Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 20(4); 2007 > Article
-
Original Article
- The Shortening and Rotational Deformity after Closed Intramedullary Nailing of Femur Shaft Fracture: According to Winquist-Hansen classification
- Dong Eun Shin, M.D., Dong Hoon Lee, Chang Soo Ahn, Ki Shik Nam
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2007;20(4):297-301.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.4.297
Published online: June 14, 2016
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Bundang CHA Hospital, College of Medicine, Pochon CHA University, Sung-Nam, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Dong Eun Shin, M.D. Department Orthopaedic Surgery, Bundang CHA Hospital, College of Medicine, Pochon CHA University, 351, Yatap-dong, Bundang-gu, Seongnam-si 463-712, Korea. Tel: 82-31-780-5289, Fax: 82-31-708-3578, shinde@cha.ac.kr
Copyright © The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved
- 695 Views
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- This study evaluated the shortening and rotational deformity after closed intramedullary nailing of femur shaft fracture according to Winquist-Hansen classification type.
-
Materials and Methods
- This study was based on 98 cases who received cloased intramedullary fixation about their femur shaft fractures between January 2000 and October 2005 with minimum 12 months follow up. The rotational deformity was analysed by Yang's method (45 cases) preoperatively and postoperatively, and the shortening by orthoradiogram (55 cases). Furthermore we analysed other complications, for example nonunion, infection, and metal failure.
-
Results
- We found more than 15 degrees anteversion difference of both femurs in 10 cases. Among them, 9 cases were classified to type 3, 4. According to Winquist-Hansen classification, rotational deformity ranged from 3.7° (Type 1) to 8.9° (Type 4). More than 2 cm leg length discrepancy (LLD) was found in 9 cases, all of them were classified as Winquist-Hansen classification type 3, 4. In the type 1, LLD was checked as 3.2 mm and type 4, 14.2 mm.
-
Conclusion
- To prevent the shortening and rotational deformity after intramedullary fixation of Winquist-Hansen classification type 3, 4 femur shaft fracture, intraoperatively the exact contralateral femoral anteversion and length should be checked.
- 1. Braten M, Terjesen T, Rossvoll I. Femoral anteversion in normal adults: ultrasound measurements in 50 men and 50 women. Acta Orthop Scand, 1992;63:29-32.
- 2. Braten M, Terjesen T, Rossvoll I. Torsional deformity after intramedullary nailing of femoral shaft fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1993;75:799-803.
- 3. Bucholz W, Jones A. Current concepts review. Fractures of the shaft of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1991;73:1561-1566.
- 4. Dunlap K, Shands AR Jr, Hollister LC Jr, Gaul Js Jr, Streit HA. A new method for determination of torsion of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1953;35:289-311.Article
- 5. Eckhoff DG, Montgomery WK, Kilcoyne RF, Stamm ER. Femoral morphometry and anterior knee pain. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1994;302:64-68.Article
- 6. Gibson PH, Papaioannou T, Kenwright J. The influence on the spine of leg-length discrepancy after femoral fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1983;65:584-587.ArticlePDF
- 7. Giles LG, Taylor JR. Low-back pain associated with leg length inequality. Spine, 1981;6:510-521.Article
- 8. Harris I, Hatfield A, Walton J. Assesing leg length discrepancy after femoral fracture: clinical examination or computed tomography? ANZ J Surg, 2005;75:319-321.
- 9. Kim YM, Bin SI. Comparative study of the roentgenographic methods for the measurement of the femoral anteversion. J Korean Orthop Assoc, 1986;21:387-396.ArticlePDF
- 10. Kim JS, Park YS, Choi JY, Choi AS. Rotational deformity after closed interlocking nailing of femoral fracture. J Korean Orthop Assoc, 1995;30:673-679.ArticlePDF
- 11. Krettek C, Miclau T, Blauth M, Lindsey RW, Donow C, Tscherne H. Recurrent rotational deformity of the femur after static locking of intramedullary nails: case reports. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1997;79:4-8.
- 12. Marphy SB, Simon SR, Kijewski PK, Wilkinson RH, Griscom NT. Femoral anteversion. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1987;69:1169-1176.Article
- 13. Mohr VD, Eickhoff U, Haaker R, Klammer HL. External fixation of open femoral shaft fractures. J Trauma, 1995;38:648-652.Article
- 14. Winquist RA, Hansen ST Jr, Clawson DK. Closed intramedullary nailing of femoral fractures. A report of five hundred and twenty cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1984;66:529-539.Article
- 15. Ricci WM, Bellabarba C, Lewis R, et al. Angular malalignment after intramedullary nailing of femoral shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma, 2001;15:90-95.Article
- 16. Winquist RA, Hansen ST Jr. Comminuted fractures of the femoral shaft treated by intramedullary nailing. Orthop Clin North Am, 1980;11:633-648.Article
- 17. Canale S. Terry. Fractures of Lower Extremity. Vol.3. Campbell's operative orthopaedics. 9th ed. Mosby Inc; 1998. p. 2042-2066.
- 18. Salminen S, Pihlajamaki H, Avikainen V, Kyro A, Bostman O. Specific features associated with femoral shaft fractures caused by low-energy trauma. J Trauma, 1997;43:117-122.Article
- 19. Wolinsky PR, McCarty E, Shyr Y, Johnson K. Reamed intramedullary nailing of the femur: 551 cases. J Trauma, 1999;46:392-399.
- 20. Yang KH, Han DY, Shin DE, Jeong JH. Malrotation deformity following intramedullary nailing in femoral shaft fracture does true neutral rotation of the distal fragment prevent the deformity? J Korean Orthop Assoc, 1998;33:121-126.ArticlePDF
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- The Fate of Butterfly Fragments in Extremity Shaft Comminuted Fractures Treated with Closed Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing
Ki-Chan An, Yoon-Jun Kim, Jang-Suk Choi, Seung Suk Seo, Hi-Chul Gwak, Dae-Won Jung, Dong-Woo Jeong
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(1): 46. CrossRef - Limited Open Reduction and Intramedullary Nailing of Proximal Femoral Shaft Fracture
Sang Ho Ha, Jun Young Lee, Sang Hong Lee, Sung Hwan Jo, Jae Cheul Yu
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(4): 225. CrossRef
The Shortening and Rotational Deformity after Closed Intramedullary Nailing of Femur Shaft Fracture: According to Winquist-Hansen classification
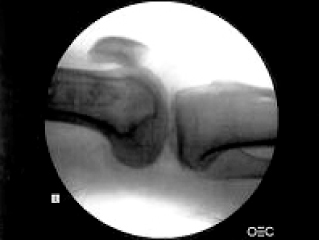
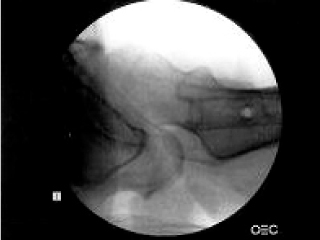
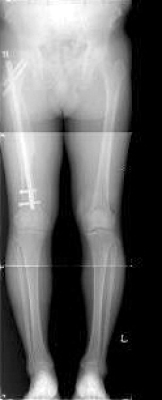
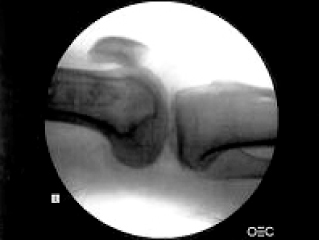
Fig. 1
Lt knee true lateral view is set to both femoral condyle parallel on the ground.
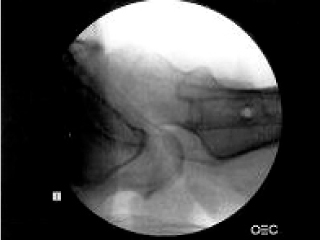
Fig. 2
Axial view of Lt hip is checked under Lt knee in true lateral state.
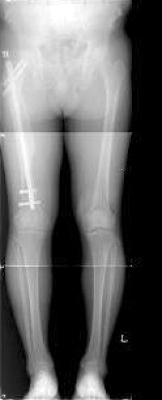
Fig. 3
Orthoradiogram shows the leg length discrepancy.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
The Shortening and Rotational Deformity after Closed Intramedullary Nailing of Femur Shaft Fracture: According to Winquist-Hansen classification
Difference in anteversion angle (Braten et al 1992)
Table 1
Difference in anteversion angle (Braten et al 1992)

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 Cite
Cite

