Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 29(1); 2016 > Article
-
Case Report
- Breakage of Cephalomedullary Nail Used in the Treatment of Proximal Femur Fractures: Case Report
- Seok Hyun Kweon, M.D., Chang Hyun Shin, M.D., Jin Sung Park, M.D., Byoung San Choi, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2016;29(1):42-49.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.1.42
Published online: January 19, 2016
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea.
*Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Presbyterian Medical Center, Seonam University School of Medicine, Jeonju, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Byoung San Choi, M.D. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Presbyterian Medical Center, Seonam University School of Medicine, 365 Seowon-ro, Wansangu, Jeonju 54987, Korea. Tel: 82-63-230-1430, Fax: 82-63-230-1439, bhinder@naver.com
• Received: August 17, 2015 • Revised: September 2, 2015 • Accepted: November 7, 2015
Copyright © 2016 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 701 Views
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
- Internal fixation using a cephalomedullary nail as treatment for proximal femur fracture has recently been popular for early ambulation and rehabilitation. However metal breakage at the lag screw insertion site was reported due to non-union, delayed-union, and early weight bearing. In our orthopedic department, we experienced 2 cases of nail breakage at the lag screw insertion site, therefore we report on evaluation of the cause of metal failure and prevention of complications with literature review.
- 1. Bridle SH, Patel AD, Bircher M, Calvert PT. Fixation of intertrochanteric fractures of the femur. A randomised prospective comparison of the gamma nail and the dynamic hip screw. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1991;73:330-334.PDF
- 2. Leung KS, So WS, Shen WY, Hui PW. Gamma nails and dynamic hip screws for peritrochanteric fractures. A randomised prospective study in elderly patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1992;74:345-351.PDF
- 3. Kasimatis GB, Lambiris E, Tyllianakis M, Giannikas D, Mouzakis D, Panagiotopoulos E. Gamma nail breakage: a report of four cases. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong), 2007;15:368-372.PDF
- 4. Vanderschot P, Vanderspeeten K, Verheyen L, Broos P. A review on 161 subtrochanteric fractures: risk factors influencing outcome: age, fracture pattern and fracture level. Unfallchirurg, 1995;98:265-271.
- 5. Sadowski C, Lübbeke A, Saudan M, Riand N, Stern R, Hoffmeyer P. Treatment of reverse oblique and transverse intertrochanteric fractures with use of an intramedullary nail or a 95 degrees screw-plate: a prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2002;84:372-381.
- 6. Curtis MJ, Jinnah RH, Wilson V, Cunningham BW. Proximal femoral fractures: a biomechanical study to compare intramedullary and extramedullary fixation. Injury, 1994;25:99-104.
- 7. Iwakura T, Niikura T, Lee SY, et al. Breakage of a third generation gamma nail: a case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Orthop, 2013;2013:172352. PDF
- 8. Valverde JA, Alonso MG, Porro JG, Rueda D, Larrauri PM, Soler JJ. Use of the Gamma nail in the treatment of fractures of the proximal femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1998;(350):56-61.
- 9. Zafiropoulos G, Pratt DJ. Fractured Gamma nail. Injury, 1994;25:331-336.
- 10. Alvarez DB, Aparicio JP, Fernández EL, Múgica IG, Batalla DN, Jiménez JP. Implant breakage, a rare complication with the Gamma nail. A review of 843 fractures of the proximal femur treated with a Gamma nail. Acta Orthop Belg, 2004;70:435-443.
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
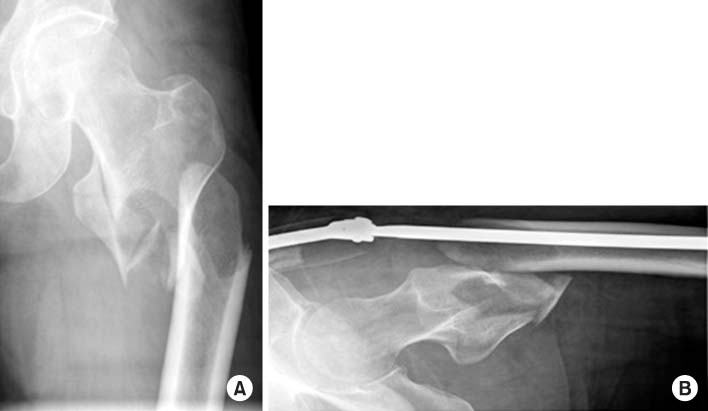
Radiographs showed an AO/OTA classification 31-A3.3, Seinsheimer classification type IIIa, Russel-Taylor classification type II-B subtrochanteric fracture of the left femur. (A) Anteroposterior view. (B) Axial view.

Fig. 2
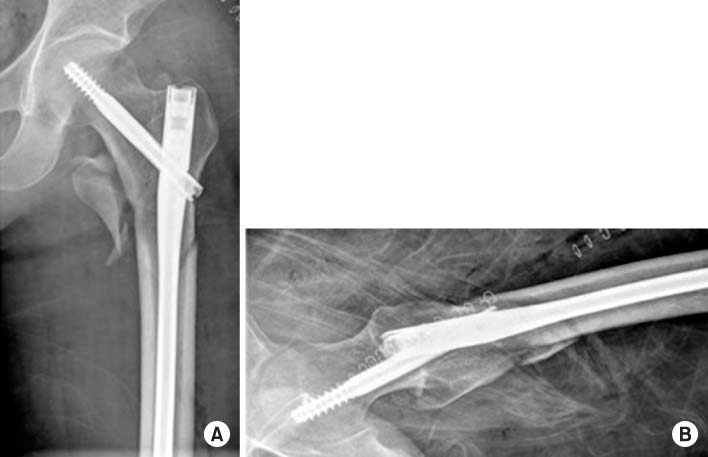
Postoperative radiographs showed long gamma nail insertion state. (A) Anteroposterior view. (B) Axial view.

Fig. 3
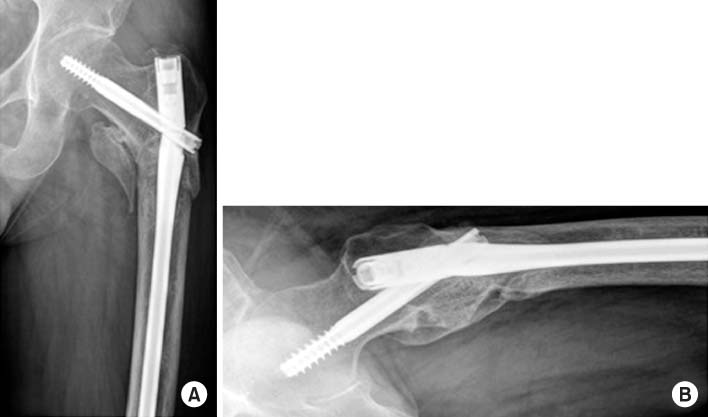
Failure of the long gamma nail through the insertion point of the lag screw at 8-month postoperative followup. (A) Anteroposterior view. (B) Axial view.

Fig. 4
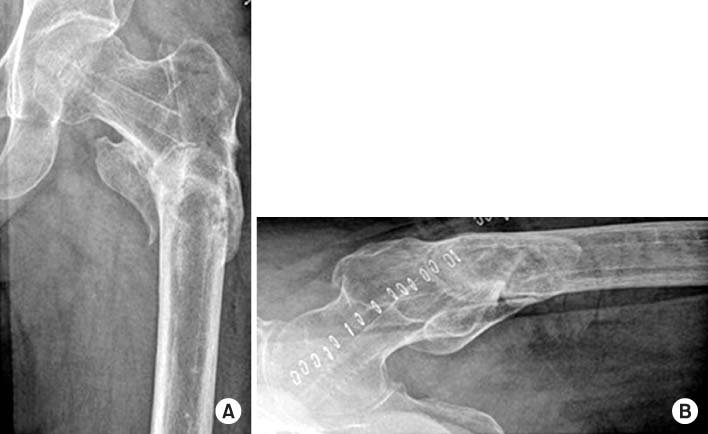
Radiographs taken at the last follow-up 1 year and 7 months postoperative, showing metal removed, and union state of the left femur. (A) Anteroposterior view. (B) Axial view.

Fig. 5
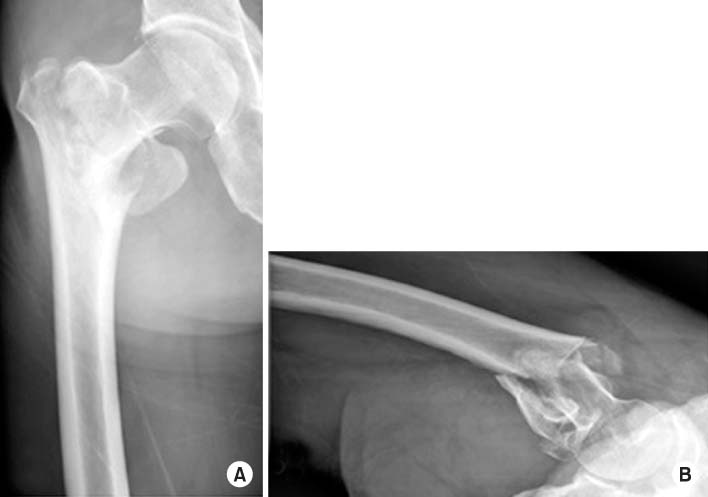
Radiographs showed an AO/OTA classification 31-A2.1, Boyd-Griffin classification type II intertrochanteric fracture of the right femur. (A) Anteroposterior view. (B) Axial view.

Fig. 6
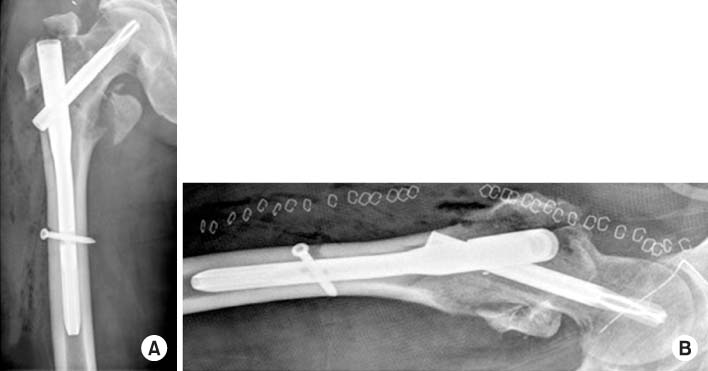
Postoperative radiographs showed proximal femoral nail antirotation insertion state. (A) Anteroposterior view. (B) Axial view.

Fig. 7
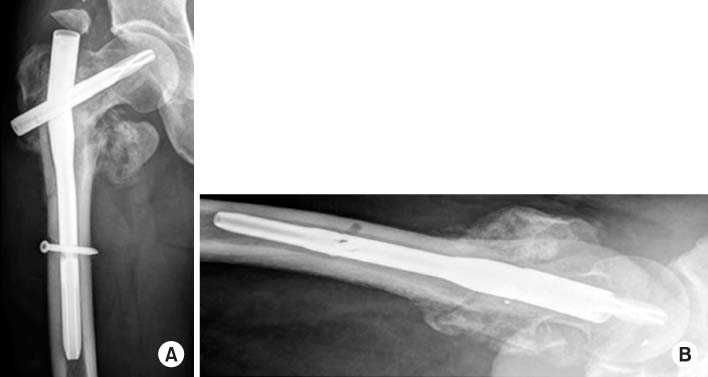
Failure of the proximal femoral nail antirotation through the insertion point of the lag screw at 4-month postoperative follow-up. (A) Anteroposterior view. (B) Axial view.

Fig. 8
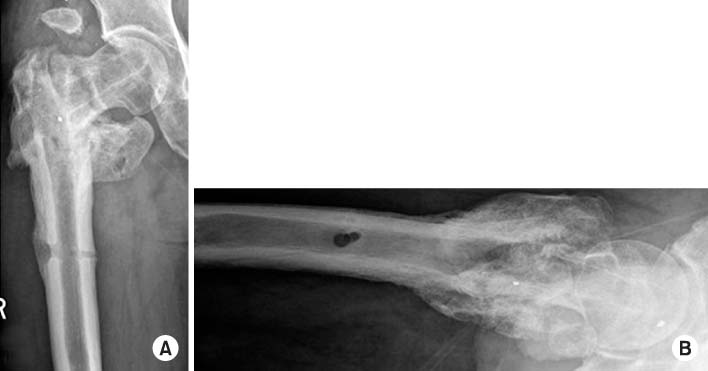
Radiographs taken at the last follow-up 1 year and 2 months postoperative, showing metal removed, and bone union state of the right femur. (A) Anteroposterior view. (B) Axial view.

Fig. 9
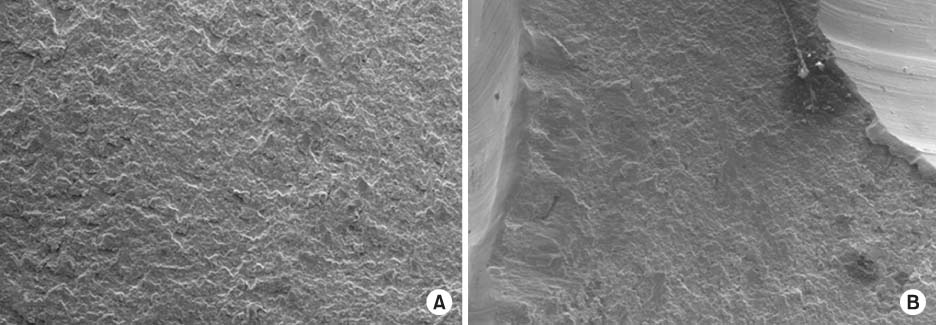
Scanning electron microscopic study (SEM) showed the implant horizontal fracture surface in the Case 2 patient. (A, B) SEM images showed a tough fracture surface indicating that a primary crack occurred by continuous stress and the final fracture was due to traumatic force from sometimes (×100).

Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Breakage of the Tail Portion of the Lag Screw during Removal of Proximal Femoral Zimmer Natural Nail: Report of Two Cases with Technical Notes
Asep Santoso, Ik-Sun Choi, Kyung-Soon Park, Taek-Rim Yoon
Hip & Pelvis.2017; 29(3): 199. CrossRef
Breakage of Cephalomedullary Nail Used in the Treatment of Proximal Femur Fractures: Case Report

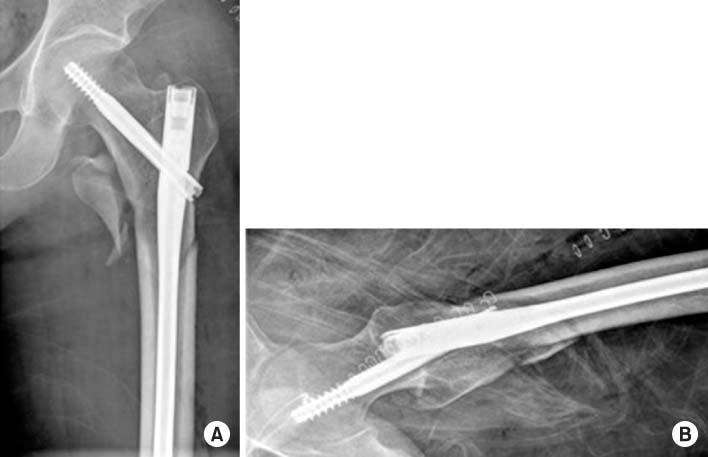
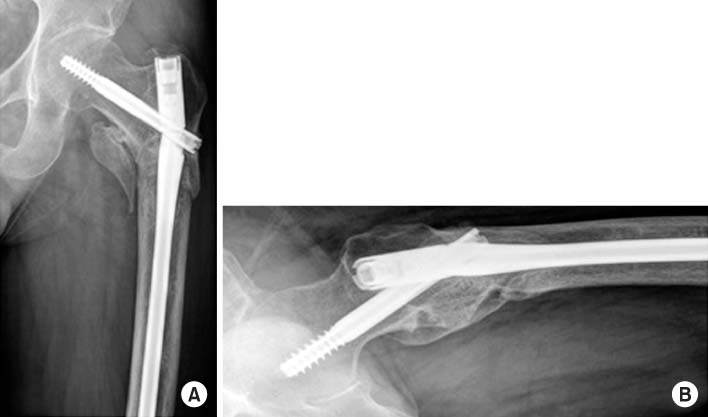
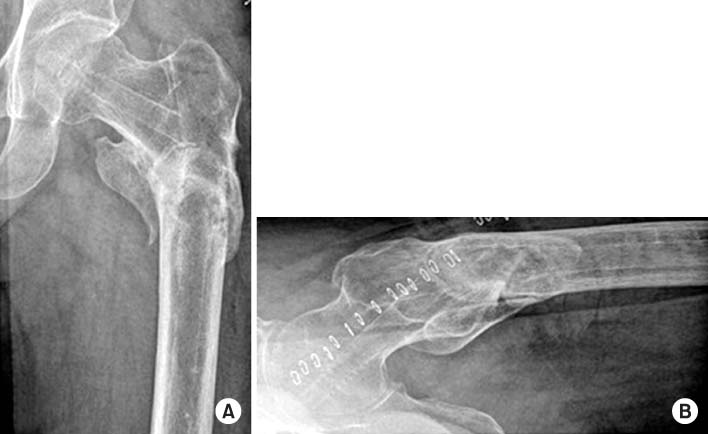
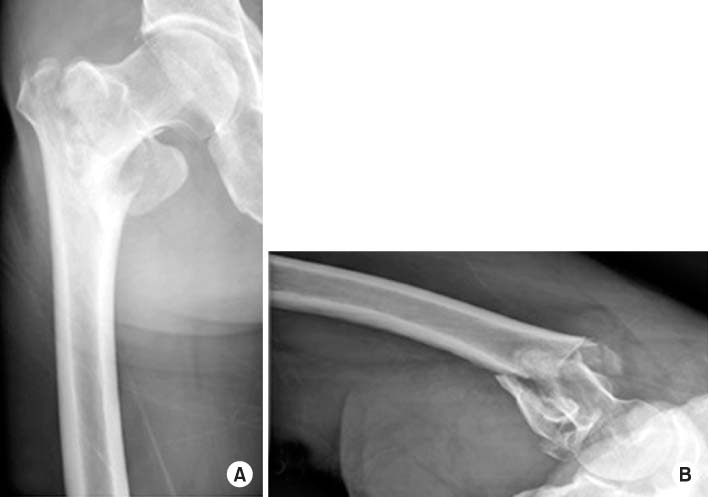
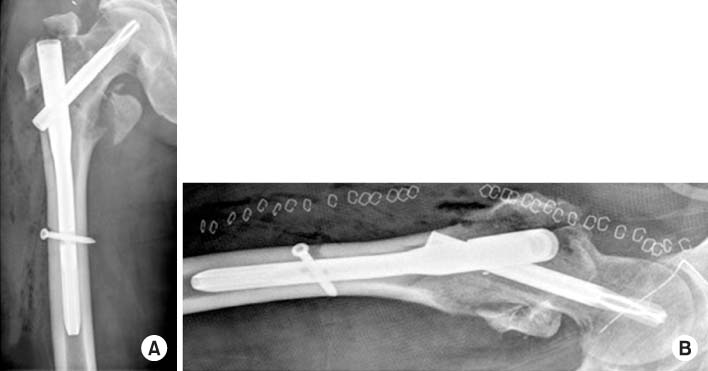
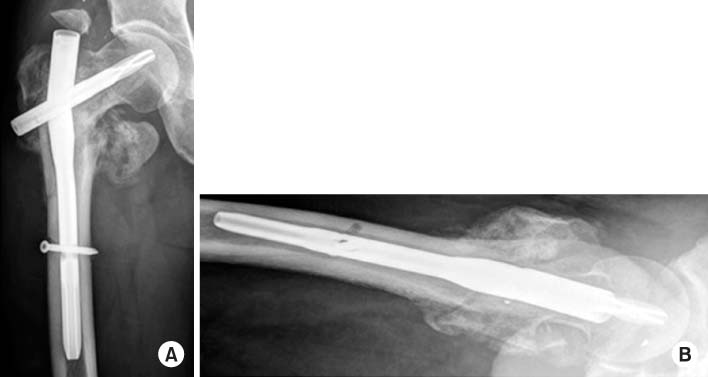
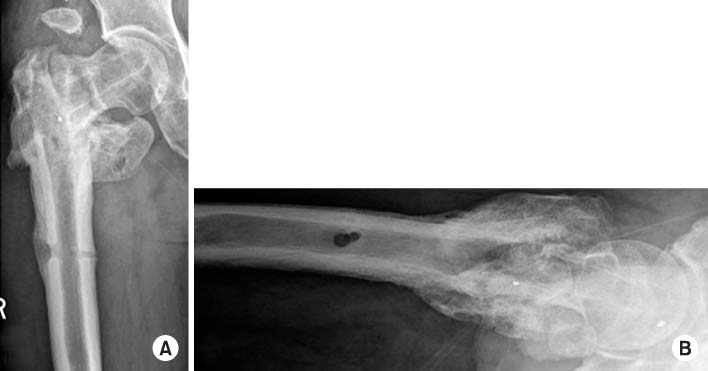
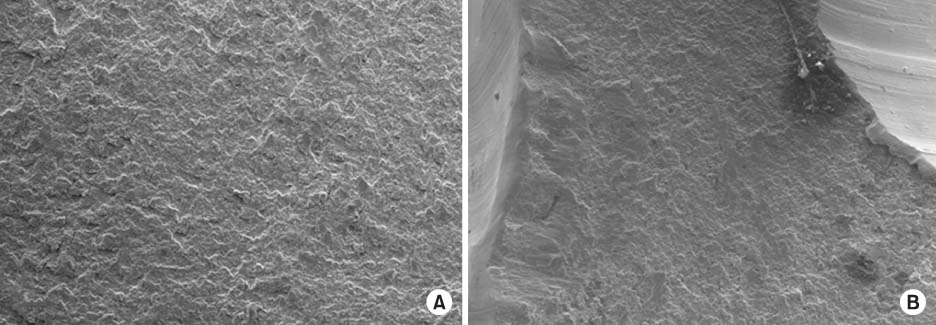
Fig. 1
Radiographs showed an AO/OTA classification 31-A3.3, Seinsheimer classification type IIIa, Russel-Taylor classification type II-B subtrochanteric fracture of the left femur. (A) Anteroposterior view. (B) Axial view.
Fig. 2
Postoperative radiographs showed long gamma nail insertion state. (A) Anteroposterior view. (B) Axial view.
Fig. 3
Failure of the long gamma nail through the insertion point of the lag screw at 8-month postoperative followup. (A) Anteroposterior view. (B) Axial view.
Fig. 4
Radiographs taken at the last follow-up 1 year and 7 months postoperative, showing metal removed, and union state of the left femur. (A) Anteroposterior view. (B) Axial view.
Fig. 5
Radiographs showed an AO/OTA classification 31-A2.1, Boyd-Griffin classification type II intertrochanteric fracture of the right femur. (A) Anteroposterior view. (B) Axial view.
Fig. 6
Postoperative radiographs showed proximal femoral nail antirotation insertion state. (A) Anteroposterior view. (B) Axial view.
Fig. 7
Failure of the proximal femoral nail antirotation through the insertion point of the lag screw at 4-month postoperative follow-up. (A) Anteroposterior view. (B) Axial view.
Fig. 8
Radiographs taken at the last follow-up 1 year and 2 months postoperative, showing metal removed, and bone union state of the right femur. (A) Anteroposterior view. (B) Axial view.
Fig. 9
Scanning electron microscopic study (SEM) showed the implant horizontal fracture surface in the Case 2 patient. (A, B) SEM images showed a tough fracture surface indicating that a primary crack occurred by continuous stress and the final fracture was due to traumatic force from sometimes (×100).
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Fig. 6
Fig. 7
Fig. 8
Fig. 9
Breakage of Cephalomedullary Nail Used in the Treatment of Proximal Femur Fractures: Case Report

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

