Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 24(1); 2011 > Article
-
Review Article from Symposium
- Epidemiology and Economic Burden of Osteoporosis in South Korea
- Yong-Chan Ha, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2011;24(1):114-120.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.1.114
Published online: January 21, 2011
- Address reprint requests to: Yong-Chan Ha, M.D. Demartment of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chung-Ang University Hospital, 224-1, Heukseok-dong, Dongjak-gu, Seoul 156-755, Korea. Tel: 82-2-6299-1591·Fax: 82-2-822-1710, hayongch@naver.com
Copyright © 2011 The Korean Fracture Society
- 847 Views
- 3 Download
- 7 Crossref
- 1. Abrahamsen B, van Staa T, Ariely R, Olson M, Cooper C. Excess mortality following hip fracture: a systematic epidemiological review. Osteoporos Int, 2009;20:1633-1650.ArticlePDF
- 2. Black DM, Arden NK, Palermo L, Pearson J, Cummings SR. Prevalent vertebral deformities predict hip fractures and new vertebral deformities but not wrist fractures. Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group. J Bone Miner Res, 1999;14:821-828.Article
- 3. Clark P, Lavielle P, Franco-Marina F, et al. Incidence rates and life-time risk of hip fractures in Mexicans over 50 years of age: a population-based study. Osteoporos Int, 2005;16:2025-2030.ArticlePDF
- 4. Consensus development conference: diagnosis, prophylaxis, and treatment of osteoporosis . Am J Med, 1993;94:646-650.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Cooper C, Campion G, Melton LJ 3rd. Hip fractures in the elderly: a world-wide projection. Osteoporos Int, 1992;2:285-289.ArticlePDF
- 6. Cornwall R, Gilbert MS, Koval KJ, Strauss E, Siu AL. Functional outcomes and mortality vary among different types of hip fractures: a function of patient characteristics. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 2004;425:64-71.Article
- 7. Ha YC, Kim SR, Koo KH, et al. An epidemiological study of hip fracture in Jeju Island, Korea. J Korean Orthop Assoc, 2004;39:131-136.ArticlePDF
- 8. Ha YC, Lee JS, An SH, et al. An epidemiological study of osteoporosis in ibansung-meon, Jinju, by using quantitative ultrasound. Korean J Bone Metab, 2005;12:217-223.Article
- 9. Hagino H, Katagiri H, Okano T, Yamamoto K, Teshima R. Increasing incidence of hip fracture in Tottori Prefecture, Japan: trend from 1986 to 2001. Osteoporos Int, 2005;16:1963-1968.ArticlePDF
- 10. Ho SC, Bacon WE, Harris T, Looker A, Maggi S. Hip fracture rates in Hong Kong and the United States, 1988 through 1989. Am J Public Health, 1993;83:694-697.Article
- 11. Iki M, Kagamimori S, Kagawa Y, Matsuzaki T, Yoneshima H, Marumo F. Bone mineral density of the spine, hip and distal forearm in representative samples of the Japanese female population: Japanese Population-Based Osteoporosis (JPOS) Study. Osteoporos Int, 2001;12:529-537.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 12. Jang S, Park CM, Jang SH, et al. Medical Service Utilization with Osteoporosis. Endocrinol Metab, 2010;25:326-339.Article
- 13. Kado DM, Browner WS, Palermo L, Nevitt MC, Genant HK, Cummings SR. Vertebral fractures and mortality in older women: a prospective study. Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group. Arch Intern Med, 1999;159:1215-1220.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Kang HY, Kang DR, Jang YH, et al. Estimating the economic burden of osteoporotic vertebral fracture among elderly Korean women. J Prev Med Public Health, 2008;41:287-294.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Kang HY, Yang KH, Kim YN, et al. Incidence and mortality of hip fracture among the elderly population in South Korea: a population-based study using the national health insurance claims data. BMC Public Health, 2010;10:230. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 16. Kanis JA, Johnell O, Oden A, et al. Intervention thresholds for osteoporosis in men and women: a study based on data from Sweden. Osteoporos Int, 2005;16:6-14.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 17. Kenzora JE, McCarthy RE, Lowell JD, Sledge CB. Hip fracture mortality Relation to age, treatment, preoperative illness, time of surgery, and complications. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1984;186:45-56.Article
- 18. Kim SR, Ha YC, Kim JR, Kim R, Kim SY, Koo KH. Incidence of hip fractures in jeju island, South Korea: a prospective study (2002-2006). Clin Orthop Surg, 2010;2:64-68.Article
- 19. Kirke PN, Sutton M, Burke H, Daly L. Outcome of hip fracture in older Irish women: a 2-year follow-up of subjects in a case-control study. Injury, 2002;33:387-391.Article
- 20. Korea National Statistical Office. STAT-Korea, 2009;(http://www.nso.go.kr).Article
- 21. Koval KJ, Aharonoff GB, Rokito AS, Lyon T, Zuckerman JD. Patients with femoral neck and intertrochanteric fractures. Are they the same? Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1996;330:166-172.Article
- 22. Lau E, Ong K, Kurtz S, Schmier J, Edidin A. Mortality following the diagnosis of a vertebral compression fracture in the Medicare population. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2008;90:1479-1486.Article
- 23. Lau EM, Lee JK, Suriwongpaisal P, et al. The incidence of hip fracture in four Asian countries: the Asian Osteoporosis Study (AOS). Osteoporos Int, 2001;12:239-243.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 24. Lee SR, Kim SR, Chung KH, et al. Mortality and activity after hip fracture: a prospective study. J Korean Orthop Assoc, 2005;40:423-427.ArticlePDF
- 25. Lim S, Koo BK, Lee EJ, et al. Incidence of hip fractures in Korea. J Bone Miner Metab, 2008;26:400-405.ArticlePDF
- 26. Lofthus CM, Osnes EK, Falch JA, et al. Epidemiology of hip fractures in Oslo, Norway. Bone, 2001;29:413-418.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Looker AC, Orwoll ES, Johnston CC Jr, et al. Prevalence of low femoral bone density in older U.S. adults from NHANES III. J Bone Miner Res, 1997;12:1761-1768.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 28. Miller CW. Survival and ambulation following hip fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1978;60:930-934.ArticlePubMed
- 29. NIH consensus development panel on osteoporosis prevention, diagnosis, and therapy, march 7-29, 2000: highlights of the conference. South Med J, 2001;94:569-573.ArticlePubMed
- 30. Ray NF, Chan JK, Thamer M, Melton LJ 3rd. Medical expenditures for the treatment of osteoporotic fractures in the United States in 1995: report from the National Osteoporosis Foundation. J Bone Miner Res, 1997;12:24-35.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 31. Rowe SM, Song EK, Kim JS, et al. Rising incidence of hip fracture in Gwangju City and Chonnam Province, Korea. J Korean Med Sci, 2005;20:655-658.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 32. Rowe SM, Yoon TR, Ryang DH. An epidemiological study of hip fracture in Honam, Korea. Int Orthop, 1993;17:139-143.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 33. Sanders KM, Seeman E, Ugoni AM, et al. Age- and gender-specific rate of fractures in Australia: a population-based study. Osteoporos Int, 1999;10:240-247.Article
- 34. Shin A, Choi JY, Chung HW, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of distal radius and calcaneus bone mineral density in Korean population. Osteoporos Int, 2004;15:639-644.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 35. Shin CS, Choi HJ, Kim MJ, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of osteoporosis in Korea: a community-based cohort study with lumbar spine and hip bone mineral density. Bone, 2010;47:378-387.ArticlePubMed
- 36. The Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survery (KNHANES IV-2), Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.Article
- 37. Tsuboi M, Hasegawa Y, Suzuki S, Wingstrand H, Thorngren KG. Mortality and mobility after hip fracture in Japan: a ten-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2007;89:461-466.ArticlePubMed
- 38. Yang NP, Deng CY, Chou YJ, et al. Estimated prevalence of osteoporosis from a Nationwide Health Insurance database in Taiwan. Health Policy, 2006;75:329-337.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- A Study of Prevalence and Awareness of Low Bone Density of Female Utilizing Dental Panoramic Radiographs
Sung Jin Kim, In-Ja Song, Eun Joo Lee, Suk-Ja Yoon
The Korean Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology.2024; 48(3): 23. CrossRef - Cost-effectiveness Analysis of Conservative Treatment, Vertebroplasty, and Balloon Kyphoplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures in South Korea
Hee Jung Son, Sung Hoon Choi, Ji Won Jung, Dong Hong Kim, Hyun Sik Shin, Chang-Nam Kang
Journal of Korean Society of Spine Surgery.2023; 30(2): 53. CrossRef - Sex Difference in the Socioeconomic Burden of Osteoporosis among South Koreans
Eun-Whan Lee, Jin Young Nam
Healthcare.2021; 9(10): 1304. CrossRef - Association between Metabolic Syndrome and Osteoporosis in Korean Adults Aged Over 50 Years Old Using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2016-2017
Hyeon Hwa Lee, Mi Ah Han, Jong Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2019; 44(3): 245. CrossRef - Cost-Effectiveness of Denosumab for Post-Menopausal Osteoporosis in South Korea
Green Bae, Hye-Young Kwon
Korean Journal of Clinical Pharmacy.2018; 28(2): 131. CrossRef - Gender Differences and Socioeconomic Factors Related to Osteoporosis: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of Nationally Representative Data
Jin-Won Noh, Hyunchun Park, Minji Kim, Young Dae Kwon
Journal of Women's Health.2018; 27(2): 196. CrossRef - Comparison of Musculoskeletal Characteristics and Bone Mineral Density Related Factors between Male and Female University Students
Seung-Hye Choi, Haeyoung Lee, MiJeong Park, Seungmi Park
Journal of muscle and joint health.2013; 20(3): 161. CrossRef
Epidemiology and Economic Burden of Osteoporosis in South Korea
Epidemiology and Economic Burden of Osteoporosis in South Korea
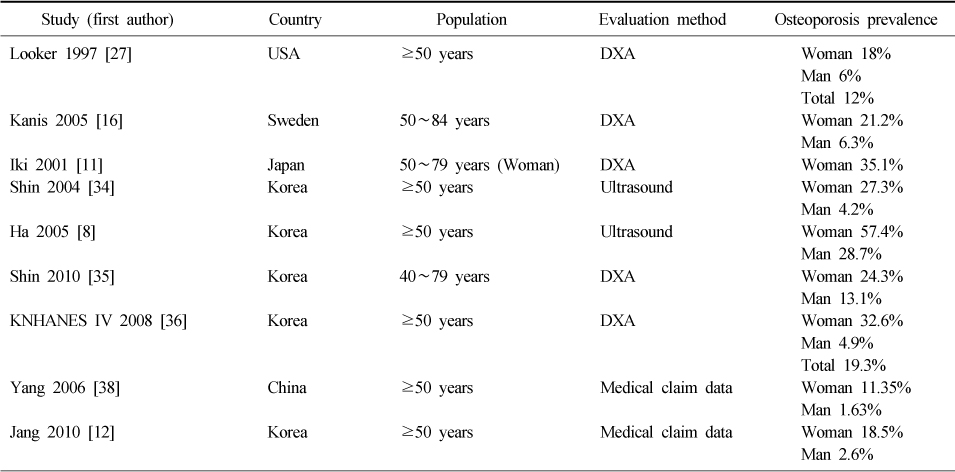
Summary of studies of the osteoporosis prevalences
DXA: Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry.
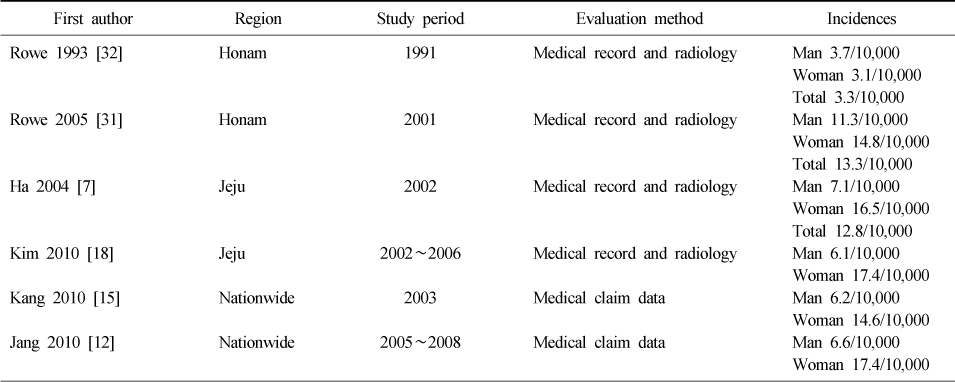
Sumamry of hip fracture incidence in Korea
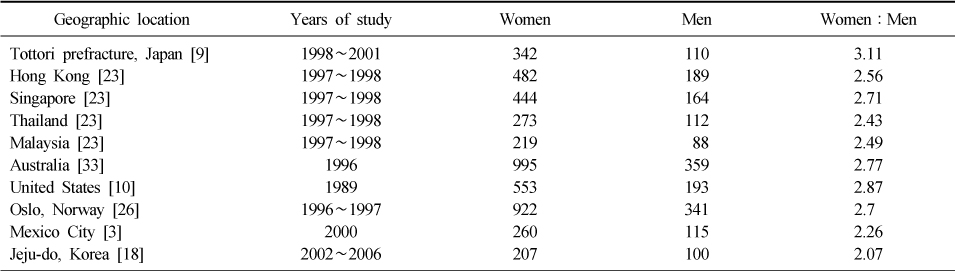
Geographical variation of hip fracture incidence (per 100,000)
Incidence figures are age adjusted to the 1990 U.S. Caucasian civilians ≥50 years of age.
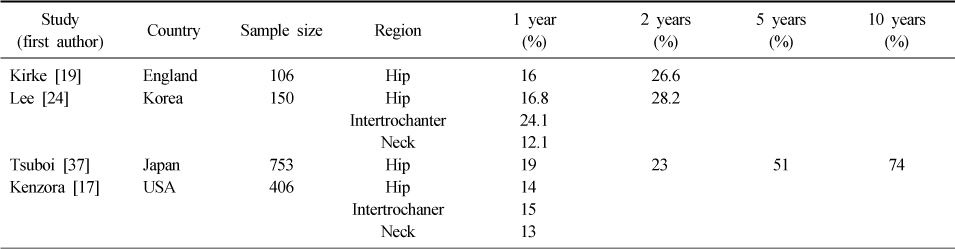
Summary of hip fracture mortality rates
Table 1
Summary of studies of the osteoporosis prevalences
DXA: Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry.
Table 2
Sumamry of hip fracture incidence in Korea
Table 3
Geographical variation of hip fracture incidence (per 100,000)
Incidence figures are age adjusted to the 1990 U.S. Caucasian civilians ≥50 years of age.
Table 4
Summary of hip fracture mortality rates

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

