Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 30(3); 2017 > Article
-
Review Article
- Osteotomy Selection: Advantages, Disadvantages, and Indication
-
Ki-Chul Park, M.D.
 , Hyun Uk Kim, M.D.
, Hyun Uk Kim, M.D. , Young-Sik Song, M.D.
, Young-Sik Song, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2017;30(3):167-172.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.3.167
Published online: July 21, 2017
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Guri, Korea.
- Correspondence to: Ki-Chul Park, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, 153 Gyeongchun-ro, Guri 11923, Korea. Tel: +82-31-560-2187, Fax: +82-31-557-8781, kcpark@hanyang.ac.kr
Copyright © 2017 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 723 Views
- 8 Download
Abstract
- Malunion causes not only cosmetic problems, but also degenerative osteoarthritis due to changes in the anatomical and mechanical axes. Corrective osteotomy may be required in some cases to prevent these complications. The corrective osteotomy is divided into two types: Straight and dome. The straight type is divided into open and closed wedge, in accordance with the correction method. Surgeons should understand the indication, surgical procedure, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of each osteotomy method. Deciding on the method of corrective osteotomy depends on the degree of angulation, soft tissue condition, approximate with joint, implant type, and the experience of the surgeon.
- 1. Weber D, Weber M. Corrective osteotomies for malunited malleolar fractures. Foot Ankle Clin, 2016;21:37-48.PubMed
- 2. Sanders R, Anglen JO, Mark JB. Oblique osteotomy for the correction of tibial malunion. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1995;77:240-246.PubMed
- 3. Bråten M, Terjesen T, Rossvoll I. Torsional deformity after intramedullary nailing of femoral shaft fractures. Measurement of anteversion angles in 110 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1993;75:799-803.PubMed
- 4. Dunlap K, Shands AR Jr, Hollister LC Jr, Gaul JS Jr, Streit HA. A new method for determination of torsion of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1953;35:289-311.PubMed
- 5. Murphy SB, Simon SR, Kijewski PK, Wilkinson RH, Griscom NT. Femoral anteversion. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1987;69:1169-1176.PubMed
- 6. Johnson KD, Johnston DW, Parker B. Comminuted femoral-shaft fractures: treatment by roller traction, cerclage wires and an intramedullary nail, or an interlocking intramedullary nail. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1984;66:1222-1235.PubMed
- 7. Mize RD, Bucholz RW, Grogan DP. Surgical treatment of displaced, comminuted fractures of the distal end of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1982;64:871-879.PubMed
- 8. Wright JG, Treble N, Feinstein AR. Measurement of lower limb alignment using long radiographs. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1991;73:721-723.PubMedPDF
- 9. Hollister AM, Jatana S, Singh AK, Sullivan WW, Lupichuk AG. The axes of rotation of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1993;(290):259-268.
- 10. Paley D, Tetsworth K. Mechanical axis deviation of the lower limbs. Preoperative planning of uniapical angular deformities of the tibia or femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1992;(280):48-64.
- 11. Psley D. Principles of deformity correction. New York: Spring; 2002. p. 102-108.
- 12. Paley D, Herzenberg JE, Tetsworth K, McKie J, Bhave A. Deformity planning for frontal and sagittal plane corrective osteotomies. Orthop Clin North Am, 1994;25:425-465.PubMed
- 13. Krackow KA, Pepe CL, Galloway EJ. A mathematical analysis of the effect of flexion and rotation on apparent varus/valgus alignment at the knee. Orthopedics, 1990;13:861-868.PubMed
- 14. Paccola CA. A simplified way of determining the direction of a single-cut osteotomy to correct combined rotational and angular deformities of long bones. Rev Bras Ortop, 2011;46:329-334.PubMed
- 15. Johnson EE. Multiplane correctional osteotomy of the tibia for diaphyseal malunion. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1987;(215):223-232.
- 16. Sangeorzan BJ, Sangeorzan BP, Hansen ST Jr, Judd RP. Mathematically directed single-cut osteotomy for correction of tibial malunion. J Orthop Trauma, 1989;3:267-275.PubMed
- 17. Russell GV, Graves ML, Archdeacon MT, Barei DP, Brien GA Jr, Porter SE. The clamshell osteotomy: a new technique to correct complex diaphyseal malunions. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2009;91:314-324.PubMed
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
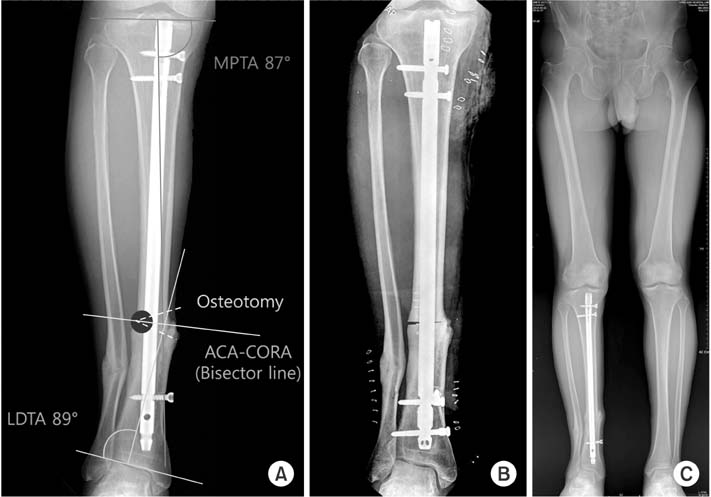
(A) There was valgus malalignment after tibia nailing. Closing wedge osteotomy was planned and angulation correction axis-center of rotation of angulation (ACA-CORA) was on the concave axis. (B) Intramedullary nail was inserted after the closing wedge osteotomy. (C) Postoperative 6 months radiography shows good alignment with bone union. MPTA: medial proximal tibial angle, LDTA: lateral distal tibial angle.

Fig. 2
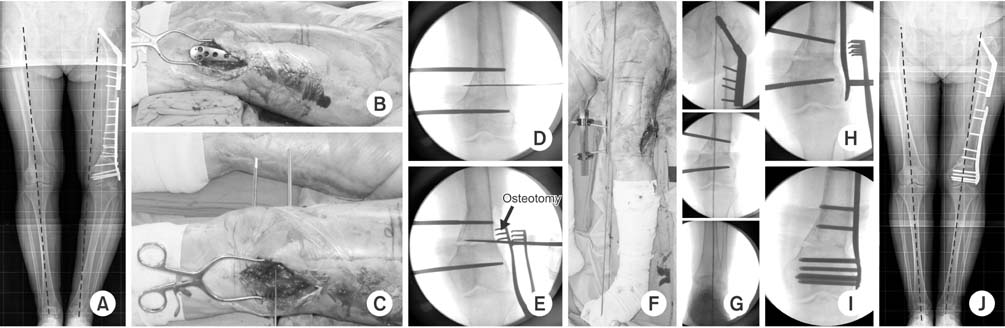
(A) There was a varus malalignment after distal femur minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO). Open wedge osteotomy was planned. (B) The plate was removed through the previous operation site. (C, D) Two shanz pins were inserted into the medial side for deformity correction. (E) Osteotomy was performed at the center of rotation of angulation. (F, G) Two shanz pins were distracted until the mechanical axis showed normal alignment. (H, I) Locking plate was applied using the MIPO technique. (J) Postoperative 10 months radiography shows good alignment with bone union (image courtesy of CW Oh, MD, Kyungpook National University, thank you for your courtesy).

Fig. 3
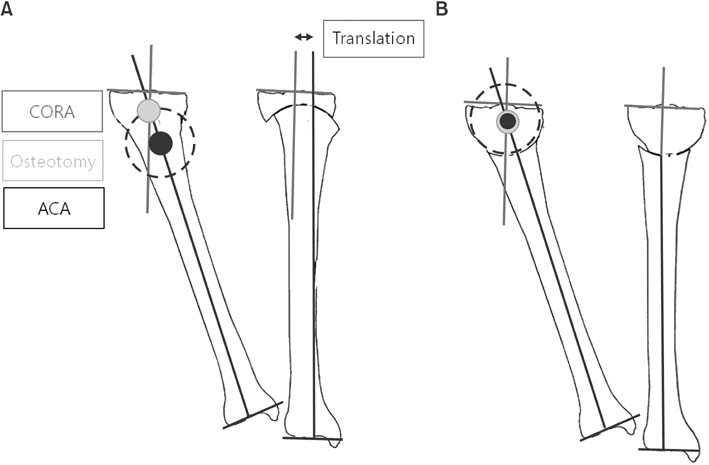
(A) When the center of rotation of angulation (CORA) and angulation correction axis (ACA) are not the same, dome osteotomy will cause translation of the proximal and distal bone axes. (B) When the CORA and ACA are the same, dome osteotomy will correct the angulation deformity without translation.

Fig. 4
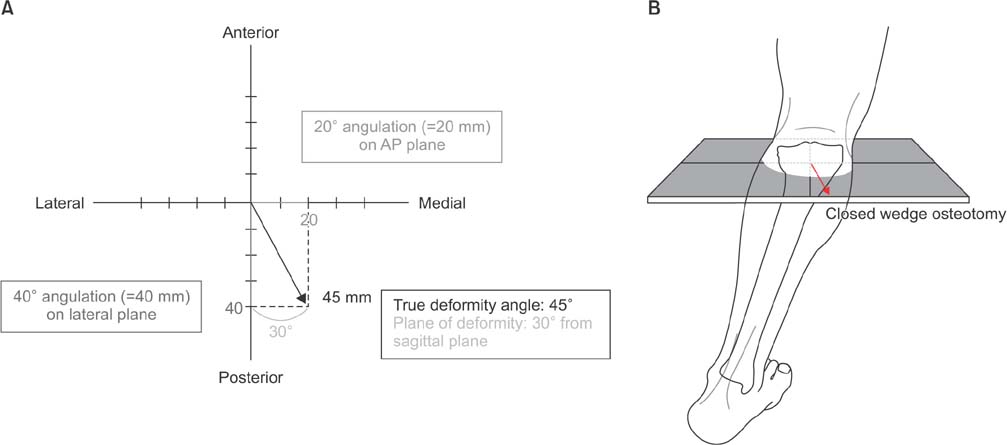
Graphic method. (A) Magnitude of angulation angulation was measured on anteroposterior (AP) and lateral radiographs (1 mm=1°). True deformity angle was 45° and 30° from the sagittal plane. (B) Closed wedge osteotomy is performed on the forward angulation correction axis (ACA), and opening wedge osteotomy is performed on the backward ACA.

Fig. 5
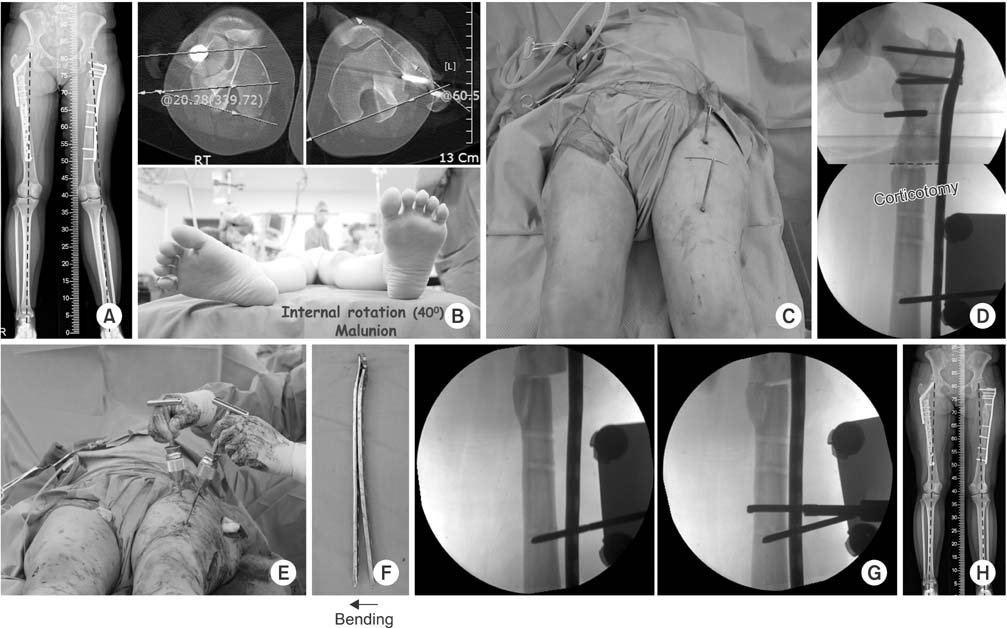
(A) There was a valgus malalignment after proximal femur minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO). (B) The angle of 40° internal rotation deformity was found on the computed tomography and physical examination. (C) Two parallel shanz pins were inserted into the proximal and distal segments to correct the rotational deformity after plate removal. (D) Osteotomy was performed at the center of rotation of angulation. (E) Distal shanz pin was externally rotated until the lessor trochanter shape showed to be the same as the opposite site. (F) The plate was bent 8° varus compared with the previous plate to correct the valgus deformity. (G) Locking plate was applied using the MIPO technique. (H) Postoperative 4 months radiography shows good alignment.

Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

Osteotomy Selection: Advantages, Disadvantages, and Indication
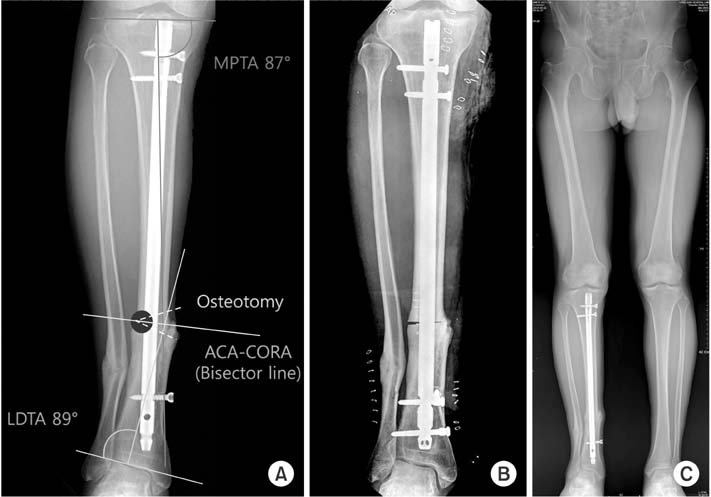
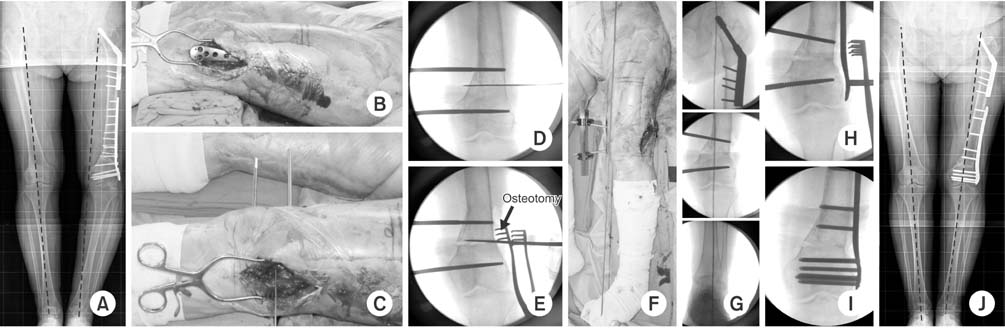
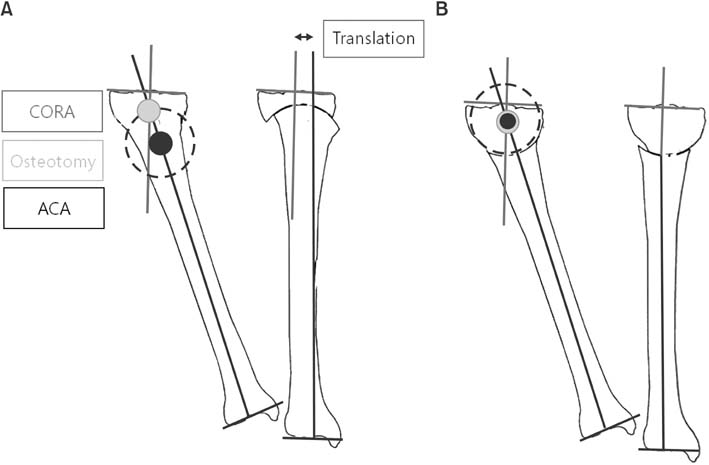
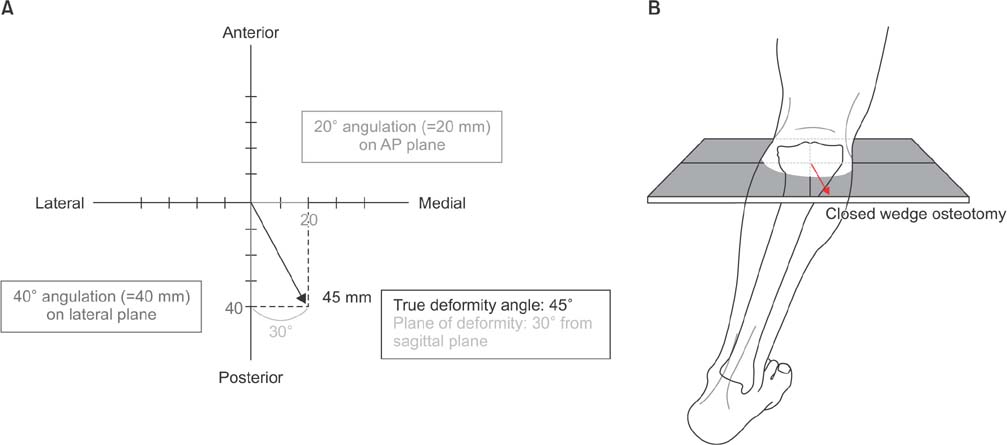
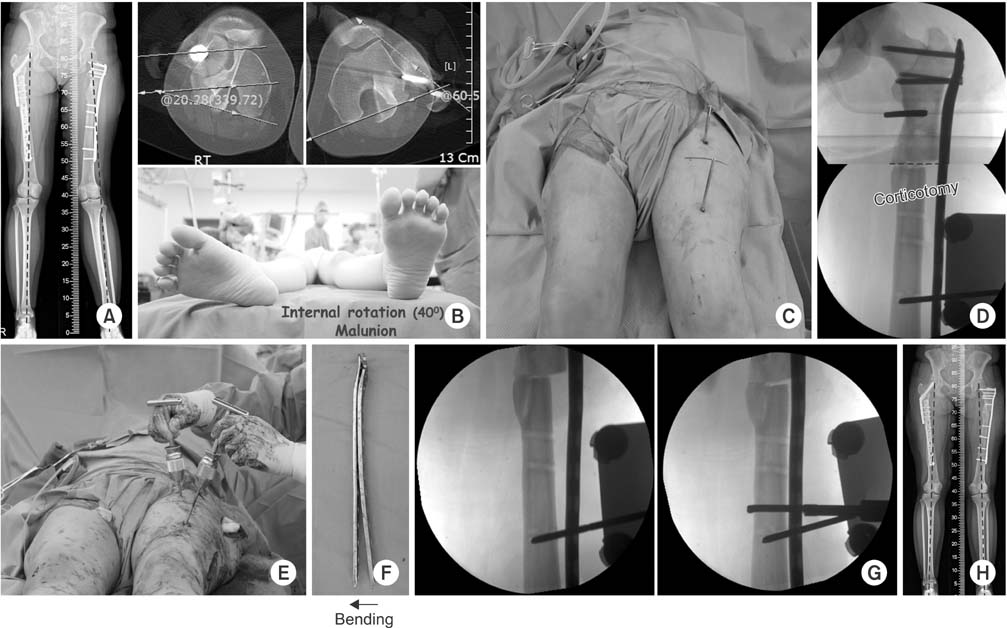
Fig. 1
(A) There was valgus malalignment after tibia nailing. Closing wedge osteotomy was planned and angulation correction axis-center of rotation of angulation (ACA-CORA) was on the concave axis. (B) Intramedullary nail was inserted after the closing wedge osteotomy. (C) Postoperative 6 months radiography shows good alignment with bone union. MPTA: medial proximal tibial angle, LDTA: lateral distal tibial angle.
Fig. 2
(A) There was a varus malalignment after distal femur minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO). Open wedge osteotomy was planned. (B) The plate was removed through the previous operation site. (C, D) Two shanz pins were inserted into the medial side for deformity correction. (E) Osteotomy was performed at the center of rotation of angulation. (F, G) Two shanz pins were distracted until the mechanical axis showed normal alignment. (H, I) Locking plate was applied using the MIPO technique. (J) Postoperative 10 months radiography shows good alignment with bone union (image courtesy of CW Oh, MD, Kyungpook National University, thank you for your courtesy).
Fig. 3
(A) When the center of rotation of angulation (CORA) and angulation correction axis (ACA) are not the same, dome osteotomy will cause translation of the proximal and distal bone axes. (B) When the CORA and ACA are the same, dome osteotomy will correct the angulation deformity without translation.
Fig. 4
Graphic method. (A) Magnitude of angulation angulation was measured on anteroposterior (AP) and lateral radiographs (1 mm=1°). True deformity angle was 45° and 30° from the sagittal plane. (B) Closed wedge osteotomy is performed on the forward angulation correction axis (ACA), and opening wedge osteotomy is performed on the backward ACA.
Fig. 5
(A) There was a valgus malalignment after proximal femur minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO). (B) The angle of 40° internal rotation deformity was found on the computed tomography and physical examination. (C) Two parallel shanz pins were inserted into the proximal and distal segments to correct the rotational deformity after plate removal. (D) Osteotomy was performed at the center of rotation of angulation. (E) Distal shanz pin was externally rotated until the lessor trochanter shape showed to be the same as the opposite site. (F) The plate was bent 8° varus compared with the previous plate to correct the valgus deformity. (G) Locking plate was applied using the MIPO technique. (H) Postoperative 4 months radiography shows good alignment.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Osteotomy Selection: Advantages, Disadvantages, and Indication

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

