Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 22(4); 2009 > Article
-
Original Article
- Percutaneous Kirschner Wire Fixation of Acute Mallet Fractures Percutaneousely Reduced by Towel Clip
- Chung Soo Han, M.D., Duke Whan Chung, M.D., Bi O Jeong, M.D., Hyun Chul Park, M.D., Jin Young Kim, M.D., Cheol Hee Park, M.D., Jin Sung Park, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2009;22(4):283-287.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.4.283
Published online: October 30, 2009
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
*Department of Orthopedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Duke Whan Chung, M.D. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, 1, Hoegi-dong, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul 130-701, Korea. Tel: 82-2-958-8368, Fax: 82-2-964-3865, dukech@khmc.or.kr
• Received: May 7, 2009 • Revised: June 15, 2009 • Accepted: August 8, 2009
Copyright © 2009 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 602 Views
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- To analyze the treatment of clinical results of the percutaneous Kirschner wire fixation of acute mallet fractures percutaneousely reduced by towel clip.
-
Materials and Methods
- From August 2005 to April 2009, we evaluated nine fingers in eight patients, more than three months follow up. The type of injury was a axial loading in seven cases and direct blow in two. The average follow-up period was 10.1 months (range: 3~41 months). The indication of operative treatment was the presence of large bony fragment or the palmar subluxation of the distal phalnx.
-
Results
- The range of motion was 3.7° (0~10°) in extension lag and 76.7° (60~90°) of flexion of the distal interphalangeal joint.
-
Conclusion
- The percutaneous Kirschner wire fixation of acute mallet fractures percutaneousely reduced by towel clip is one of the easy and simple method to stabilizing of bony mallet fracture.
- 1. Bischoff R, Buechler U, De Roche R, Jupiter J. Clinical results of tension band fixation of avulsion fractures of the hand. J Hand Surg Am, 1994;19:1019-1026.
- 2. Choi JY, Jung HJ, Lee HJ, Son KM, Kim YH. Treatment of bony mallet finger: closed reduction using extension block K-wire. J Korean Fract Soc, 2004;17:362-367.
- 3. Damron TA, Engber WD. Surgical treatment of mallet finger fractures by tension band technique. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1994;300:133-140.
- 4. Hofmeister EP, Mazurek MT, Shin AY, Bishop AT. Extension block pinning for large mallet fractures. J Hand Surg Am, 2003;28:453-459.
- 5. Inoue G. Closed reduction of mallet fractures using extension-block kirschner wire. J Orthop Trauma, 1992;6:413-415.
- 6. Ishiguro T, Imai N, Tomatsu T, Noguchi T, Hashizume N. A new method of closed reduction using the spring action of Kirschner wires for fractures of the tibial plateau--a preliminary report. Nippon Seikeigeka Gakkai Zasshi, 1986;60:227-236.
- 7. King HJ, Shin SJ, Kang ES. Complications of operative treatment for mallet fractures of the distal phalanx. J Hand Surg Br, 2001;26:28-31.PDF
- 8. Mazurek MT, Hofmeister EP, Shin AY, Bishop AT. Extension-block pinning for treatment of displaced mallet fractures. Am J Orthop, 2002;31:652-654.
- 9. Tetik C, Gudemez E. Modification of the extension block Kirschner wire technique for mallet fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 2002;404:284-290.
- 10. Wehbé MA, Schneider LH. Mallet fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1984;66:658-669.
- 11. Yi SR, Hahn SH, Yang BK, et al. The result of the modified extension block technique in bony mallet finger. J Korean Fract Soc, 2006;19:236-240.
REFERENCES
Fig. 2Reduction using a towel clip under fluoroscopic guidance. Full extended DIP joint can reduce and compress the bone fragment by tips of a towel clip. Occasionally, manipulation of the distal phalanx with a towel clip is required to obtain an anatomic reduction.


Fig. 3Maintaining reduction by a towel clip, a 0.035 inch K-wire is inserted through the bony fragment at a 45 angle into the of distal phalanx from dorsal to palmar cortex.


Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Comparison of Surgical Outcomes of Percutaneous K-Wire Fixation in Bony Mallet Fingers with Use of Towel Clip versus 18-Gauge Needle
Ho-Seung Jeon, Chan-Sam Moon, Seo-Goo Kang, Kyeong-Seop Song, Uk-Hyun Choi
Journal of the Korean Society for Surgery of the Hand.2013; 18(1): 1. CrossRef
Percutaneous Kirschner Wire Fixation of Acute Mallet Fractures Percutaneousely Reduced by Towel Clip
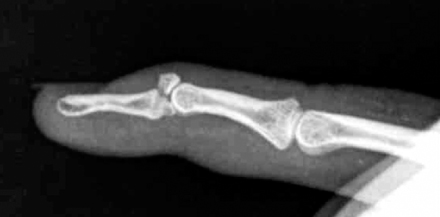
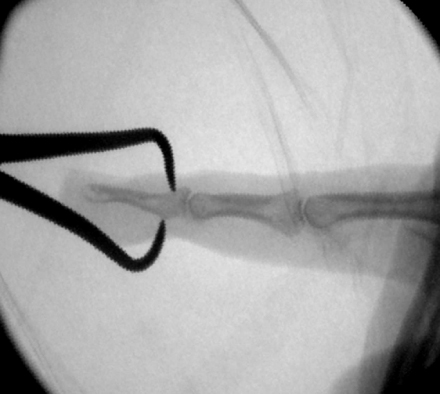
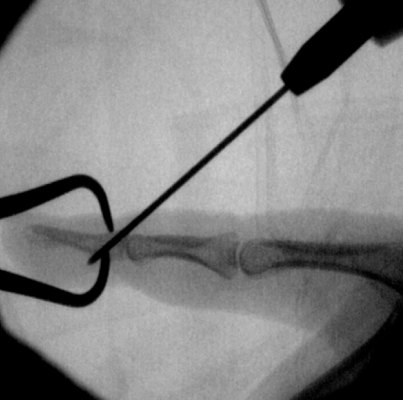
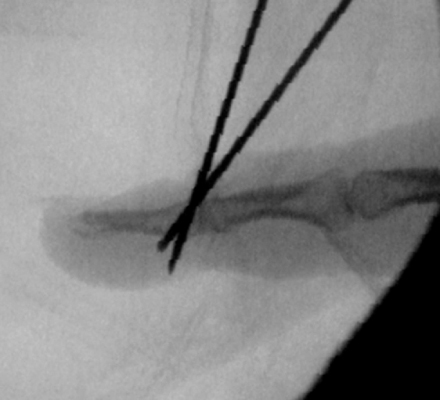
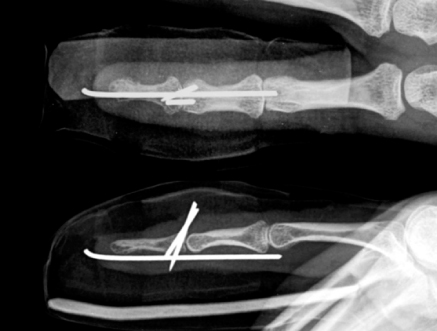
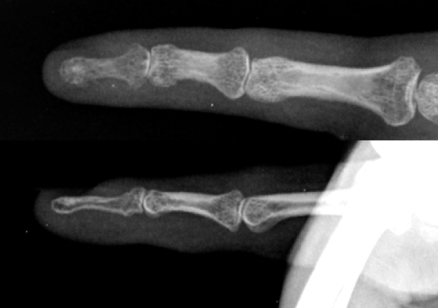
Fig. 1
Preoperative lateral radiograph shows a displaced mallet fracture.
Fig. 2
Reduction using a towel clip under fluoroscopic guidance. Full extended DIP joint can reduce and compress the bone fragment by tips of a towel clip. Occasionally, manipulation of the distal phalanx with a towel clip is required to obtain an anatomic reduction.
Fig. 3
Maintaining reduction by a towel clip, a 0.035 inch K-wire is inserted through the bony fragment at a 45 angle into the of distal phalanx from dorsal to palmar cortex.
Fig. 4
After removal of a towel clip, a second K-wire is inserted through the bony fragment to distal phalanx.
Fig. 5
A temporally additional K-wire is inserted for stability.
Fig. 6
6 weeks follow up radiograph after the removal of the K-wires.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Fig. 6
Percutaneous Kirschner Wire Fixation of Acute Mallet Fractures Percutaneousely Reduced by Towel Clip
Demographics and clinical outcome of the patients
*K-wire: Kirschner wire.
Table 1
Demographics and clinical outcome of the patients
*K-wire: Kirschner wire.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS





 Cite
Cite

