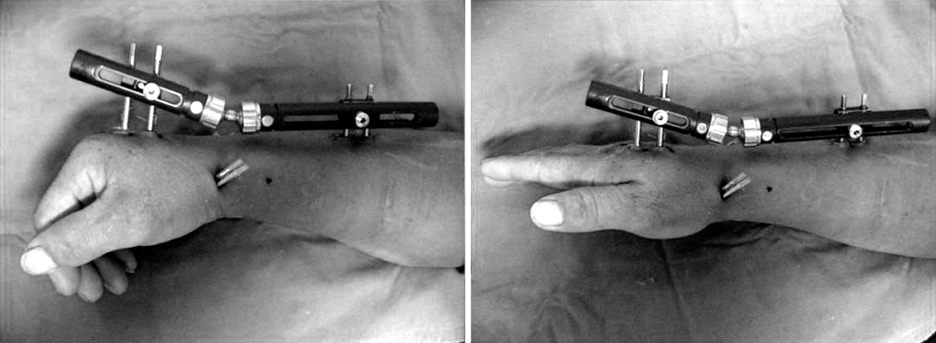
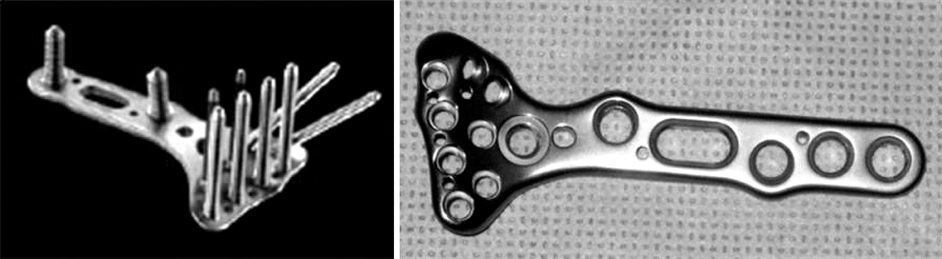
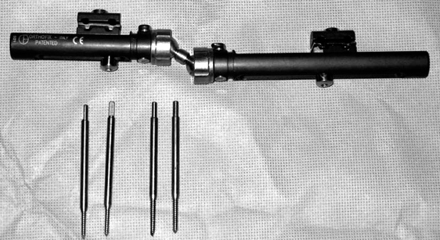
Fig. 1
Acu-loc® volar fixed angle plate
Fig. 2
67-year-old woman with unstable distal radius fracture was treated by OR & IF with Acu-loc® volar fixed angle plate (BMD: -3.5).
(A) Preoperative radiographs show AO classification C2.
(B) Immediate postoperative radiographs show reduction and fixation.
(C) Radiographs at 13 months postoperatively show no significant change.
Fig. 3
Penning Orthofix® external fixator.
Fig. 4
65-years-old woman with unstable distal radius fracture was treated by CR pinning & EF with Penning Orthofix® external fixation and MIIG® injection (BMD: -5.2).
(A) Preoperative radiographs and CT shows AO classification C3. In CT, there was severe comminution and joint depression, the fracture lines in tidal mark of distal radius. Therefore, it was not available internal fixation.
(B) Immediate postoperative radiographs shows closed reduction and percutaneous pinning with K-wires with external fixator and MIIG® injection.
(C) Postoperative radiographs at 6 months shows bony union and restroring joint congruity.
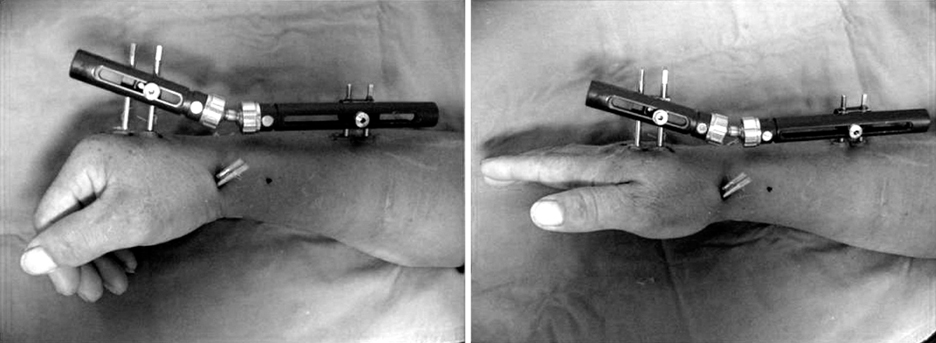
Fig. 5
Postop active ROM exercise after CR pinning & EF with Penning Orthofix® external fixation (BMD: -2.7).
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Treatment for Unstable Distal Radius Fracture with Osteoporosis: Internal Fixation versus External Fixation
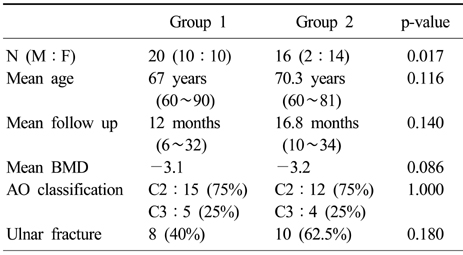
Patient demographics of group 1 (OR & IF) and Group 2 (CR and pinning and external fixation)
Clinical results of group 1 and group 2
Radiological result and complication of group 1 and group 2
Table 1
Patient demographics of group 1 (OR & IF) and Group 2 (CR and pinning and external fixation)
Table 2
Clinical results of group 1 and group 2
Table 3
Radiological result and complication of group 1 and group 2

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

