Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 33(1); 2020 > Article
- Review Article Periprosthetic Fractures following Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Byung Hoon Lee, Jae Ang Sim
-
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma 2020;33(1):52-61.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.1.52
Published online: January 31, 2020

-
Corresponding author:
Jae Ang Sim, Tel: +82-32-460-3384, Fax: +82-32-423-3384,
Email: sim_ja@gilhospital.com
- 878 Views
- 16 Download
- 0 Crossref
- 0 Scopus
Abstract
Recently, as the elderly population increases, the incidence of total knee arthroplasty has increased, with a concomitant increase in the frequency of periprosthetic fractures. To determine the treatment plan for fractures, the treatment method should be determined by the patient's age, osteoporosis, fixation status of the implant, and type of fracture. In recent years, operative treatment with reduction and stable fixation, rather than non-operative treatment, was used to promote early joint movement and gait. On the other hand, it is necessary to select an appropriate operative method to reduce complications of surgery, such as nonunion and infection, and expect a good prognosis. In this review, periprosthetic fractures were divided into femur, tibia, and patella fractures, and their causes, risk factors, classification, and treatment are discussed.
Published online Jan 23, 2020.
https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.1.52
Periprosthetic Fractures following Total Knee Arthroplasty
 , M.D., Ph.D.
and Jae Ang Sim
, M.D., Ph.D.
and Jae Ang Sim , M.D., Ph.D.
, M.D., Ph.D.
Abstract
Recently, as the elderly population increases, the incidence of total knee arthroplasty has increased, with a concomitant increase in the frequency of periprosthetic fractures. To determine the treatment plan for fractures, the treatment method should be determined by the patient's age, osteoporosis, fixation status of the implant, and type of fracture. In recent years, operative treatment with reduction and stable fixation, rather than non-operative treatment, was used to promote early joint movement and gait. On the other hand, it is necessary to select an appropriate operative method to reduce complications of surgery, such as nonunion and infection, and expect a good prognosis. In this review, periprosthetic fractures were divided into femur, tibia, and patella fractures, and their causes, risk factors, classification, and treatment are discussed.
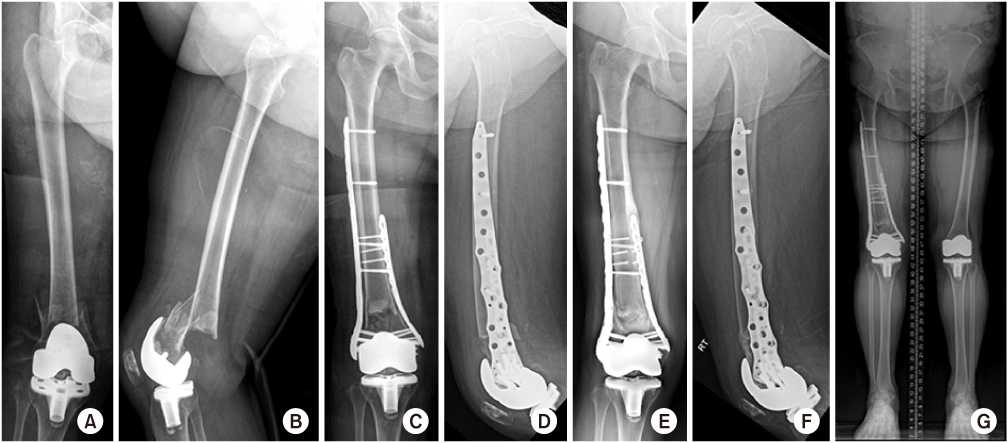
Fig. 1
Periprosthetic fracture with a comminuted fracture in the medial cortex of the distal femur was fixed with dual locking plates using the minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) technique. (A, B) Preoperative radiographs. (C, D) Postoperative radiographs. (E-G) Radiographs one year after surgery.
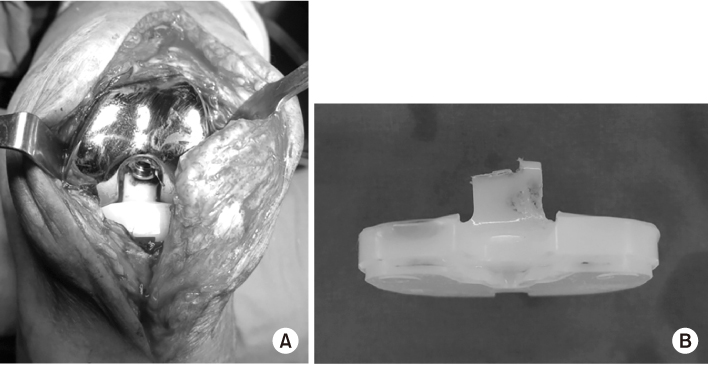
Fig. 2
Extruded nail (A) caused the wear of polyethylene post (B).
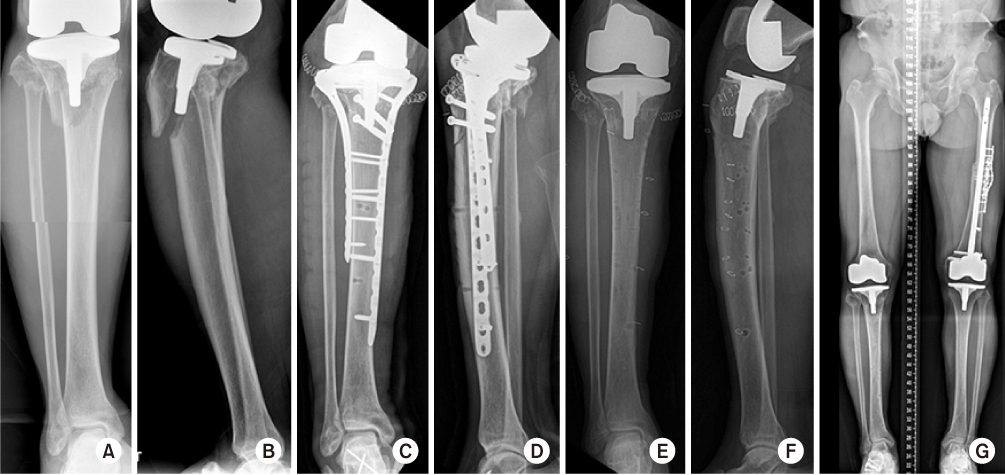
Fig. 3
Periprosthetic fracture of the proximal tibia was fixed with dual locking plates using the minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) technique. (A, B) Preoperative radiographs. (C, D) Postoperative radiographs. (E-G) Radiographs 1 year after surgery.
Fig. 4
Patellar fracture with non-operative treatment obtained bony union. (A) Radiograph at the time of injury. (B) Radiograph six months after injury.
References
-
Hozack WJ, Goll SR, Lotke PA, Rothman RH, Booth RE Jr. The treatment of patellar fractures after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Rela Res 1988;(236):123–127.
-

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS


 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite

