Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Risk factors for ankle fractures in older adults based on clinical components of the Fracture Risk Assessment (FRAX) tool and comorbidities in Korea: a retrospective case-control study
- Myeong Jun Song, Se Woong Jang, Jun Young Lee, Seojin Park
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):193-202. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Ankle fractures are common in older adults; however, their relationship with osteoporotic fractures remains unclear. This study aimed to evaluate potential risk factors for ankle fractures in older adults by analyzing individual clinical components of the Fracture Risk Assessment (FRAX) tool and comorbidities.
Methods
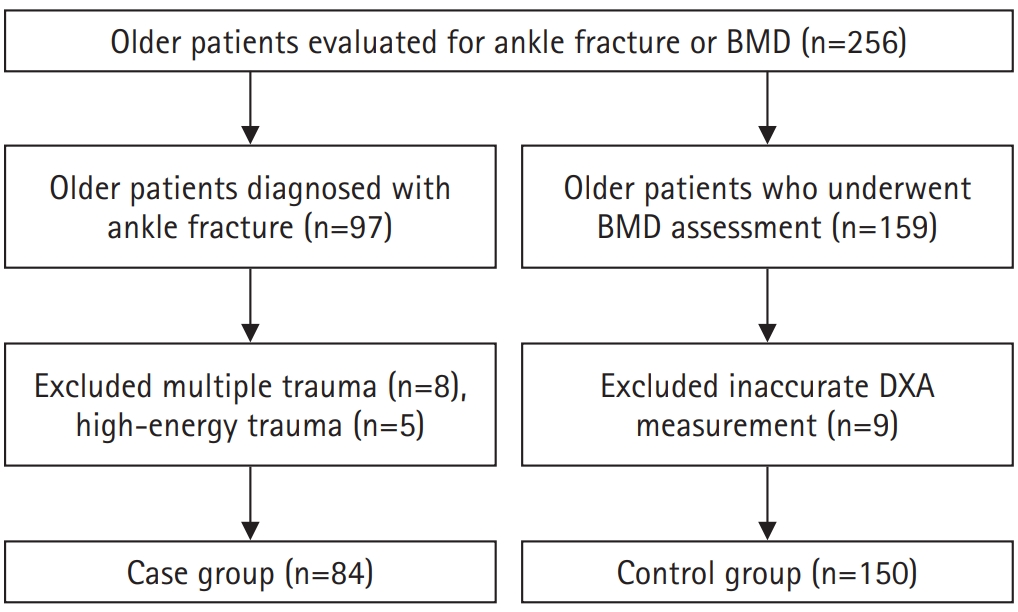
We conducted a retrospective case-control study including 84 patients aged ≥65 years with ankle fractures and 150 controls who underwent bone mineral density (BMD) testing without prior ankle fractures. The variables analyzed included age, sex, body mass index, smoking, alcohol consumption, prior fracture history, and comorbidities such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and dementia. BMD was measured at the spine, total hip, and femoral neck.
Results
Univariate analysis showed that alcohol consumption, diabetes mellitus, and total hip T-score categories were significantly associated with ankle fractures. In binary logistic regression, alcohol consumption remained significantly associated with higher ankle fracture risk (odds ratio [OR], 5.302; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.778–15.811; P=0.003), and both osteopenia and osteoporosis at the total hip were also associated with increased risk (OR, 3.260, P=0.049; OR, 3.561, P=0.031, respectively). Diabetes mellitus did not reach statistical significance in the adjusted model (P=0.074). Model fit was adequate (Hosmer-Lemeshow P=0.377), and post hoc power analysis confirmed sufficient sample size.
Conclusions
These findings suggest that lower total hip BMD and alcohol-related factors may be associated with ankle fracture risk in older adults. The FRAX score itself was not calculated; instead, this study focused on analyzing selected clinical components. Limitations include the retrospective design, lack of fall and medication data, and cross-sectional BMD assessment. Level of evidence: III.
- 1,046 View
- 21 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 First
First Prev
Prev


