Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 25(3); 2012 > Article
-
Original Article
- Results of the Kapandji Procedure in the AO Type C Distal Radius Fracture in Patients over Age 60
- Chul Hong Kim, M.D., Sung Soo Kim, M.D., Myung Jin Lee, M.D., Hyeon Jun Kim, M.D., Bo Kun Kim, M.D., Young Hoon Lim, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2012;25(3):191-196.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.3.191
Published online: July 16, 2012
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Hyeon Jun Kim, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Dong-A Medical Center, Dong-A University College of Medicine, 26, Daesingongwon-ro, Seo-gu, Busan 602-715, Korea. Tel: 82-51-240-5167, Fax: 82-51-254-6757, hyeonjun@dau.ac.kr
• Received: July 29, 2011 • Revised: August 24, 2011 • Accepted: March 12, 2012
Copyright © 2012 The Korean Fracture Society
- 391 Views
- 2 Download
Abstract
-
Purpose
- To evaluate the clinical and radiologic results of the Kapandji procedure in AO classification type C distal radius fracture patients over 60 years old.
-
Materials and Methods
- Twenty-one type C distal radius fracture patients over the age of 60 years who were treated with the Kapandji procedure from June 2004 to June 2009 in our hospital and had a post-operative follow-up period of more than 1 year were enrolled. The volar tilt, radial inclination, and radial length were measured for the radiographic analysis using the modified Lidstrom scoring system about post-operative reduction loss in every follow-up radiogram. The clinical result was assessed with a visual analogue scale (VAS) and Korean Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand Questionnaire (DASH) score at the last follow-up.
-
Results
- The mean radiologic loss of volar tilt was 1.1° and the mean loss of radial length was 2.6 mm and the mean radial inclination loss was 2.7° compared with the immediate post-operative period and last follow-up period. The average VAS and DASH scores were 1.4 and 15.9.
-
Conclusion
- The radiologic results of closed reduction and percutaneous pinning using the Kapandji technique for distal radius AO type C fracture patients over 60 years of age was not satisfactory. Nevertheless, the clinical results were satisfactory.
- 1. Ark J, Jupiter JB. The rationale for precise management of distal radius fractures. Orthop Clin North Am, 1993;24:205-210.
- 2. Board T, Kocialkowski A, Andrew G. Does Kapandji wiring help in older patients? A retrospective comparative review of displaced intra-articular distal radial fractures in patients over 55 years. Injury, 1999;30:663-669.
- 3. Chung KC, Shauver MJ, Birkmeyer JD. Trends in the United States in the treatment of distal radial fractures in the elderly. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2009;91:1868-1873.
- 4. Dowdy PA, Patterson SD, King GJ, Roth JH, Chess D. Intrafocal (Kapandji) pinning of unstable distal radius fractures: a preliminary report. J Trauma, 1996;40:194-198.
- 5. Dunning CE, Lindsay CS, Bicknell RT, Patterson SD, Johnson JA, King GJ. Supplemental pinning improves the stability of external fixation in distal radius fractures during simulated finger and forearm motion. J Hand Surg Am, 1999;24:992-1000.
- 6. Frykman G. Fracture of the distal radius including sequelae--shoulder-hand-finger syndrome, disturbance in the distal radio-ulnar joint and impairment of nerve function. A clinical and experimental study. Acta Orthop Scand, 1967;Suppl 108. 3+.
- 7. Gehrmann SV, Windolf J, Kaufmann RA. Distal radius fracture management in elderly patients: a literature review. J Hand Surg Am, 2008;33:421-429.
- 8. Hastings H 2nd, Leibovic SJ. Indications and techniques of open reduction. Internal fixation of distal radius fractures. Orthop Clin North Am, 1993;24:309-326.
- 9. Kapandji A. Internal fixation by double intrafocal plate. Functional treatment of non articular fractures of the lower end of the radius (author's transl). Ann Chir, 1976;30:903-908.
- 10. Kapandji A. Intra-focal pinning of fractures of the distal end of the radius 10 years later. Ann Chir Main, 1987;6:57-63.
- 11. Kim JH, Lee KH, Hwang KT. The factors of reduction loss in Kapandji technique for distal radius fractures. J Korean Soc Surg Hand, 2004;9:250-256.
- 12. Kim JK, Park HS, Jeong BJ. Comparative analysis of the results of dorsally unstable distal radius fractures between Kapandji technique and volar locking plate fixation. J Korean Soc Surg Hand, 2008;13:217-222.
- 13. Lidstrom A. Fractures of the distal end of the radius. A clinical and statistical study of end results. Acta Orthop Scand, 1959;41:Suppl 41. 1-118.
- 14. McQueen MM, Hajducka C, Court-Brown CM. Redisplaced unstable fractures of the distal radius: a prospective randomised comparison of four methods of treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1996;78:404-409.
- 15. McQueen MM, MacLaren A, Chalmers J. The value of remanipulating Colles' fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1986;68:232-233.PDF
- 16. Moon ES, Kim MS, Kong IK. The amount and related factors of reduction loss in distal radius fracture after treatment by Kapandji technique. J Korean Fract Soc, 2007;20:252-259.
- 17. Orbay JL, Fernandez DL. Volar fixation for dorsally displaced fractures of the distal radius: a preliminary report. J Hand Surg Am, 2002;27:205-215.
- 18. Orbay JL, Fernandez DL. Volar fixed-angle plate fixation for unstable distal radius fractures in the elderly patient. J Hand Surg Am, 2004;29:96-102.
- 19. Park JW. Surgical treatment of common osteoporotic fracture: distal radius. J Korean Fract Soc, 2010;23:391-398.
- 20. Peyroux LM, Dunaud JL, Caron M, Ben Slamia I, Kharrat M. The Kapandji technique and its evolution in the treatment of fractures of the distal end of the radius. Report on a series of 159 cases. Ann Chir Main, 1987;6:109-122.
- 21. Stewart HD, Innes AR, Burke FD. Factors affecting the outcome of Colles' fracture: an anatomical and functional study. Injury, 1985;16:289-295.
- 22. Walton NP, Brammar TJ, Hutchinson J, Raj D, Coleman NP. Treatment of unstable distal radial fractures by intrafocal, intramedullary K-wires. Injury, 2001;32:383-389.
- 23. Wolfe SW, Austin G, Lorenze M, Swigart CR, Panjabi MM. A biomechanical comparison of different wrist external fixators with and without K-wire augmentation. J Hand Surg Am, 1999;24:516-524.
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
A 75-year-old female with unstable distal radius fracture was treated using a Kapandji technique.
(A, B) Pre-operative radiographs and computed tomography scan show AO classification type C1 distal radius fracture.
(C) Immediate postoperative radiographs show acceptable reduction and fixation.
(D) On last follow-up after removal of K-wires, radiographs show changes in the radiologic indices that reflect reduction loss (radial length, volar tilting and radial inclination are 3.0 mm, 4.3° and 1.9°, respectively).
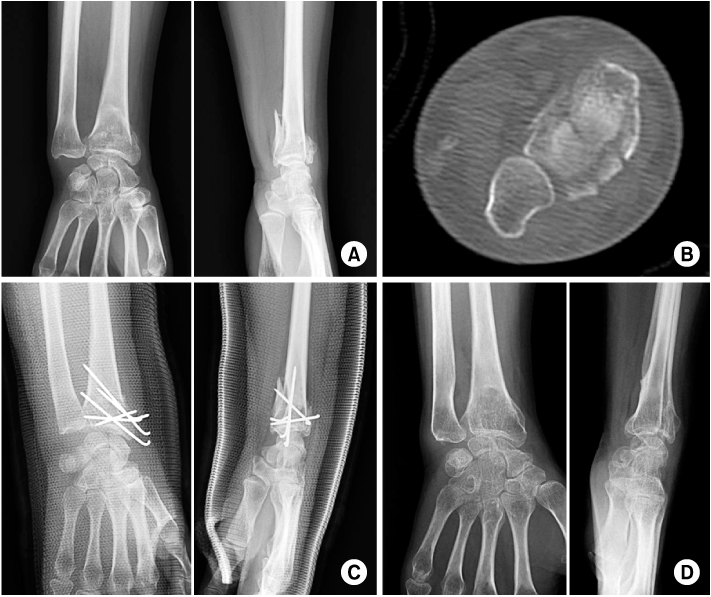

Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

Results of the Kapandji Procedure in the AO Type C Distal Radius Fracture in Patients over Age 60
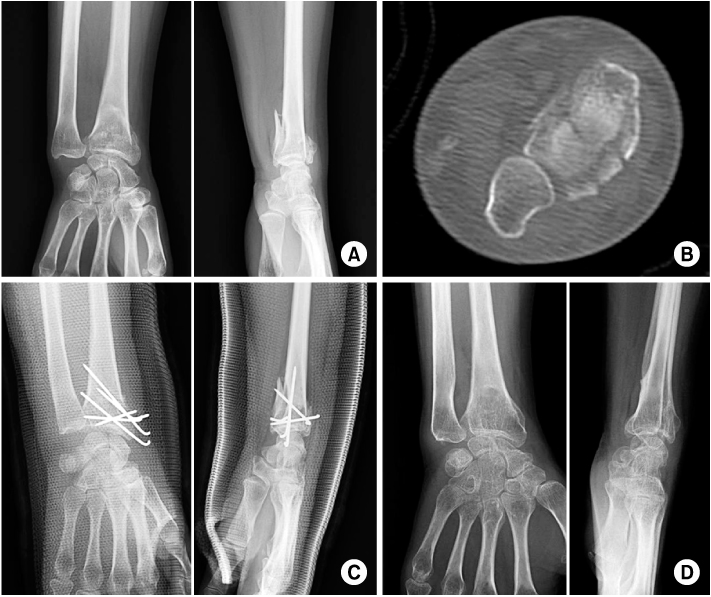
Fig. 1
A 75-year-old female with unstable distal radius fracture was treated using a Kapandji technique.
(A, B) Pre-operative radiographs and computed tomography scan show AO classification type C1 distal radius fracture.
(C) Immediate postoperative radiographs show acceptable reduction and fixation.
(D) On last follow-up after removal of K-wires, radiographs show changes in the radiologic indices that reflect reduction loss (radial length, volar tilting and radial inclination are 3.0 mm, 4.3° and 1.9°, respectively).
Fig. 1
Results of the Kapandji Procedure in the AO Type C Distal Radius Fracture in Patients over Age 60
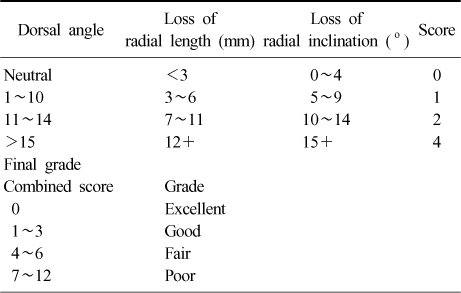
Radiological score
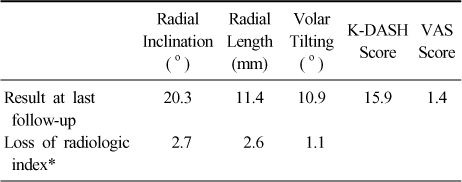
Outcomes at last follow-up
VAS: Visual analogue scale. K-DASH: Korean Version of the Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand Questionnaire. *Mean loss of each radiologic index between immediate post-operative period and last follow-up period.
Table 1
Radiological score
Table 2
Outcomes at last follow-up
VAS: Visual analogue scale. K-DASH: Korean Version of the Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand Questionnaire. *Mean loss of each radiologic index between immediate post-operative period and last follow-up period.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

