Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Risk factors for ankle fractures in older adults based on clinical components of the Fracture Risk Assessment (FRAX) tool and comorbidities in Korea: a retrospective case-control study
- Myeong Jun Song, Se Woong Jang, Jun Young Lee, Seojin Park
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):193-202. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Ankle fractures are common in older adults; however, their relationship with osteoporotic fractures remains unclear. This study aimed to evaluate potential risk factors for ankle fractures in older adults by analyzing individual clinical components of the Fracture Risk Assessment (FRAX) tool and comorbidities.
Methods
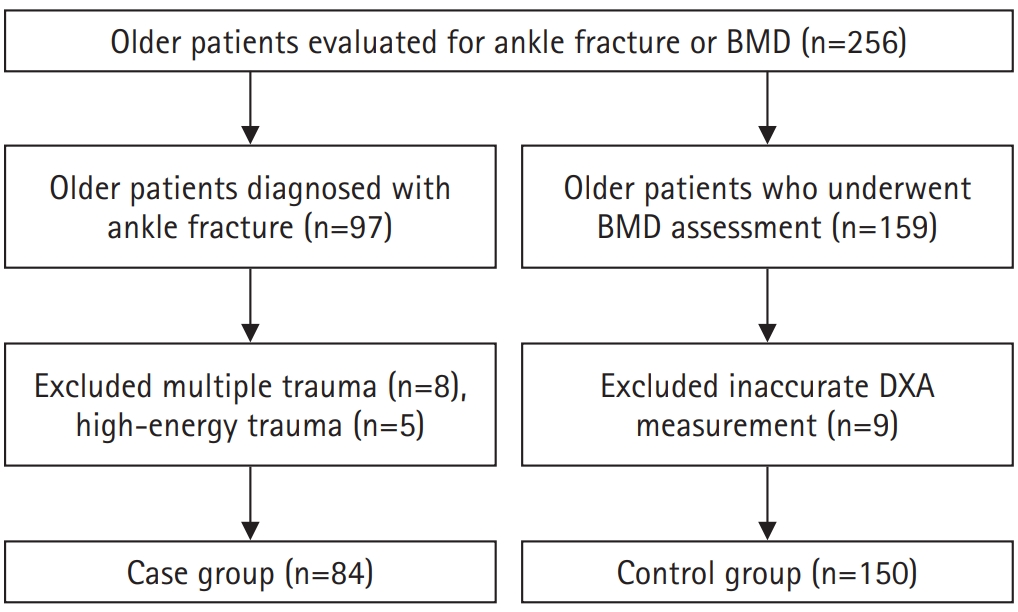
We conducted a retrospective case-control study including 84 patients aged ≥65 years with ankle fractures and 150 controls who underwent bone mineral density (BMD) testing without prior ankle fractures. The variables analyzed included age, sex, body mass index, smoking, alcohol consumption, prior fracture history, and comorbidities such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and dementia. BMD was measured at the spine, total hip, and femoral neck.
Results
Univariate analysis showed that alcohol consumption, diabetes mellitus, and total hip T-score categories were significantly associated with ankle fractures. In binary logistic regression, alcohol consumption remained significantly associated with higher ankle fracture risk (odds ratio [OR], 5.302; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.778–15.811; P=0.003), and both osteopenia and osteoporosis at the total hip were also associated with increased risk (OR, 3.260, P=0.049; OR, 3.561, P=0.031, respectively). Diabetes mellitus did not reach statistical significance in the adjusted model (P=0.074). Model fit was adequate (Hosmer-Lemeshow P=0.377), and post hoc power analysis confirmed sufficient sample size.
Conclusions
These findings suggest that lower total hip BMD and alcohol-related factors may be associated with ankle fracture risk in older adults. The FRAX score itself was not calculated; instead, this study focused on analyzing selected clinical components. Limitations include the retrospective design, lack of fall and medication data, and cross-sectional BMD assessment. Level of evidence: III.
- 287 View
- 12 Download

- Morbidity and Mortality of the Elderly after Early Operation for Trochanteric Fractures
- Se Ang Jang, Young Ho Cho, Young Soo Byun, Ki Hong Park, Hyun Seong Yoo, Chul Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(3):199-204. Published online July 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.3.199
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To find out the effect of early closed reduction and internal fixation (within 24 hours after admission to hospital) on the morbidity and mortality in the elderly with intertrochanteric fractures of the femur.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Retrospectively, we analyzed 99 patients with intertrochanteric fracture of the femur who underwent surgery from January, 2009 to December, 2010. We reviewed 89 of the 99 patients and checked for early complications and reviewed the mortality rates 3 months, 6 months and 1 year after surgery. There were 24 males and 65 females. The average age was 79.8 years (61-99 years). According to the American Society of Anesthesiologists classification, 25 patients were class 1, 37 patients were class 2, 26 patients were class 3, and 1 patient was class 4. All patients were operated on by one surgeon, who was skilled in inserting intramedullary nail.
RESULTS
The average surgical time was 43 minutes and the average intraoperative blood loss was 165 ml. Sixteen patients experienced delirium but all of them recovered. One patient had pneumonia at one month after surgery. Pressure sores developed in one patient but improved with conservative treatment. Pulmonary thromboembolism developed in some patients one month after surgery. Three patients (3.4%) died within three months and one patient (1.1%) died between three and six months after surgery, but no patient died between six months and one year after surgery.
CONCLUSION
If patients are optimized for the operation, early internal fixation of trochanteric fracture in elderly patients after arrival at the hospital should be considered to reduce early complications and mortality. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- PREOPERATIVE NUTRITIONAL STATUS OF HIP FRACTURE PATIENTS: A PILOT STUDY IN 116 PATIENTS
Myung-Sang Moon, Min-Suk Park, Bong-Keun Park, Dong-Hyeon Kim, Min-Geun Yoon
Journal of Musculoskeletal Research.2017; 20(01): 1750002. CrossRef
- PREOPERATIVE NUTRITIONAL STATUS OF HIP FRACTURE PATIENTS: A PILOT STUDY IN 116 PATIENTS
- 474 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Morbidity and Mortality of Bilateral Hip Fractures in Elderly Patients
- Suk Ku Han, Nam Yong Choi, Seong Jin Park, Seong Keun Lee, Chan Woong Moon
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(4):788-794. Published online October 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.4.788
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to estimate the morbidity and mortality rate of bilateral hip fractures in elderly patients compared to that in unilateral hip fractures and to evaluate it's related risk factors.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty-two cases of bilateral hip fractures in patients who were older than 70 years with at least two year follow-up were included in our study. We analysed the risk factors of bilateral hip fractures by comparing with age, sex and diagnosis matched 22 cases of ipsilateral hip fractures including onset of secondary fracture, injury mechanism and the rate of morbidity and mortality, respectively.
RESULTS
The onset of secondary fracture and death were mostly within 1 year after operation for the first hip fracture. Comorbidity of cardiovascular, neurologic, urologic or history of previous fracture and decreased ambulation ability were related with the occurrence of bilateral hip fractures. The rate of morbidity and mortality of bilateral hip fractures were about two- fold than that of ipsilateral hip fractures. High mortality rate was noted in patients who had operation delay from injury. But no significant relationship between nutrition, body weight or bone mineral density and the development of secondary hip fractures.
CONCLUSION
To prevent the occurence of bilateral hip fractures which had more serious results than that of ipsilateral hip fractures, more aggressive rehabilitation to improve walking ability and appropriate environmental circumstances to avoid falls were important, especially in older patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of the Clinical Features of Bilateral Sequential Hip Fractures in the Elderly
Duk-Hwan Kho, Ju-Yong Shin, Hyeung-June Kim, Dong-Heon Kim
The Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2009; 44(3): 369. CrossRef
- Assessment of the Clinical Features of Bilateral Sequential Hip Fractures in the Elderly
- 501 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


