Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Article
- Fracture-related infections: a comprehensive review of diagnosis and prevention
- HoeJeong Chung, Hoon-Sang Sohn
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):86-95. Published online April 25, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00164
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
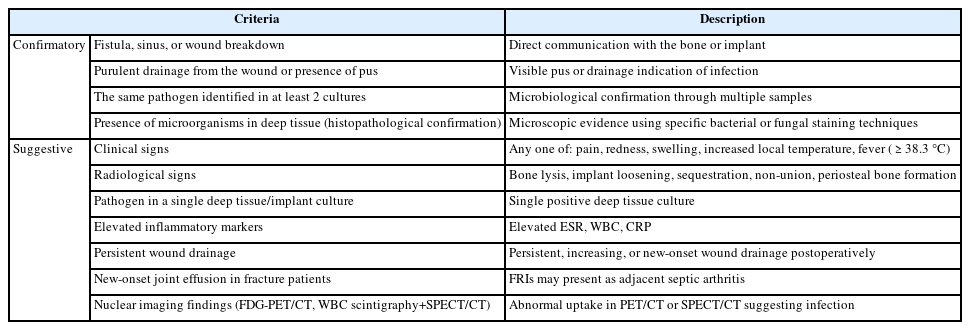
PDF - Fracture-related infections are challenging complications in orthopedic trauma that often require prolonged treatment and impose a significant healthcare burden. Accurate diagnosis and effective prevention strategies are essential for minimizing their occurrence. A recent international consensus has established standardized diagnostic criteria based on clinical, microbiological, radiological, and histopathological findings. Prevention is the top priority and involves a thorough preoperative risk assessment, along with glycemic control, nutritional optimization, and management of comorbidities, as well as intraoperative and postoperative measures such as appropriate antibiotic prophylaxis, surgical site antisepsis, and meticulous wound care. A multidisciplinary approach involving orthopedic surgeons, infectious disease specialists, and microbiologists is crucial for successfully reducing the burden of fracture-related infections.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Personalized Approaches to Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies in Periprosthetic Fracture-Related Infections (PFRIs): Case Series and Literature Review
Marianna Faggiani, Marco Zugnoni, Matteo Olivero, Salvatore Risitano, Giuseppe Malizia, Silvia Scabini, Marcello Capella, Stefano Artiaco, Simone Sanfilippo, Alessandro Massè
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2025; 15(12): 576. CrossRef - Pathogen-Specific Risk for Iterative Surgical Debridement in Orthopedic Infections: A Prospective Multicohort Analysis
Flamur Zendeli, Anna Jędrusik, Raymond O. Schaefer, David Albrecht, Michael Betz, Felix W. A. Waibel, Tanja Gröber, Nathalie Kühne, Sören Könneker, İlker Uçkay
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(24): 8750. CrossRef
- Personalized Approaches to Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies in Periprosthetic Fracture-Related Infections (PFRIs): Case Series and Literature Review
- 5,992 View
- 219 Download
- 2 Crossref


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


